Feedback-based access schemes in CR networks: A reinforcement learning approach
In this paper, we propose a Reinforcement Learning-based MAC layer protocol for cognitive radio networks, based on exploiting the feedback of the Primary User (PU). Our proposed model relies on two pillars, namely an infinite-state Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) to model the system dynamics besides a queuing-theoretic model for the PU queue, where the states represent whether a packet is delivered or not from the PU's queue and the PU channel state. Based on the stability constraint for the primary user queue, the quality of service (QoS) for the PU is guaranteed. Towards
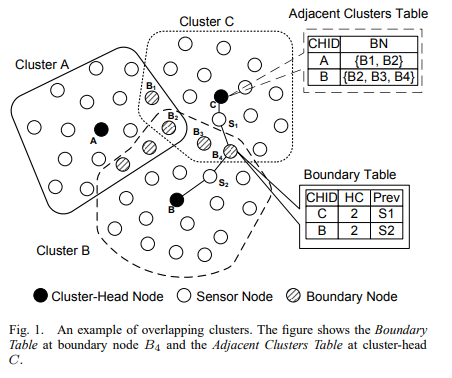
Overlapping multihop clustering for wireless sensor networks
Clustering is a standard approach for achieving efficient and scalable performance in wireless sensor networks. Traditionally, clustering algorithms aim at generating a number of disjoint clusters that satisfy some criteria. In this paper, we formulate a novel clustering problem that aims at generating overlapping multihop clusters. Overlapping clusters are useful in many sensor network applications, including intercluster routing, node localization, and time synchronization protocols. We also propose a randomized, distributed multihop clustering algorithm (KOCA) for solving the overlapping
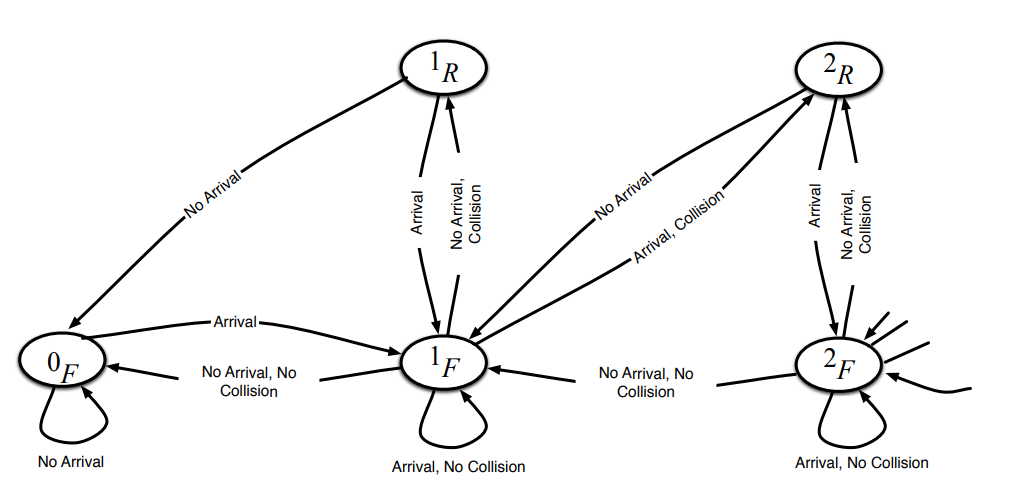
A reinforcement learning approach to ARQ feedback-based multiple access for cognitive radio networks
In this paper, we propose a reinforcement learning (RL) approach to design an access scheme for secondary users (SUs) in a cognitive radio (CR) network. In the proposed scheme, we introduce a deep Q-network to enable SUs to access the primary user (PU) channel based on their past experience