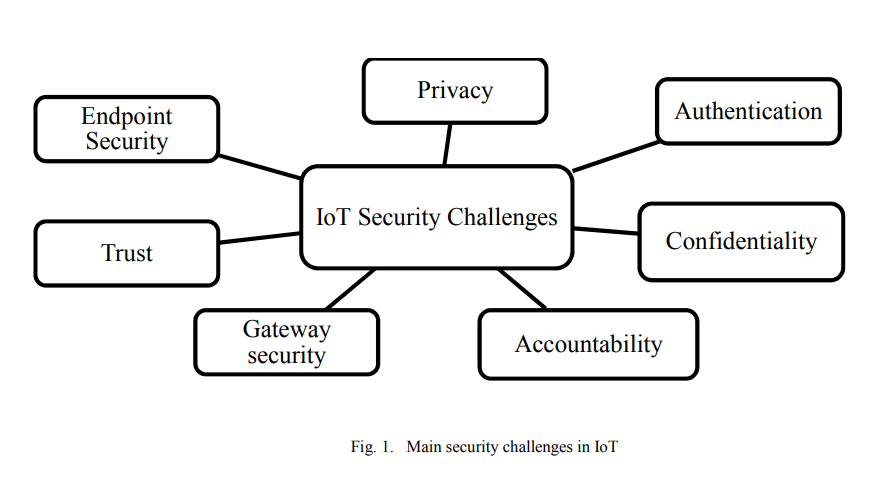
Internet of Things security framework
For the past decade, Internet of Things (IoT) had an important role in our lives. It connects a large number of embedded devices. These devices fulfill very difficult and complicated tasks, which facilitate our work. Till now the security of IoT faces many challenges such as privacy, authentication, confidentiality, trust, middleware security, mobile security and policy enforcement. In order to provide a secure environment for IoT, this paper proposes a framework for IoT devices. © 2017 IEEE.
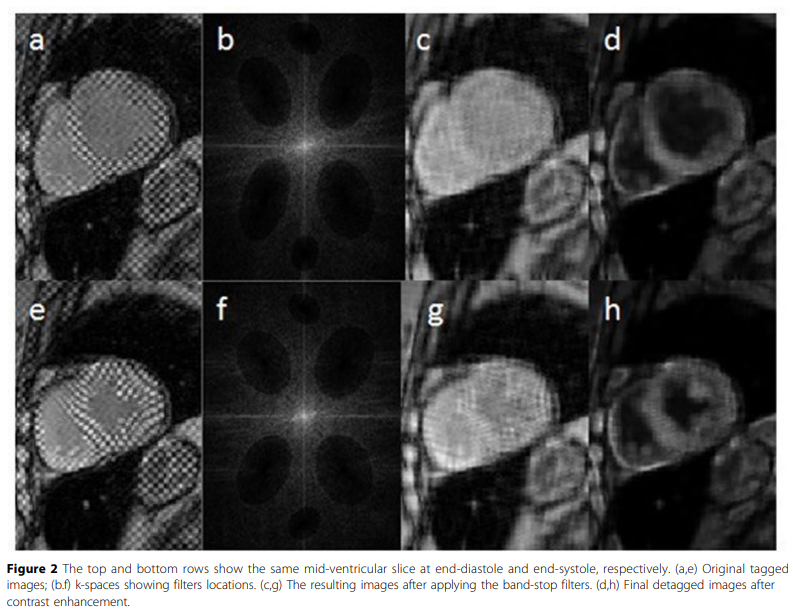
Evaluation of the cardiac global function from tagged magnetic resonance images
Tagged Magnetic Resonance (MR) images are considered the gold standard for evaluating the cardiac regional function. Nevertheless, the low myocardium-to-blood contrast in tagged MR images prevents accurate segmentation of the myocardium, and hence, hinders the quantitative assessment of the global function of the heart. In this work, a method for enhancing the myocardium-to-blood contrast in tagged MR images is proposed. First, the tag pattern in each input tagged MR image is removed using technique based on the image texture and the frequency components of the tag pattern to produce two
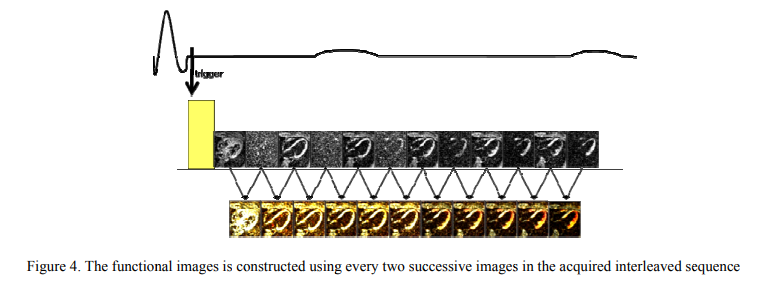
Strain correction in interleaved strain-encoded (SENC) cardiac MR
The strain encoding (SENC) technique directly encodes regional strain of the heart into the acquired MR images and produces two images with two different tunings so that longitudinal strain, on the short-axis view, or circumferential strain on the long-axis view, are measured. Interleaving acquisition is used to shorten the acquisition time of the two tuned images by 50%, but it suffers from errors in the strain calculations due to inter-tunings motion of the heart. In this work, we propose a method to correct for the inter-tunings motion by estimating the motion-induced shift in the spatial
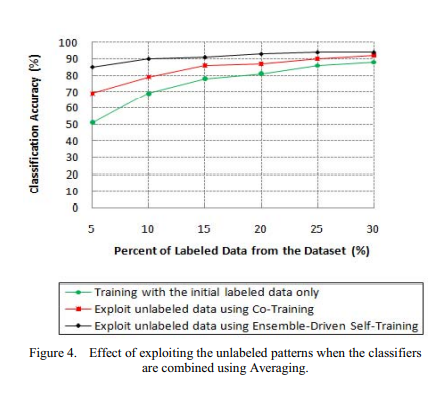
A semi-supervised learning approach for soft labeled data
