Application of nano waste particles in concrete for sustainable construction: a comparative study
Nano particles contribute as a partial substitute in the production of eco-friendly building materials. This research presents a quantitative assessment of the sustainability effect of partially replacing cement in the green concrete mix with two types of nano-waste particles. The assessment is achieved using two weighing criteria developed by a Sustainable Decision Support System (SDSS) model. This assesses the alternatives using scoring systems based on both the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) technique and Multi-Criteria decision analysis method. Ten sustainable aspects comprising four
Coagulation/flocculation process for textile mill effluent treatment: experimental and numerical perspectives
This study investigates the feasibility of applying coagulation/flocculation process for real textile wastewater treatment. Batch experiments were performed to detect the optimum performance of four different coagulants; Ferric Sulphate (Fe2(SO4)3), Aluminium Chloride (AlCl3), Aluminium Sulphate (Al2(SO4)3) and Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) at diverse ranges of pH (1–11) on the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), colour, total nitrogen (TN) and turbidity from real textile wastewater. At pH 9, FeCl3 demonstrated the most effective removal for all studied
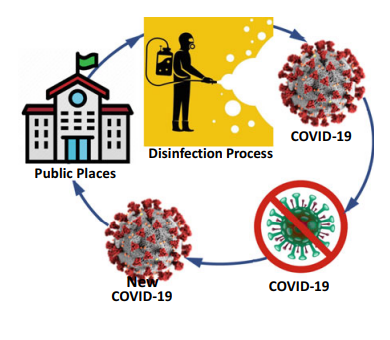
Optimum Scheduling of the Disinfection Process for COVID-19 in Public Places with a Case Study from Egypt, a Novel Discrete Binary Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
The aim of this paper is to introduce an improved strategy for controlling COVID-19 and other pandemic episodes as an environmental disinfection culture for public places. The scheduling aims at achieving the best utilization of the available working day-time hours, which is calculated as the total consumed disinfection times minus the total loosed transportation times. The proposed problem in network optimization identifies a disinfection group who is likely to select a route to reach a subset of predetermined public places to be regularly disinfected with the most utilization of the
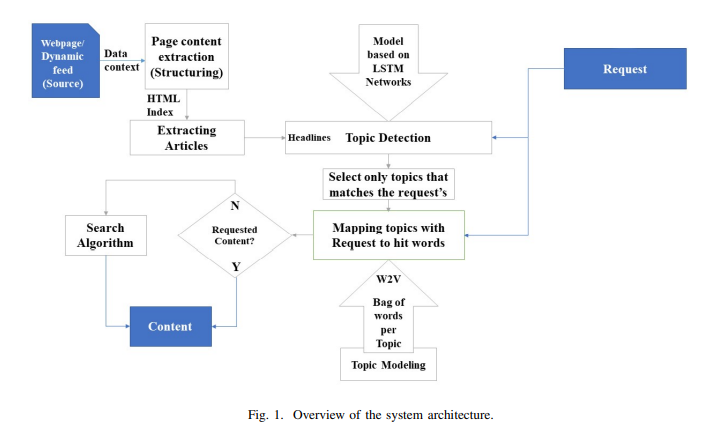
Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learning
