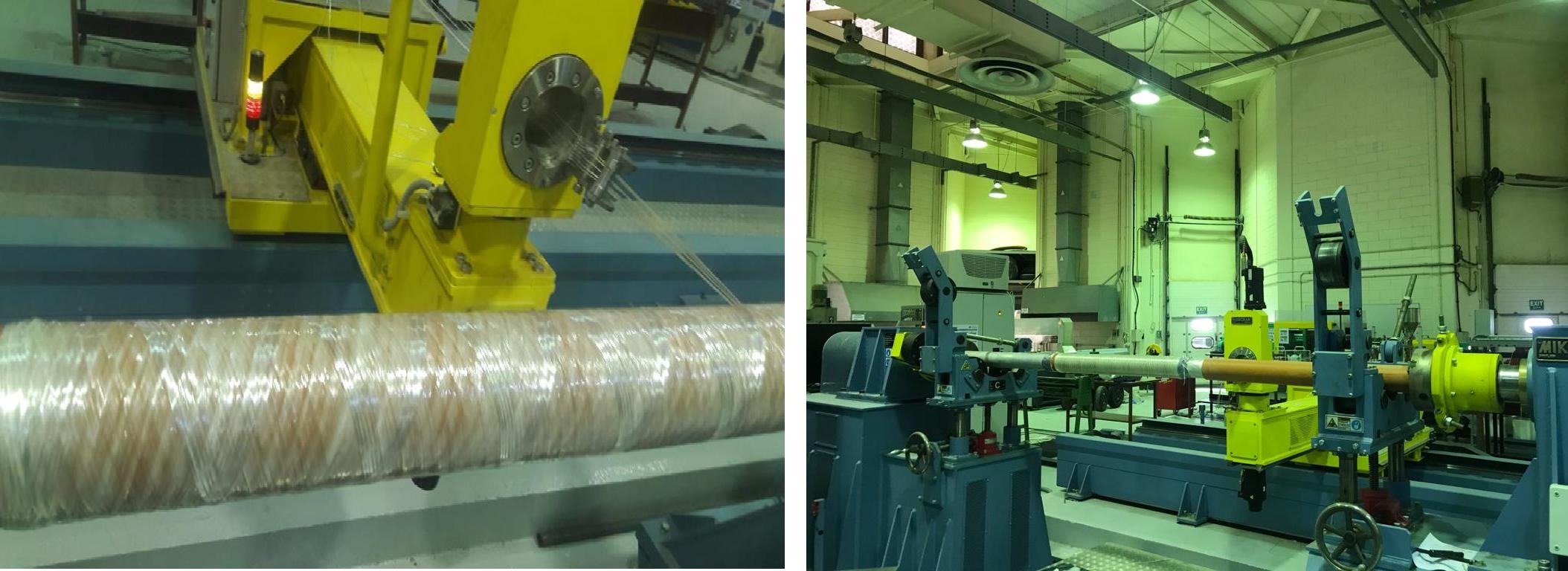

Experimental investigation of the dynamic characteristics of wrapped and wound fiber and metal/fiber reinforced composite pipes
This paper experimentally investigates the effect of the manufacturing method and metal reinforcement option on the natural frequency and damping behavior of five polymer and Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) composite pipes. The five pipes are made of polymer, roll-wrapped woven glass FRP, metal-reinforced roll-wrapped woven glass FRP, filament-wound glass FRP, and metal reinforced filament-wound-up glass FRP. The composite pipes can replace conventional pipes in oil and gas industries and conventional metallic shafts in many applications. Logarithmic decay, logarithmic decrement, and random
Turbulent Axisymmetric Non-Isothermal Flow of the Hitec Molten Salt with Temperature Dependent Properties: A Numerical Investigation
This study aims to investigate the Hitec molten salt's thermal-hydraulic behavior in a smooth round pipe under broad ranges of surface heat flux and Reynolds number (q = 104 - 105 W/m2, Re = 104 - 105). Mesh independent study was performed to ensure the robustness of the model to achieve accurate solutions. Presentation of temperature, pressure and thermophysical properties for multiple cases are presented and discussed. Temperature gradient decreases at high Reynolds number leading to small change in thermo-physical properties. While pressure seems not to be affected by the change in the
Modeling complex flow induced by water waves propagation over submerged square obstacles
Submerged breakwaters are efficient structures used for shore protection. Many design features of these structures are captured upon modeling wave propagation over submerged square obstacles. The presence of separation vortices and large free surface deformations complicates the problem. A multiphase turbulent numerical model is developed using ANSYS commercial package. Careful domain discretization is done employing suitable mesh clustering to capture high gradients. Various numerical model parameters are provided, including grid size and time step. Special attention is directed towards
Analysis of Tapered Timoshenko and Euler-Bernoulli Beams on an Elastic Foundation with Moving Loads
This research studies the vibration analysis of Euler-Bernoulli and Timoshenko beams utilizing the differential quadrature method (DQM) which has wide applications in the field of basic vibration of different components, for example, pillars, plates, round and hollow shells, and tanks. The free vibration of uniform and nonuniform beams laying on elastic Pasternak foundation will be studied under three sets of boundary conditions, that is, mixing between being simply upheld and fixed while utilizing the DQM. The natural frequencies and deflection values were produced through the examination of
The effect of the geometric and thermal parameters on the thermal stresses during the passive cooling of printed circuit boards
The effect of components' thermal properties in addition to their geometric configuration on the developed thermal stress in a model printed circuit board (PCB) is investigated. This effect is quantified through three parameters, the average normalized temperature gradient, maximum normalized temperature gradient and the uniformity factor. It is found that the effect of the geometric configuration, especially that of the heat-generating component, is more significant than the thermal properties of the components. © 2019 IEEE.
