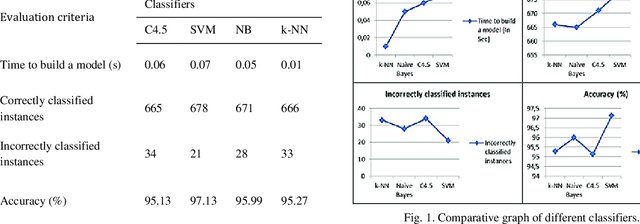
Using machine learning algorithms for breast cancer diagnosis
There are many cancer patients, especially breast cancer patients as it is the most common type of cancer. Due to the huge number of breast cancer patients, many breast cancer-focused hospitals aren't able to process the huge number of patients and might expose some women to late stages of cancer. Thus, the automation of the process can help these hospitals in speeding up the process of cancer detection. In this paper, the authors test several machine learning models such as k-nearest neighbours (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), and artificial neural network (ANN). They then compare their
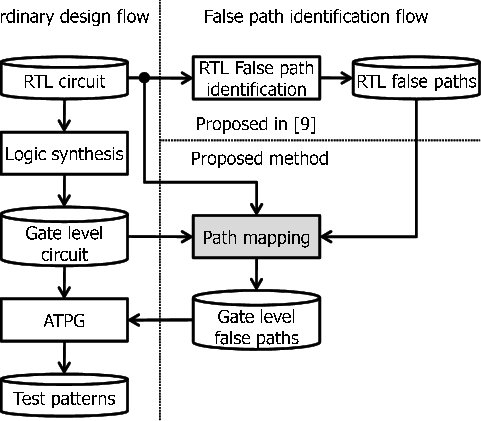
Utilization of Machine Learning In RTL-GL Signals Correlation
Verification is an important part of the Electronic Design Automation (EDA) design flow which currently takes a considerable amount of time. During the synthesis process, Different optimizations are done to the Register-Transfer-Level (RTL) code to optimize the power, area, and speed of the circuit. These optimizations result in changes in the names of signals at the gate level. Automatic signal mapping can improve the verification process and can be used to guide functional verification activities between the two presentations using (Clock domain crossing (CDC) analysis in RTL, Gate Level CDC
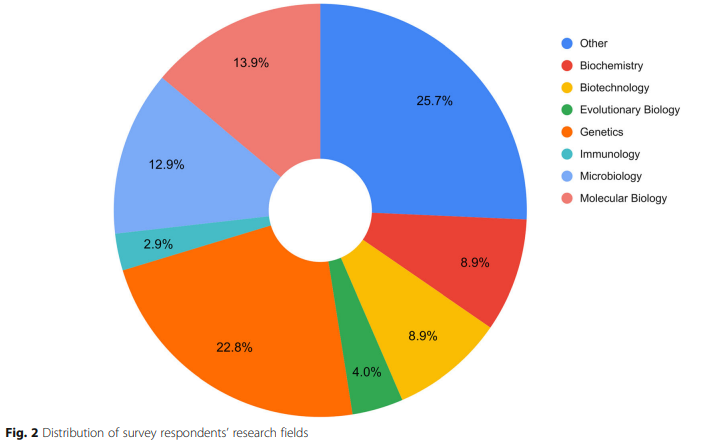
The H3ABioNet helpdesk: An online bioinformatics resource, enhancing Africa's capacity for genomics research
Background: Currently, formal mechanisms for bioinformatics support are limited. The H3Africa Bioinformatics Network has implemented a public and freely available Helpdesk (HD), which provides generic bioinformatics support to researchers through an online ticketing platform. The following article reports on the H3ABioNet HD (H3A-HD)'s development, outlining its design, management, usage and evaluation framework, as well as the lessons learned through implementation. Results: The H3A-HD evaluated using automatically generated usage logs, user feedback and qualitative ticket evaluation
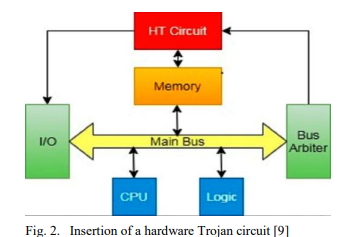
Securing Hardware from Malicious Attacks
Hardware security is considered a major design and manufacturing target area with a broad range of research and development topics such as protection of intellectual property (IP), metering of hardware, detection of hardware Trojans, and a lot of other topics. This paper discusses Trojan realization in integrated circuits (ICs), as well as the possible security measures, also exploring the usage of the 3-D integration in hardware security where additional hardware can be mounted after fabrication to foster secure execution just for those systems which need it. © 2021 IEEE.
