Asymmetric degrees of freedom of the full-duplex MIMO 3-way channel
In this paper, we characterize the asymmetric total degrees of freedom (DoF) of a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) 3-way channel. Each node has a separate-antenna full-duplex MIMO transceiver with a different number of antennas, where each antenna can be configured for either signal transmission or reception. Each node has two unicast messages to be delivered to the two other nodes. We first derive upper bounds on the total DoF of the system. Cut-set bounds in conjunction with genie-aided bounds are derived to characterize the achievable total DoF. Afterwards, we analytically derive the
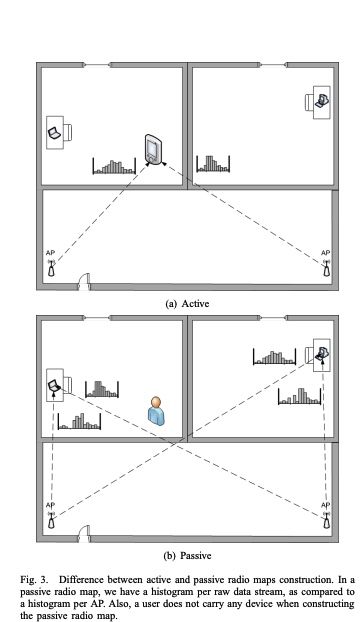
A deterministic large-scale device-free passive localization system for wireless environments
The widespread usage of wireless local area networks and mobile devices has fostered the interest in localization systems for wireless environments. The majority of research in the context of wirelessbased localization systems has focused on device-based active localization, in which a device is attached to tracked entities. Recently, device-free passive localization (DfP) has been proposed where the tracked entity is neither required to carry devices nor participate actively in the localization process. DfP systems are based on the fact that RF signals are affected by the presence of people
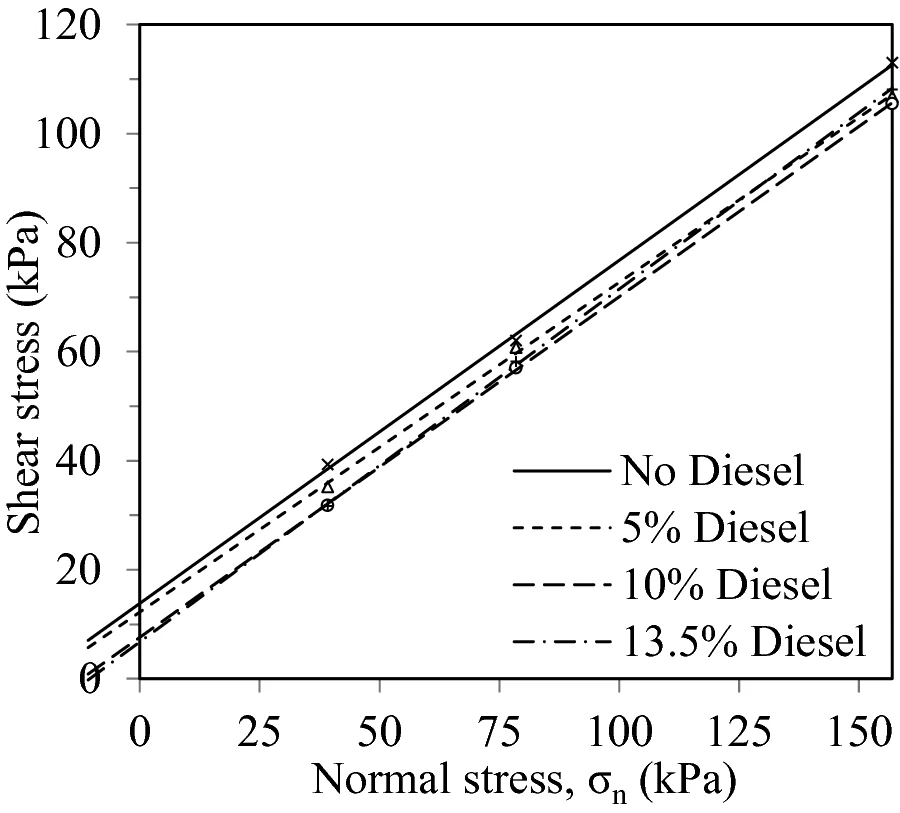
Characterization of Shear Strength and Compressibility of Diesel Contaminated Sand
Soil contamination with petroleum products and/or waste are a problem that can be detected nearby industrial areas and other amenities that include underground leaking tanks or pipelines. The negative effect of oil contamination on the soil properties is significant and can completely alter the strength as well as the serviceability limit states of the bearing stratum. In this study, Diesel was mixed with cohesionless soils using four different mixing percentages, starting with 5% up to 13.5% by weight, to cover a wide range of contamination ratios. The effects of contamination on the soil
EPS inclusion to reduce vertical stresses on shallow tunnels