and the history of the PU network's automatic repeat request (ARQ) feedback. In essence, SUs cooperate to avoid collisions with other SUs and, more importantly, with the PU network. Since SUs cannot observe the state of the PUs queues, they partially observe the system's state by listening to the PUs' ARQ
Optimum Location of Field Hospitals for COVID-19: A Nonlinear Binary Metaheuristic Algorithm
Determining the optimum location of facilities is critical in many fields, particularly in healthcare. This study proposes the application of a suitable location model for field hospitals during the novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The used model is the most appropriate among the threemost common locationmodels utilized to solve healthcare problems (the set covering model, the maximal covering model, and the P-median model). The proposed nonlinear binary constrained model is a slight modification of the maximal covering model with a set of nonlinear constraints. The model is used to
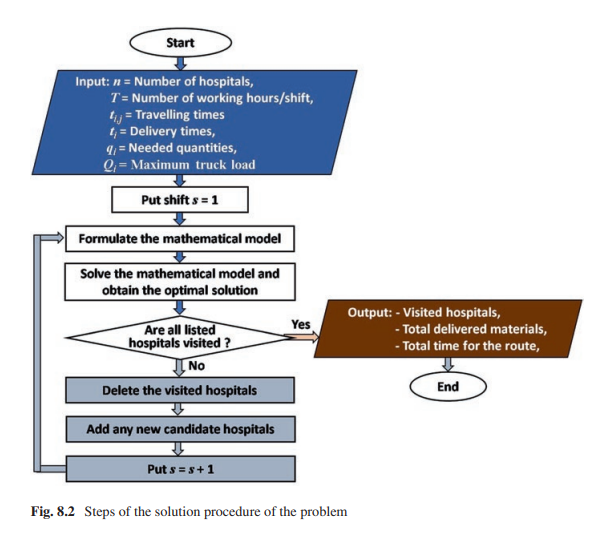
Optimum distribution of protective materials for COVID−19 with a discrete binary gaining-sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm
Many application problems are formulated as nonlinear binary programming models which are hard to be solved using exact algorithms especially in large dimensions. One of these practical applications is to optimally distribute protective materials for the newly emerged COVID-19. It is defined for a decision-maker who wants to choose a subset of candidate hospitals comprising the maximization of the distributed quantities of protective materials to a set of chosen hospitals within a specific time shift. A nonlinear binary mathematical programming model for the problem is introduced with a real
