Finite precision logistic map between computational efficiency and accuracy with encryption applications
Chaotic systems appear in many applications such as pseudo-random number generation, text encryption, and secure image transfer. Numerical solutions of these systems using digital software or hardware inevitably deviate from the expected analytical solutions. Chaotic orbits produced using finite precision systems do not exhibit the infinite period expected under the assumptions of infinite simulation time and precision. In this paper, digital implementation of the generalized logisticmap with signed parameter is considered. We present a fixed-point hardware realization of a Pseudo-Random
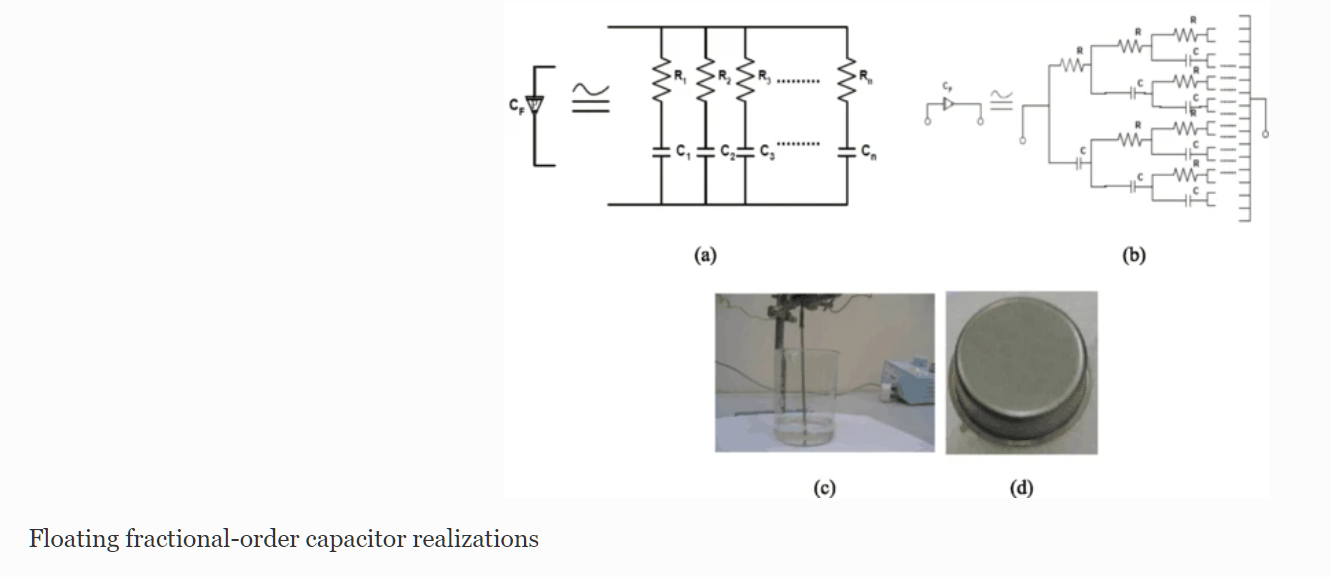
Optimization of fractional-order RLC filters
This paper introduces some generalized fundamentals for fractional-order RL β C α circuits as well as a gradient-based optimization technique in the frequency domain. One of the main advantages of the fractional-order design is that it increases the flexibility and degrees of freedom by means of the fractional parameters, which provide new fundamentals and can be used for better interpretation or best fit matching with experimental results. An analysis of the real and imaginary components, the magnitude and phase responses, and the sensitivity must be performed to obtain an optimal design
FPGA-Based Memristor Emulator Circuit for Binary Convolutional Neural Networks
Binary convolutional neural networks (BCNN) have been proposed in the literature for resource-constrained IoTs nodes and mobile computing devices. Such computing platforms have strict constraints on the power budget, system performance, processing and memory capabilities. Nonetheless, the platforms are still required to efficiently perform classification and matching tasks needed in various applications. The memristor device has shown promising results when utilized for in-memory computing architectures, due to its ability to perform storage and computation using the same physical element

Guest editorial mission critical networking
[No abstract available]
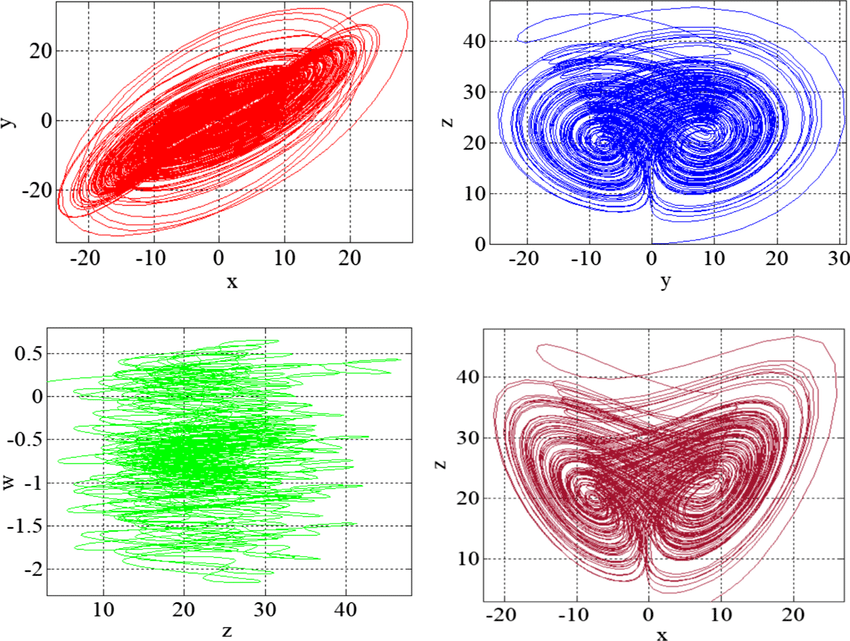
New hybrid synchronisation schemes based on coexistence of various types of synchronisation between master-slave hyperchaotic systems
In this paper, we present new approaches to study the co-existence of some types of synchronisation between hyperchaotic dynamical systems. The paper first analyses, based on stability theory of linear continuous-Time systems, the co-existence of the projective synchronisation (PS), the function projective synchronisation (FPS), the full state hybrid function projective synchronisation (FSHFPS) and the generalised synchronisation (GS) between general master and slave hyperchaotic systems. Successively, using Lyapunov stability theory, the coexistence of three different synchronisation types is
Trajectory control and image encryption using affine transformation of lorenz system