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) has long been used to reduce stresses acting on buried structures. In this study, the efficiency of utilising EPS in reducing vertical stresses acting on cut-and-cover tunnels was investigated. To gauge this, short- and long-term shear strength parameters of EPS with densities of 25, 30, and 35 kg/m3 were determined. Interface friction of EPS with various materials was measured considering the use of geotextile as a protective cover for EPS. Laboratory testing included unconfined compression, creep strain based on time-temperature-stress superposition, and modified
CHARACTERIZATION of CONCRETE MIXES for IRRIGATION CANALS
Recently, the construction of water structures and seepage reduction are critical issues. This importance was induced due to the required specifications for the desired type of concrete. Mechanical strength and permeability are the two major parameters in achieving the design mix efficiently. This study investigates the effect of different types of admixures on the performance of concrete. The performance of concrete was evaluated using the mechanical strength and permeability tests. The concrete mixes admixtures include A retarder (Sika R2004 type G), water proofing material (addicrete DM2)
Medical nanorobots: Design, applications and future challenges
Following the current technological revolution, the concept of emerging fields and getting a common benefit becomes a bright way to follow. Going deeper in nanotechnology, nanorobotics has been the glimpse of hope in many fields; particularly, in the medical field. Nanorobotics applications in medicine are divided into two main categories, diagnosis and treatment, and extensive efforts have been given to research about its operation principles and design. Unfortunately, problem have emerged regarding the implementation, methods of actuation, and customized components of nanorobotics to be used
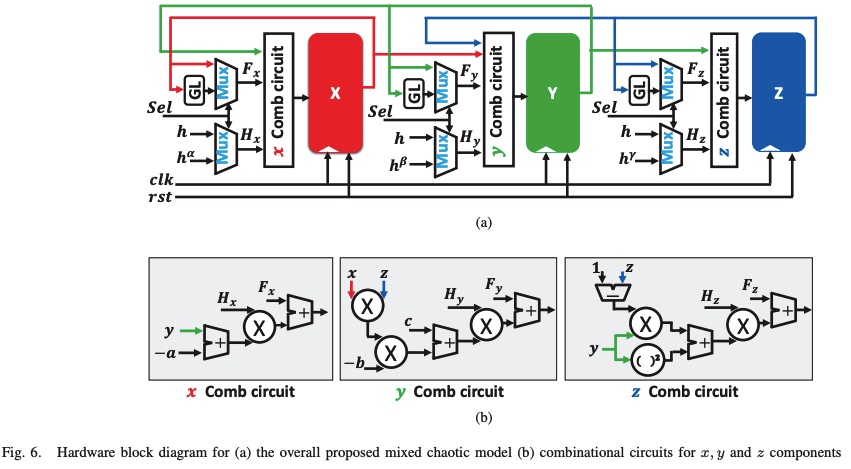
A Digital Hardware Implementation for A new Mixed-Order Nonlinear 3-D Chaotic System
This paper introduces a generic modeling for a 3-D nonlinear chaotic based on fractional-order mathematical rules. Also, a novel modeling for the system using a mixture between integer and fractional-order calculus is proposed. Dynamics of the new realization are illustrated using phase portrait diagrams with complex behavior. Also, a great change in the parameter ranges is investigated using bifurcation diagrams. MATLAB and Xilinx ISE 14.5 are used in system simulations. Furthermore, the digital hardware implementation is done using Xilinx FPGA Virtex-5 kit. The synthesis report shows that