In some machine learning applications using soft labels is more useful and informative than crisp labels. Soft labels indicate the degree of membership of the training data to the given classes. Often only a small number of labeled data is available while unlabeled data is abundant. Therefore, it is important to make use of unlabeled data. In this paper we propose an approach for Fuzzy-Input Fuzzy-Output classification in which the classifier can learn with soft-labeled data and can also produce degree of belongingness to classes as an output for each pattern. Particularly, we investigate the
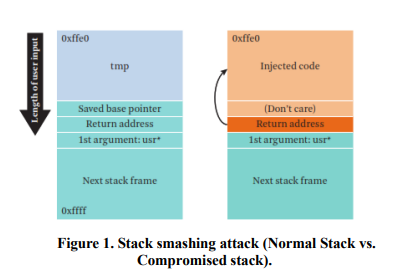
Survey of Code Reuse Attacks and Comparison of Mitigation Techniques
Code-Reuse Attacks (CRAs) are solid mechanisms to bypass advanced software and hardware defenses. Due to vulnerabilities found in software which allows attackers to corrupt the memory space of the vulnerable software to modify maliciously the contents of the memory; hence controlling the software to be able to run arbitrary code. The CRAs defenses either prevents the attacker from reading program code, controlling program memory space directly or indirectly through the usage of pointers. This paper provides a thorough evaluation of the current mitigation techniques against CRAs with regards to
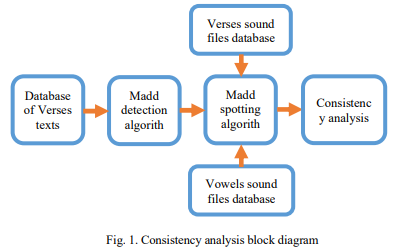
Consistency Analysis of Madd rules in the Holy Quran
A consistency analysis is performed for one of the famous Tajweed rules in the Holy Quran - Madd rules. They are tested on records of one of the famous reference reciters - Sheikh El-Hosary-to find a consistent boundaries and to evaluate the performance of other new learners. A vowel detection algorithm is used to detect the duration of the detected Madd patterns. This algorithm was applied on a dataset of 105 minutes of Quranic records of Sheikh El-Hosary. The consistency result is found to be normally distributed with a mean of 0.379 second of one movement time of Madd and standard deviation
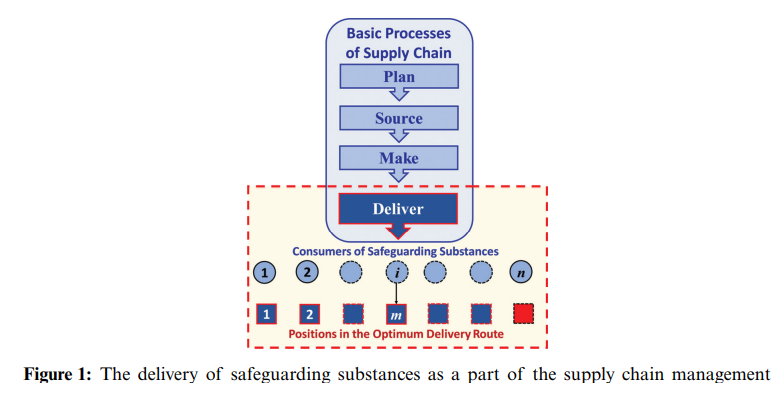
Managing Delivery of Safeguarding Substances as a Mitigation against Outbreaks of Pandemics
The optimum delivery of safeguarding substances is a major part of supply chain management and a crucial issue in the mitigation against the outbreak of pandemics. A problem arises for a decision maker who wants to optimally choose a subset of candidate consumers to maximize the distributed quantities of the needed safeguarding substances within a specic time period. A nonlinear binary mathematical programming model for the problem is formulated. The decision variables are binary ones that represent whether to choose a specic consumer, and design constraints are formulated to keep track of the