Information extraction and reasoning from massive high-dimensional data at dynamic contexts, is very demanding and yet is very hard to obtain in real-time basis. However, such process capability and efficiency might be affected and limited by the available computational resources and the consequent power consumption. Conventional search mechanisms are often incapable of real-time fetching a predefined content from data source, without concerning the increased number of connected devices that contribute to the same source. In this work, we propose and present a concept for an efficient approach
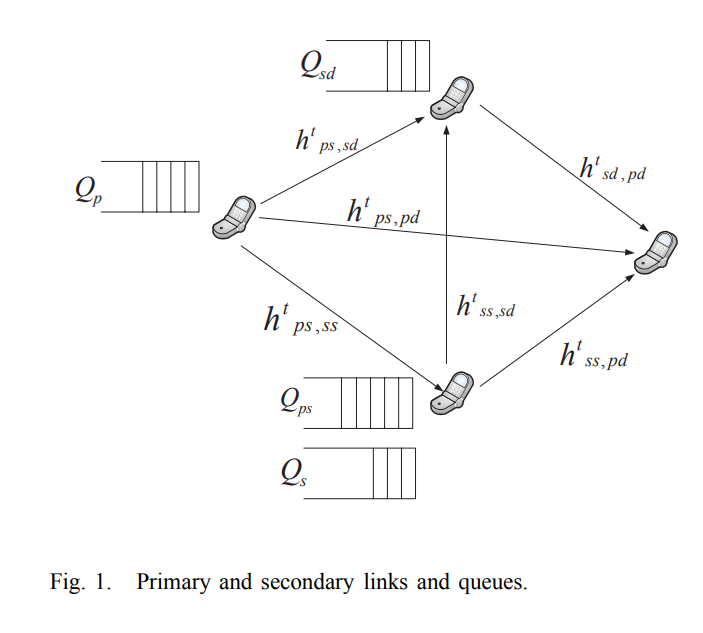
Transmit and receive cooperative cognition: Protocol design and stability analysis
In this paper, we investigate the stability of a cooperative cognitive system. We propose a cooperative secondary transmitter-receiver system (CSTR), where, the secondary transmitter (ST) and the secondary receiver (SR) increase the spectrum availability for the ST packets by relaying the unsuccessfully transmitted packets of the primary transmitter (PT). We assume receiving nodes with multipacket reception capability (MPR). We provide two inner bounds and two outer bounds on the stability region of the considered system. © 2013 ICST - The Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics
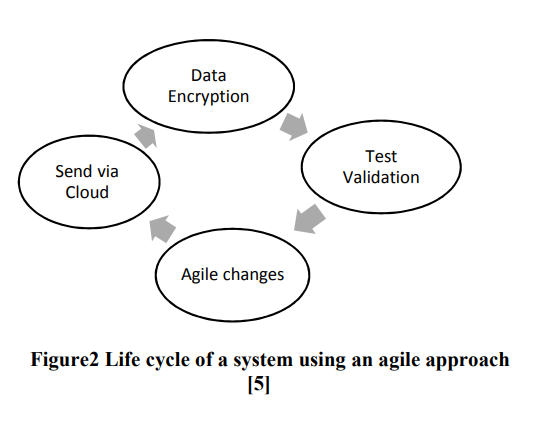
IoT Agile Framework Enhancement
Internet of Things (IoT) is considered as a trend nowadays. Devices connected to the internet interact with surrounding; this poses strong challenges in handling big data with a certain level of security. In this paper IoT devices will be divided in to two categories high vulnerability devices and low vulnerability devices. The classification depends on the ease of attacks. In order to ensure the security of IoT devices, an agile approach is used to secure high vulnerability devices as first step and then low vulnerability devices by applying encryption algorithms. © 2018 IEEE.
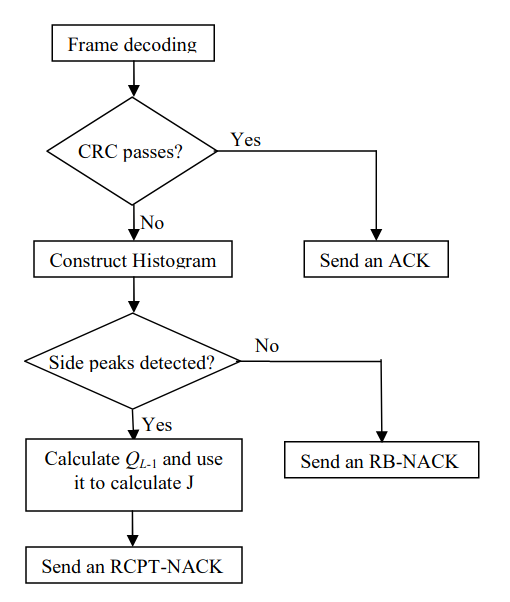
Novel reliability-based hybrid ARQ technique
In this paper we propose a novel technique for hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) systems where turbo codes are used as the forward error correction (FEC) techniques. This technique uses the histogram of the soft values generated by the turbo decoder to control the size and the contents of the retransmissions needed when the packet can not be decoded correctly. These soft values represent the reliabilities of the information bits; hence the proposed technique is a reliability-based (RB) HARQ technique. The proposed technique is compared to the conventional RB-HARQ and the conventional rate