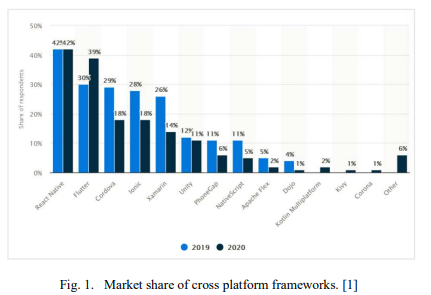
General Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications Converter
Deployment on different platforms has been a great issue for mobile companies that aim to maximize the return on investments by making their mobile applications available on different mobile platforms. Consequently, the app may be developed several times to match different platforms. Therefore, there is a need to have solutions that enable the developers to develop the app once, and run it everywhere to reduce the cost of development and reach out to maximum users across several platforms. In this paper a tool is provided with the most popular languages /frameworks (native, cross platform)
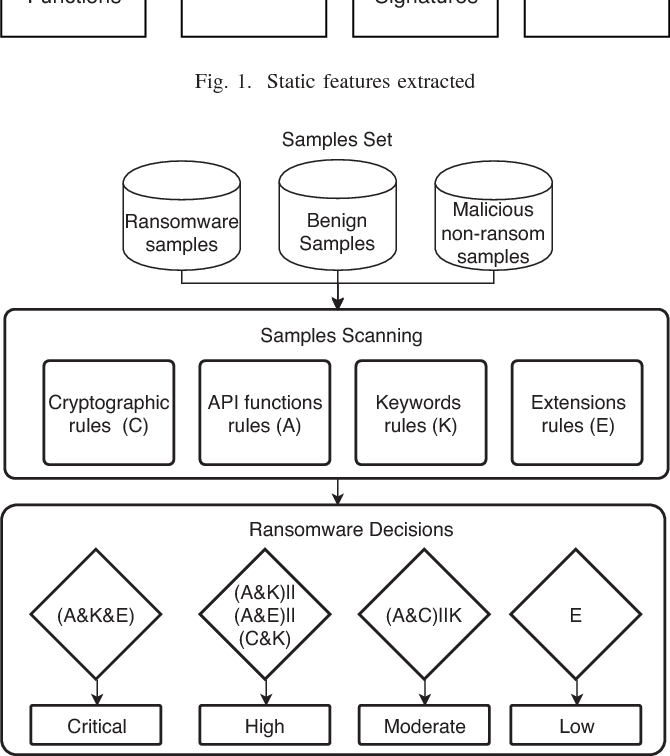
A new static-based framework for ransomware detection
Recently, ransomware attacks are on the rise hitting critical infrastructures and organizations globally. Ransomware uses advanced encryption techniques to encrypt important files on the targeted computer, then it requests payment to decrypt the encrypted files again. Therefore, the detection and prevention of ransomware attacks represent major challenges for security researchers. This research proposes a novel static-based rules ransomware detection framework. The decision rules of the proposed framework are based on static features extracted from the ransomware files. When scanned file
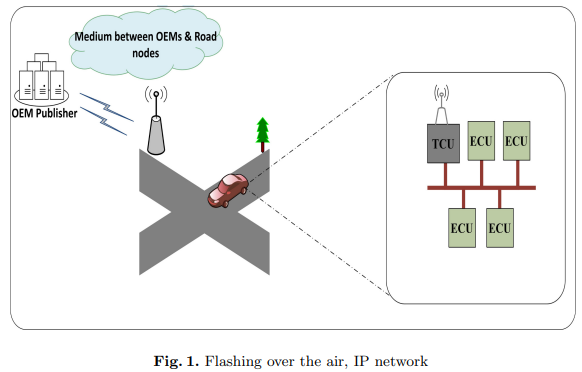
Vehicle Software Update over ICN Architectures
The Internet Protocol (IP) architecture could not fully satisfy Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) needed efficiency due to their dynamic topology and high mobility. This paper presents a technique to update the software of Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in vehicles using Information Centric Network (ICN) architecture. The proposed technique replaces Flashing Over The Air (FOTA) using IP with FOTA using ICN. The importance of FOTA is illustrated as well as the impact of applying the ICN architecture on VANETs. Through our experiments, we compare between the known FOTA over IP and the newly