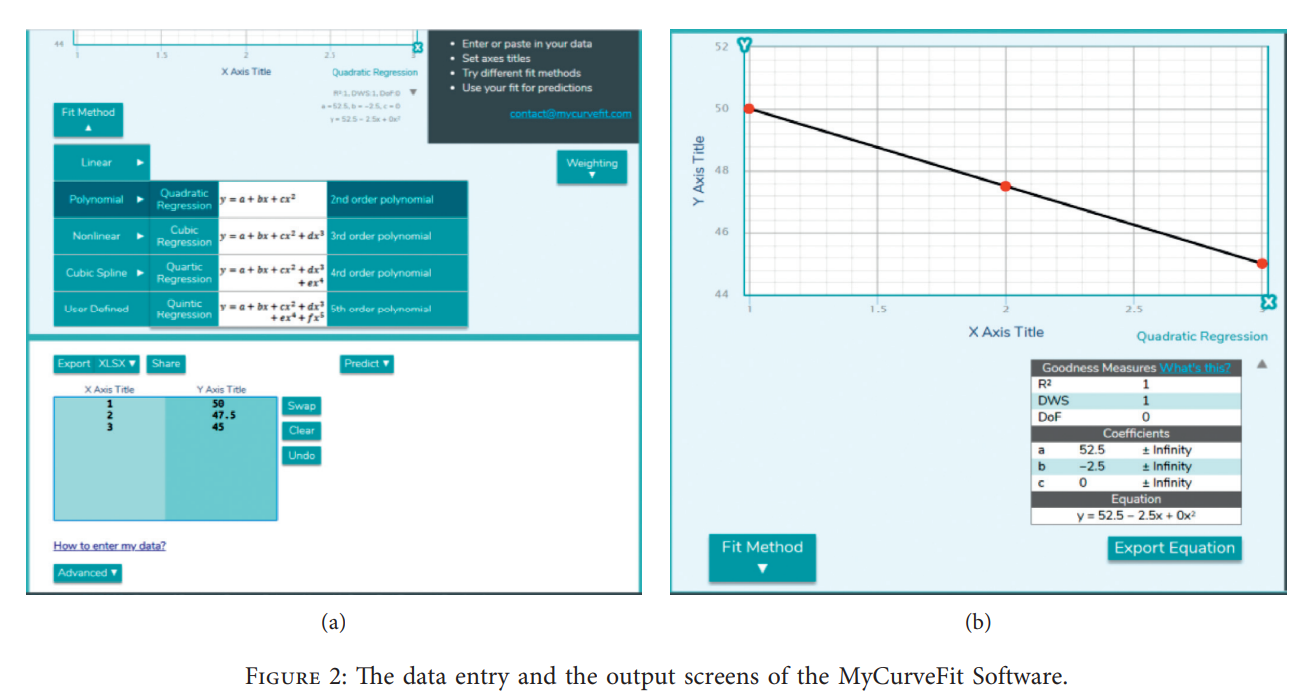
Optimum Scheduling the Electric Distribution Substations with a Case Study: An Integer Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
This work is dedicated to the economic scheduling of the required electric stations in the upcoming 10-year long-term plan. The calculation of the required electric stations is carried out by estimating the yearly consumption of electricity over a long-time plan and then determining the required number of stations. The aim is to minimize the total establishing and operating costs of the stations based on a mathematical programming model with nonlinear objective function and integer decision variables. The introduced model is applied for a real practical case study to conclude the number of
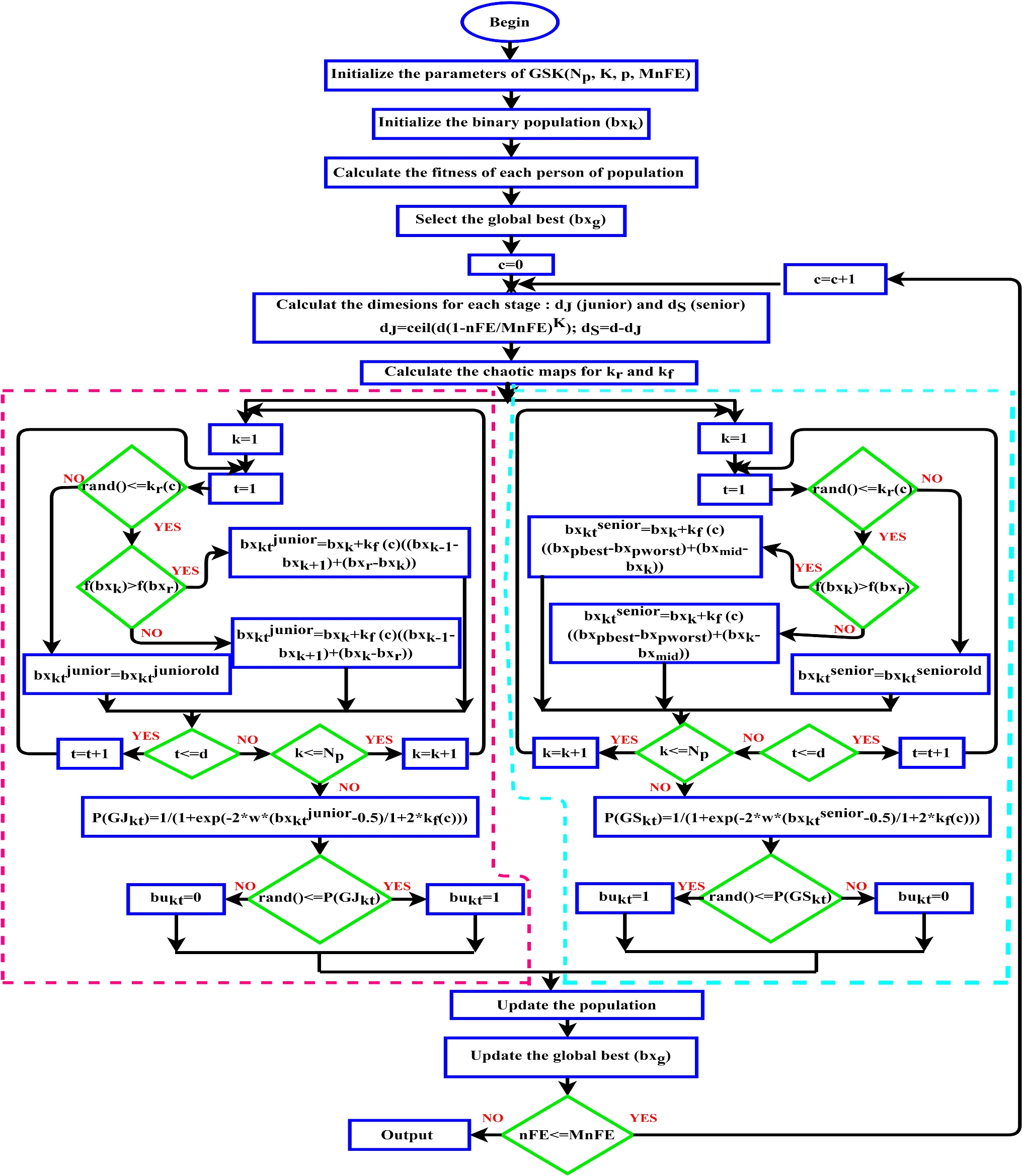
Chaotic gaining sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm: an improved metaheuristic algorithm for feature selection
The gaining sharing knowledge based optimization algorithm (GSK) is recently developed metaheuristic algorithm, which is based on how humans acquire and share knowledge during their life-time. This paper investigates a modified version of the GSK algorithm to find the best feature subsets. Firstly, it represents a binary variant of GSK algorithm by employing a probability estimation operator (Bi-GSK) on the two main pillars of GSK algorithm. And then, the chaotic maps are used to enhance the performance of the proposed algorithm. Ten different types of chaotic maps are considered to adapt the
AROMA: Automatic generation of radio maps for localization systems
