Improved Production Key Performance Indicators (KPI’s) Using Intelligent-Manufacturing Execution Systems (I-MES)
The aim of this research is to reduce the gap between manufacture expertise and management expertise by using modern technology like Manufacturing Execution System (MES) via Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machin Learning (ML). A design of MES has been proposed and implemented on El-Araby Plastic Injection Molding (PIM) factory. This work is based on the International Society of Automation Standard (ISA-S95). A fully automated data management system has been designed and implemented to control data follow between shop floor e.g. (machines and operators) and management floor e.g. (production
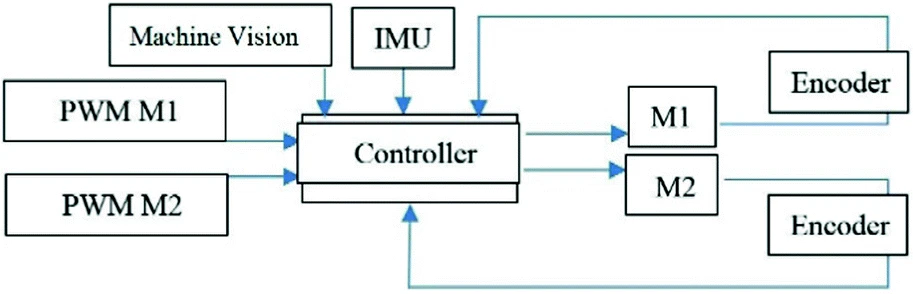
Agricultural Service Mobile Robot Modeling and Control Using Artificial Fuzzy Logic and Machine Vision
This paper represents modeling and control of an agricultural service skid steering mobile robot for the purposes of grass cutting using Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller and Fuzzy Logic techniques and feedback signals from sensors as IMU, encoders, and Machine Vision. The paper deals with the system modeling into two methods: The first is using Fuzzy modeling as a modeling tool for complex nonlinear system, the second is using MATLAB software system Identification Tool. The study Uses PID, Fuzzy logic controller and fuzzy self-tuning of PID controller to control the path
Gripping Force Modeling of a Variable Inclined Air Pillow Soft Pneumatic Actuator
Soft pneumatic actuators grasping tasks is one of the essential rules in robot manipulation methods. The grasping forces can be adapted to handle delicate and hard objects without leaving any damages on the object surfaces. This paper investigates the influence of the inclination angle of the soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) on its gripping force at its end tip. A range of inclination angles for SPA is analyzed using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to estimate the gripping force at the end tip regarding SPA inner faces pressure. FEA study is conducted based on Hyperelastic material modeling
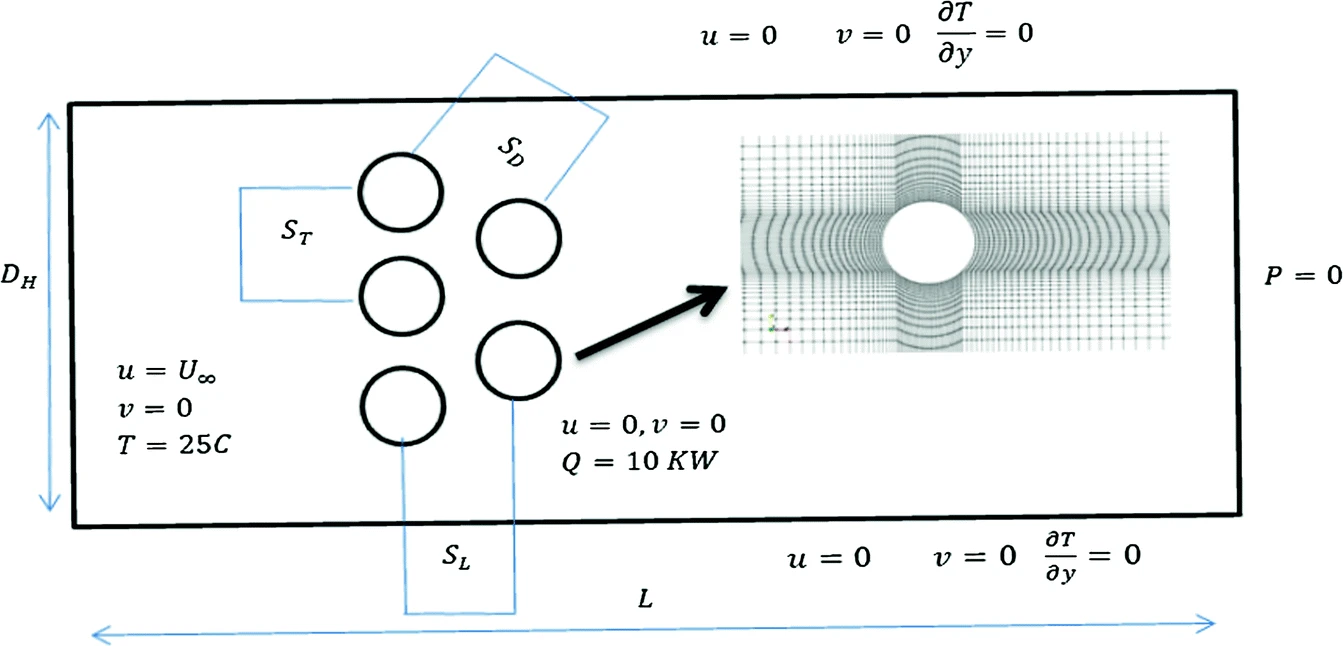
Tuning of PID Controller Using Particle Swarm Optimization for Cross Flow Heat Exchanger Based on CFD System Identification
This paper illustrates the design of proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID) controller of 10 KW air heaters for achieving the set point temperature as fast as possible with minimum response overshoot. Computational fluid dynamic (CFD) numerical simulations are utilized to predict the natural response of 10 KW input power for the air heater. CFD results are validated with experimental empirical correlations that insure the reliability of open loop results. The open loop response of CFD transient simulations is used to model the air heater transfer function and design the classical
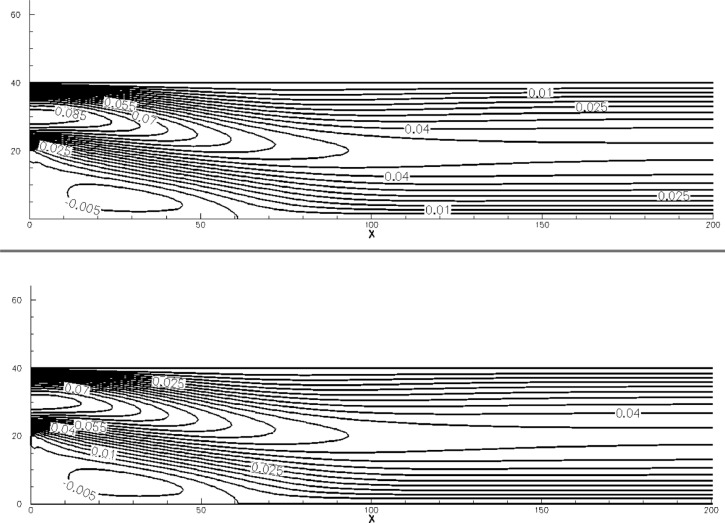
An Asymptotically Adaptive Successive Equilibrium Relaxation approach for the accelerated convergence of the Lattice Boltzmann Method
A new approach is proposed to accelerate the convergence of the Lattice Boltzmann method for steady-state problems. The proposed approach uses an adaptive relaxation frequency to accelerate the convergence by assigning more weight to selected parts of the standard algorithm corresponding to different phases of the convergence to the steady-state solution. The proposed algorithm is simple, straightforward and does not impose any additional computational cost to the standard algorithm. Different simulation cases are presented with the corresponding speedup. Finally, guidelines for the selection