Decoding arm kinematics from EMG signals using Kalman filter
Myoelectric control of prosthetic arms provides a new hope for providing naturalistic movements to amputees. Extensive work has been made in recent years to use Electromyography (EMG) signals to enhance the operation of prosthetic arms. In this paper, we propose an EMG Kalman filter-based model, where we identify the relationship between the joint angles and recorded EMG signals. EMG signals were recorded from biceps and triceps muscles and used to train a Kalman filter decoder. We assessed the performance of the decoder by computing the correlation and the normalized root mean-square error
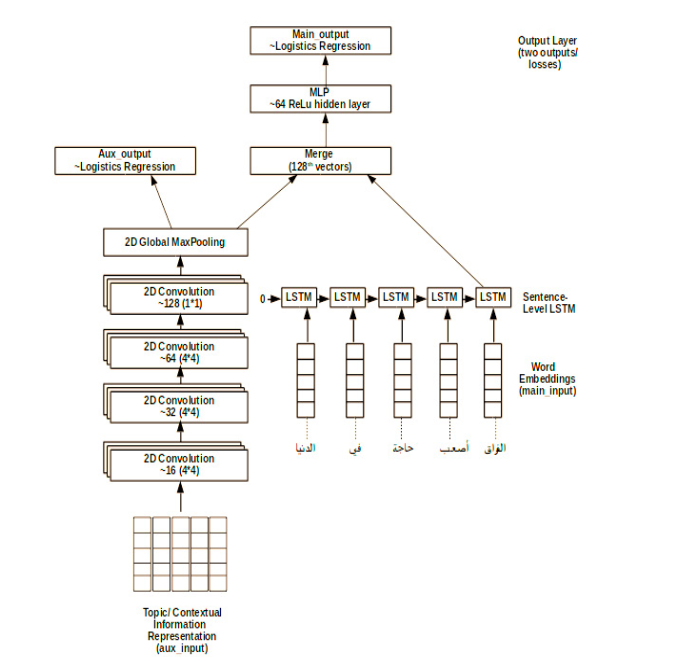
A Context Integrated Model for Multi-label Emotion Detection
This paper explores the impact of taking the environment within which a tweet is made, on the task of analyzing sentiment orientations of tweets produced by people in the same community. The paper proposes C-GRU (Context-aware Gated Recurrent Units), which extracts the contextual information (topics) from tweets and uses them as an extra layer to determine sentiments conveyed by the tweet. The proposed architecture learns direct co-relations between such information and the task's predication. The multi-modal model combines both outputs learnt (from topics and sentences) by learning the
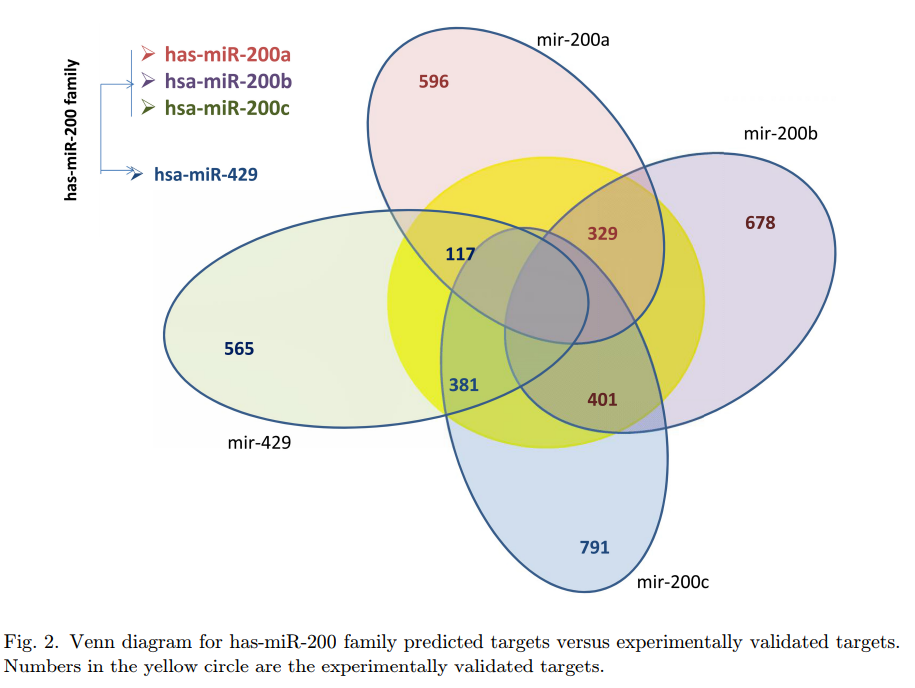
MicroTarget: MicroRNA target gene prediction approach with application to breast cancer
MicroRNAs are known to play an essential role in gene regulation in plants and animals. The standard method for understanding microRNA-gene interactions is randomized controlled perturbation experiments. These experiments are costly and time consuming. Therefore, use of computational methods is essential. Currently, several computational methods have been developed to discover microRNA target genes. However, these methods have limitations based on the features that are used for prediction. The commonly used features are complementarity to the seed region of the microRNA, site accessibility
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 32
- Next page ››