The overexpression of DNA repair genes in invasive ductal and lobular breast carcinomas: Insights on individual variations and precision medicine
In the era of precision medicine, analyzing the transcriptomic profile of patients is essential to tailor the appropriate therapy. In this study, we explored transcriptional differences between two invasive breast cancer subtypes; infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) and lobular carcinoma (LC) using RNA-Seq data deposited in the TCGA-BRCA project. We revealed 3854 differentially expressed genes between normal ductal tissues and IDC. In addition, IDC to LC comparison resulted in 663 differentially expressed genes. We then focused on DNA repair genes because of their known effects on patients'
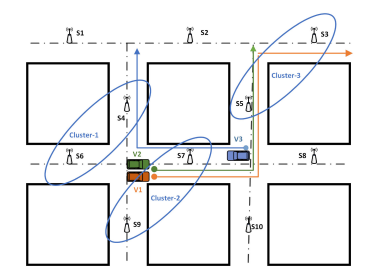
Mobility-Aware Edge Caching for Minimizing Latency in Vehicular Networks
This work proposes novel proactive caching schemes for minimizing the communication latency in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs) under freeway and city mobility models. The main philosophy that underlies these schemes is to exploit information that may be available a priori for vehicles' demands and mobility patterns. We consider two paradigms: cooperative, wherein multiple Roadside Units (RSUs) collaborate to expedite the transfer of information to the intended user, and non-cooperative, wherein each RSU operates independently of other RSUs in the network. To develop the proposed schemes
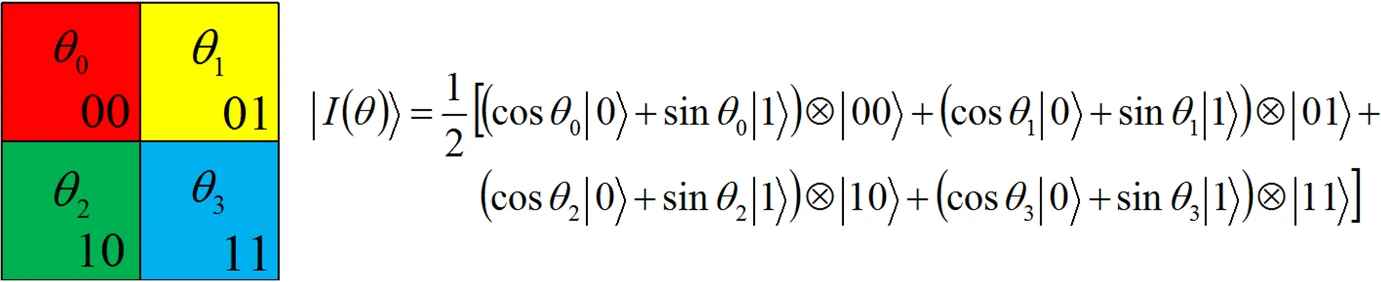
QIRHSI: novel quantum image representation based on HSI color space model
We present QIRHSI, a novel quantum image representation method based on the HSI color space model. QIRHSI integrates the advantages of the Flexible Representation of Quantum Images (FRQI) model and the Novel Enhanced Quantum Representation (NEQR) model. On the one hand, the proposed QIRHSI model is better suited for the image processing related to intensity information via binary qubit sequence than multi-channel representation for quantum image (MCQI) (multi-channel FRQI). On the other hand, the QIRHSI model requires less storage space (10 qubits) in the hue and saturation channels, compared
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 31
- Next page ››