This paper presents a generalization of chaotic systems using two-dimensional affine transformations with six introduced parameters to achieve scaling, reflection, rotation, translation and/or shearing. Hence, the location of the strange attractor in space can be controlled without changing its chaotic dynamics. In addition, the embedded parameters enhance the randomness and sensitivity of the system and control its response. This approach overpasses performing the transformations as post-processing stages by applying them on the resulting time series. Trajectory control through dynamic
Design of Positive, Negative, and Alternating Sign Generalized Logistic Maps
The discrete logistic map is one of the most famous discrete chaotic maps which has widely spread applications. This paper investigates a set of four generalized logistic maps where the conventional map is a special case. The proposed maps have extra degrees of freedom which provide different chaotic characteristics and increase the design flexibility required for many applications such as quantitative financial modeling. Based on the maximum chaotic range of the output, the proposed maps can be classified as positive logistic map, mostly positive logistic map, negative logistic map, and
Improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator
This paper presents an improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator which offers higher frequency and wider tunning range than the existing reactance-less oscillators. It also has the capability of operating on two positive supplies or alternatively a positive and negative supply. Furthermore, it has the advantage that it can be fully integrated on-chip providing an area-efficient solution. On the other hand, The oscillation concept is discussed then a complete mathematical analysis of the proposed oscillator is introduced. Furthermore, the power consumption of the new relaxation circuit is
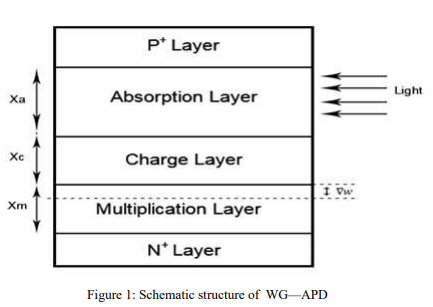
A Stochastic Modeling of the Gain in Waveguide Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs)
Waveguide photodetectors are considered as a promising candidate for high speed photodetection where the tradeoff between the transit time bandwidth and the quantum efficiency is overcome as the incident optical signal and the photogenerated carriers move in perpendicular directions. In WG-Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs), the avalanche multiplication gain enhances the photocurrent of the photodiodes. In these photodiodes, the inaccuracies in the ionizations coefficients of the photogenerated electrons and holes and in the dimensions of the multiplication layer affect the multiplication gain
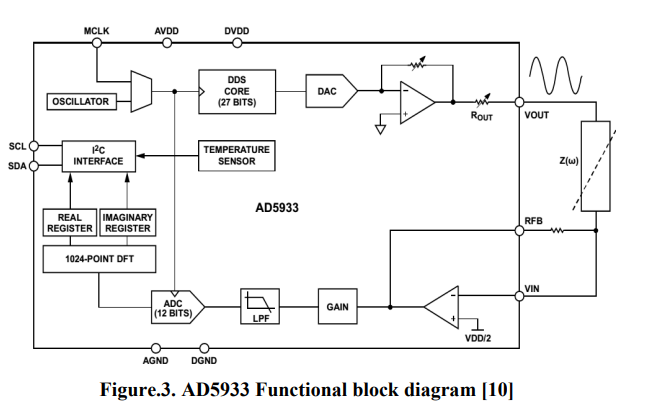
Aging effect on apples bio-impedance using AD5933
In this paper, the effect of the fruits aging on bio-impedance is experimentally studied. Bio-impedance analysis, as accurate and fast method is used to investigate and monitor group of apples properties during aging. This method provides an alternative method for investigating apples physical properties that are highly related to chemical properties. AD5933 impedance analyzer chip within the frequency range (5 KHz-100 KHz) and NI-ELVIS board within the frequency range (300 Hz-5 KHz) are used to investigate the changes in apple's properties during aging. According to experimental results, the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