Current methods for building radio maps for wireless localization systems require a tedious, manual and error-prone calibration of the area of interest. Each time the layout of the environment is changed or different hardware is used, the whole process of location fingerprinting and constructing the radio map has to be repeated. The process gets more complicated in the case of localizing multiple entities in a device-free scenario, since the radio map needs to take all possible combinations of the location of the entities into account. In this demo, we present a novel system (AROMA) that is
Transmission power adaptation for cognitive radios
In cognitive radio (CR) networks, determining the optimal transmission power for the secondary users (SU) is crucial to achieving the goal of maximizing the secondary throughput while protecting the primary users (PU) from service disruption and interference. In this paper, we propose an adaptive transmission power scheme for cognitive terminals opportunistically accessing a primary channel. The PU operates over the channel in an unslotted manner switching activity at random times. The secondary transmitter (STx) adapts its transmission power according to its belief regarding the PU's state of

Swarm intelligence application to UAV aided IoT data acquisition deployment optimization
It is feasible and safe to use unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) as the data collection platform of the Internet of things (IoT). In order to save the energy loss of the platform and make the UAV perform the collection work effectively, it is necessary to optimize the deployment of UAV. The objective problem is to minimize the sum of the lost energy of UAV and the loss of data transmission of Internet of things devices. The key to solving the problem is to calculate the location of the docking points and the number of docking points when the UAV is working to collect data. This paper proposes a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 39
- Next page ››