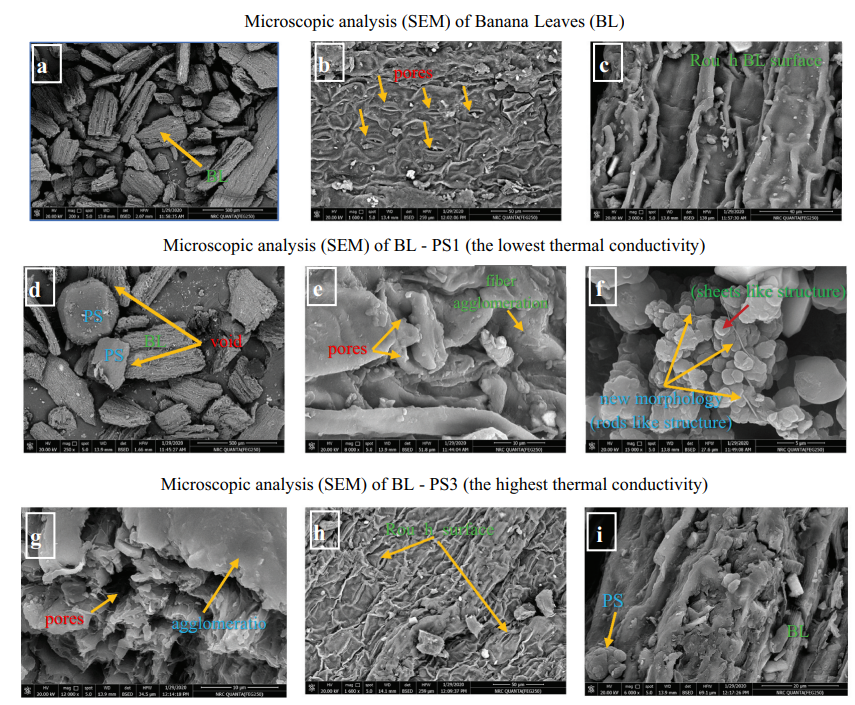
Bio-composite Thermal Insulation Materials Based on Banana Leaves Fibers and Polystyrene: Physical and Thermal Performance
Thermal insulators have a crucial role in reducing the operational building energy. They are commonly fabricated from petrochemical materials that mostly cause negative environmental impacts. This study aims to develop banana leaves-polystyrene composites (BL-PS) as a sustainable and low-cost thermal insulator. The BL powder was mixed with PS in different weight ratios (90:10, 80:20, 70:30, and 60:40). Thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, SEM, XRD, FTIR, TGA, and DSC were carried out on BL and BL-PS composites that were prepared with 10 wt.% of PS powder (BL-PS1) and 30 wt.% of PS
Discretization of emperor penguins colony algorithms with application to modular product design
Modularity concepts attracted the attention of many researchers as it plays an important role in product design problems. Modularity requires dividing a product into a set of modules that are independent between each other and dependent within. The product is represented using Design Structure Matrix (DSM). DSM works as a system representation tool; it visualizes the interrelationship between product elements. In this research, a comparison is conducted between four optimization algorithms: Emperor Penguins Colony (EPC), First Modified Emperor Penguins Colony (MEPC1), Second Modified Emperor
Implementation of PID Controller with PSO Tuning for Autonomous Vehicle
In the use of automatic control and its optimization methods, this research discusses how Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller is used to provide a smooth auto-parking for an electrical autonomous car. Different tuning methods are shown, discussed, and applied to the system looking forward to enhancing its performance. Time domain specifications are used as a criterion of comparison between tuning methods in order to select the best tuning method to the system with a proper cost function. Results show that Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) method gives the best results according
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››