Controller Design and Optimization of Magnetic Levitation System (MAGLEV) using Particle Swarm optimization technique and Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR)
Magnetic Levitation System is one of practical examples which faces some nonlinearities behavior. Such systems require special types of controller parameters consideration for accurate results. In this paper, the process of tuning is to determine the system poles and getting them away from the instability region using state feedback (SF) controller methodology. The resulted controllable system parameters are estimated using LQR controller. Since the desired goal is to minimize vital parameters in the system behavior like the steady state error, settling time, raising time of the system and
Gray Wolf Optimization of Fractional Order Control of 3-Omni Wheels Mobile Robot: Experimental Study
Committing robotics with artificial intelligence becomes mandatory collaboration with distinct environments. Omnidirectional Wheeled (Omni-WD) mobile robots are one of the robots that interact with humans in various circumstances, where it is important to function effectively and accurately. In this paper, the distinction of a 3WD-Omni model and control using machine vision is demonstrated. The use of fractional order (FO) calculus has been stated to increase the degrees of freedom of the controller over the integer ones. Hybridization of FO control and metaheuristics optimization is reported
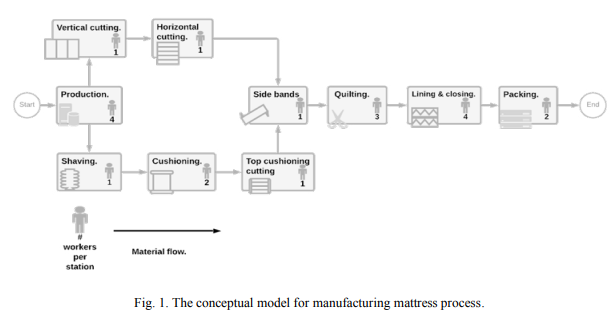
Decision Support Using Simulation to Improve Productivity: A Case Study
The use of modeling and simulation as a decision aid tool has been widely recognized in the field of production engineering. In this work, modeling and simulation is used to examine, analyze, and recommend improvements for the performance of an existing assembly line within a manufacturing facility. Several key performance indicators (KPIs) are determined to evaluate the performance of the assembly line under study. With the aid of Maynard Operation Sequence Technique (MOST) and Line Balancing methods, two improved systems are recommended to enhance the performance of the line under study
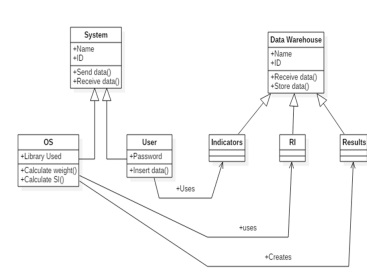
Decision making to calculate economic sustainability index: A case study
This work assesses the economic sustainability of industrial factories in Egypt based on the Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP). The authors designed an economic sustainability index calculator (ESIC) using Unified Modelling Language (UML) and implemented the software using Visual basic of Applications (VBA) tool to the code the program. UML was used for the system analysis and design only, giving an insight to the system architecture. The manual method of calculating the economic sustainability index is included in this research and verified by using the designed ESIC. The categories of
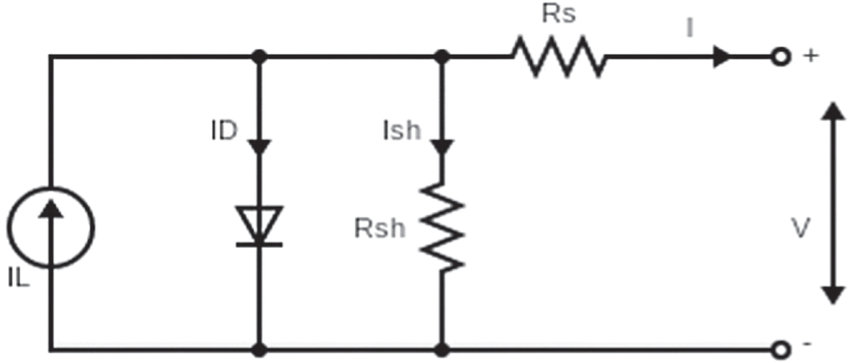
Effect of thickness and temperature on flexible organic P3HT:PCBM solar cell performance
A blend of poly 3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) and [6, 6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) is used as a photoactive layer for simulating a bulk heterojunction organic solar using general-purpose photovoltaic device model (GPVDM) software. The optical and electrical performance of the cell had been analyzed by changing the thickness of each layer and substrate material over a range of operating temperatures from -10 °C to - 40 °C. The flexible device exhibits higher PCE compared to a rigid device. The performance of the device was studied using transient simulation at different operating
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