Graph transformer for communities detection in social networks
Graphs are used in various disciplines such as telecommunication, biological networks, as well as social networks. In large-scale networks, it is challenging to detect the communities by learning the distinct properties of the graph. As deep learning has made contributions in a variety of domains, we try to use deep learning techniques to mine the knowledge from large-scale graph networks. In this paper, we aim to provide a strategy for detecting communities using deep autoencoders and obtain generic neural attention to graphs. The advantages of neural attention are widely seen in the field of
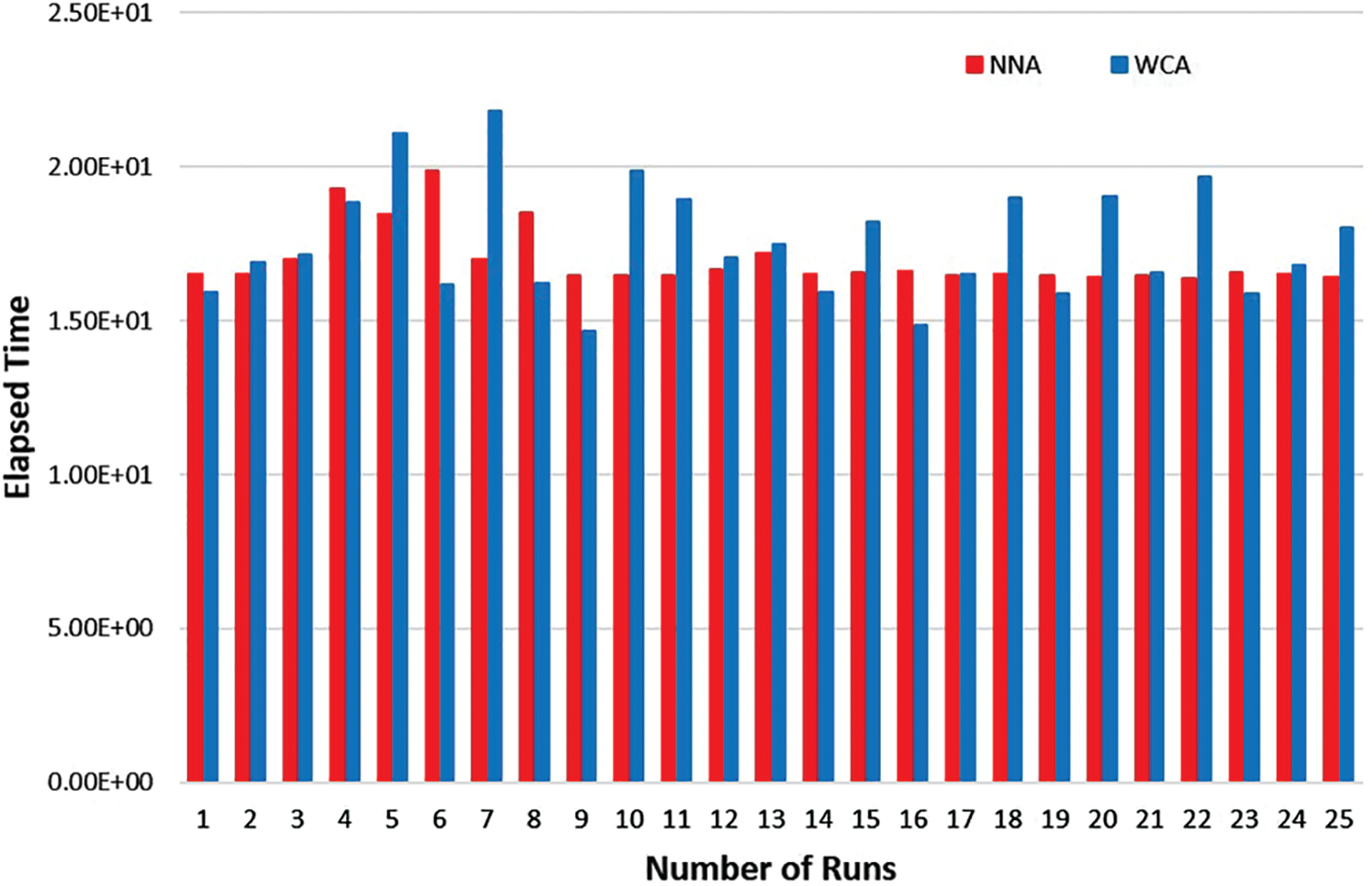
An artificial intelligence approach for solving stochastic transportation problems
Recent years witness a great deal of interest in artificial intelligence (AI) tools in the area of optimization. AI has developed a large number of tools to solve the most difficult search-and-optimization problems in computer science and operations research. Indeed, metaheuristic-based algorithms are a sub-field of AI. This study presents the use of the metaheuristic algorithm, that is, water cycle algorithm (WCA), in the transportation problem. A stochastic transportation problem is considered in which the parameters supply and demand are considered as random variables that follow the

Interference alignment for secrecy
This paper studies the frequency/time selective K-user Gaussian interference channel with secrecy constraints. Two distinct models, namely the interference channel with confidential messages and the interference channel with an external eavesdropper, are analyzed. The key difference between the two models is the lack of channel state information (CSI) of the external eavesdropper. Using interference alignment along with secrecy precoding, it is shown that each user can achieve non-zero secure degrees of freedom (DoF) for both cases. More precisely, the proposed coding scheme achieves K-2/2K-2
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 38
- Next page ››