Classifying Upper Limb Activities Using Deep Neural Networks
This paper presents a classification method using Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in order to classify six human upper limb activities. The study was also carried out to investigate whether theses activities are being performed normally or abnormally using two different neural networks: Artificial neural network (ANN) and convolutional neural network (CNN). Human activities that were included in the study: arm flexion and extension, arm pronation and supination, shoulder internal and external rotations. Before activities categorization, training data was obtained by the means of an IMU sensor
Experimental Path tracking optimization and control of a nonlinear skid steering tracked mobile robot
The skid steering tracked robot is consider one of the famous robots that used in the autonomous agricultural field. The robot model is considered as a coupled nonlinear model. So, a real kinematic model is required to develop the robot motion which will improve the high quality and quantity of the cultivated crops. So, in this research a mathematical model for the skid steering mobile robot (SSMR) and a mathamtical model has been presented to simulate the robot. The model has been validated based on experimental data for the Skid Steering model. The robot motion as position and velocity has
Experimental Lane Keeping Assist for an Autonomous Vehicle Based on Optimal PID Controller
Detection of the lane boundary is the primary task in order to control the trajectory of an autonomous car. In this paper, three methodologies for lane detection are discussed with experimental illustration: Blob analysis, Hough transformation and Birds eye view. The next task after receiving the boundary points is to apply a control law in order to trigger the steering and velocity control to the motors efficiently. In the following, a comparative analysis is made between different tuning criteria to tune PID controller for Lane Keeping Assist (LKA). In order to receive the information of the
Modelling of Continuum Robotic Arm Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
Continuum robotic arm becomes the new area of scientific research nowadays. Its technology has grown and touched several vital applications included industry and agriculture thanks to many advantages made it a better choice than the conventional serial robotic manipulator. This paper represents a new designed model of continuum arm robot, which relates the motor shaft angle as the input parameter and transfers the motor torque to combined system of compression springs and results in six outputs: x,y and z 3D coordinates for the center point of the end effector and \theta,~\psi and \gamma to
Experimental Modeling of Hexapod Robot Using Artificial Intelligence
Hexapod Robots gave us the opportunity to study walking robots without facing problems such as stability and expensive custom made hardware. It has a great deal of flexibility in moving over different terrains even if some legs become malfunctioned or facing some difficulties in movement. In this study the kinematic analysis of CH3-R 18DOF Hexapod Robot is discussed where each leg contains three revolute joints in order to mimic the structure of a spider. To develop the overall kinematic model of CH3-R robot, direct and inverse kinematic analyses for each leg have been considered where the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
