Emotions analysis of speech for call classification
Most existing research in the area of emotions recognition has focused on short segments or utterances of speech. In this paper we propose a machine learning system for classifying the overall sentiment of long conversations as being Positive or Negative. Our system has three main phases, first it divides a call into short segments, second it applies machine learning to recognize the emotion for each segment, and finally it learns a binary classifier that takes the recognized emotions of individual segments as features. We investigate different approaches for this final phase by varying how
Predicting all star player in the national basketball association using random forest
National Basketball Association (NBA) All Star Game is a demonstration game played between the selected Western and Eastern conference players. The selection of players for the NBA All Star game purely depends on votes. The fans and coaches vote for the players and decide who is going to make the All Star roster. A player who continues to receive enough votes in following years will play more All Star games. The selection of All Star players in NBA is subjective based on voting and there are no selection criteria that take out the human bias and opinion. Analyzing data from previous sports
MLP, gaussian processes and negative correlation learning for time series prediction
Time series forecasting is a challenging problem, that has a wide variety of application domains such as in engineering, environment, finance and others. When confronted with a time series forecasting application, typically a number of different forecasting models are tested and the best one is considered. Alternatively, instead of choosing the single best method, a wiser action could be to choose a group of the best models and then to combine their forecasts. In this study we propose a combined model consisting of Multi-layer perceptron (MLP), Gaussian Processes Regression (GPR) and a
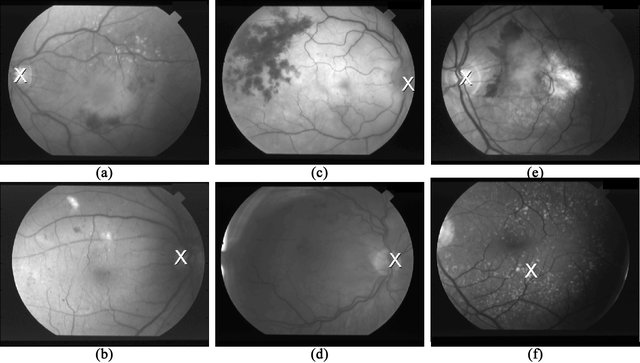
Ultrafast optic disc localization using projection of image features
Optic Disc (OD) localization is a fundamental step in developing computer-assisted diagnostics. In this work, an ultrafast method to locate the OD in retinal fundus images is presented. The proposed method is based on transforming the localization problem into two 1D problems by projecting the image features onto two perpendicular directions. Image features such as the directionality of the retinal vessels, the brightness and the size of the OD have been used in the current method. Two publicly available databases were used to evaluate the accuracy and the computation time of the proposed
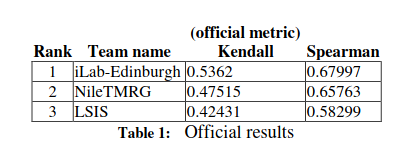
NileTMRG at SemEval-2016 Task 7: Deriving prior polarities for Arabic sentiment terms
This paper presents a model that was developed to address SemEval Task 7: "Determining Sentiment Intensity of English and Arabic Phrases", with focus on 'Arabic Phrases'. The goal of this task is to determine the degree to which some given term is associated with positive sentiment. The underlying premise behind the model that we have adopted is that determining the context (positive or negative) in which a term usually occurs can determine its strength. Since the focus is on Twitter terms, Twitter was used to collect tweets for each term for which a strength value was to be derived. An Arabic
NileTMRG at SemEval-2016 task 5: Deep convolutional neural networks for aspect category and sentiment extraction
This paper describes our participation in the SemEval-2016 task 5, Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA). We participated in two slots in the sentence level ABSA (Subtask 1) namely: aspect category extraction (Slot 1) and sentiment polarity extraction (Slot 3) in English Restaurants and Laptops reviews. For Slot 1, we applied different models for each domain. In the restaurants domain, we used an ensemble classifier for each aspect which is a combination of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) classifier initialized with pretrained word vectors, and a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier

Detecting and Integrating Multiword Expression into English-Arabic Statistical Machine Translation
In this paper we introduce a new method for detecting a type of English Multiword Expressions (MWEs), which is phrasal verbs, into an English-Arabic phrase-based statistical machine translation (PBSMT) system. The detection starts with parsing the English side of the parallel corpus, detecting various linguistic patterns for phrasal verbs and finally integrate them into the En-Ar PBSMT system. In addition, the paper explores the effect of cliticizing specific words in English that have no Arabic equivalent. The results, which reported with the BLEU scores, showed that some patterns achieved
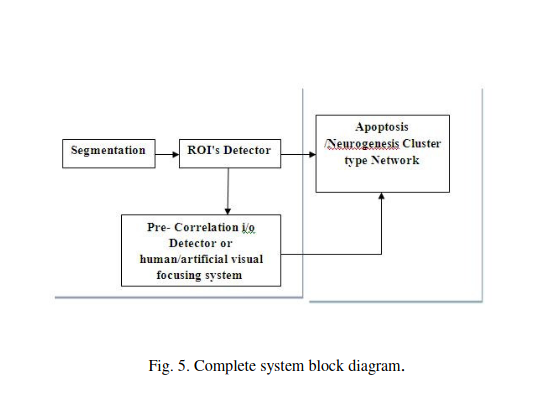
Novel computational apoptosis-neurogenesis model for multi-abstraction level perception
artificial neural network provides a cybernetic model that is similar to human intelligence in terms of parallel processing, generalization and memory stacking on the same neural network. From the era of neurogenesis, research models expect the rules that govern new neuron to depend on old mature circuitry. Other research models show the existence of catastrophic interference associated with new neurons if species is exposed to variable information content environment. In this work, the model developed provides a theoretical framework for a novel attention sensitive neural network as well as
Code Smells and Detection Techniques: A Survey
Design and code smells are characteristics in the software source code that might indicate a deeper design problem. Code smells can lead to costly maintenance and quality problems, to remove these code smells, the software engineers should follow the best practices, which are the set of correct techniques which improve the software quality. Refactoring is an adequate technique to fix code smells, software refactoring modifies the internal code structure without changing its functionality and suggests the best redesign changes to be performed. Developers who apply correct refactoring sequences

Security Perspective in RAMI 4.0
Cloud Computing, Internet of Things (IoT) are the main technologies contributing to the adoption of the fourth revolution in manufacturing, Industry 4.0 also known as smart manufacturing or digital manufacturing. Smart manufacturing facilitates and accelerates the process of manufacturing with the connection of all the systems related to the manufacturing process starting with the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, the Industrial Control Systems (ICSs) which control the production line and the Cyber Physical Systems (CPSs). Before the emerging of web applications, cloud applications
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 27
- Next page ››
