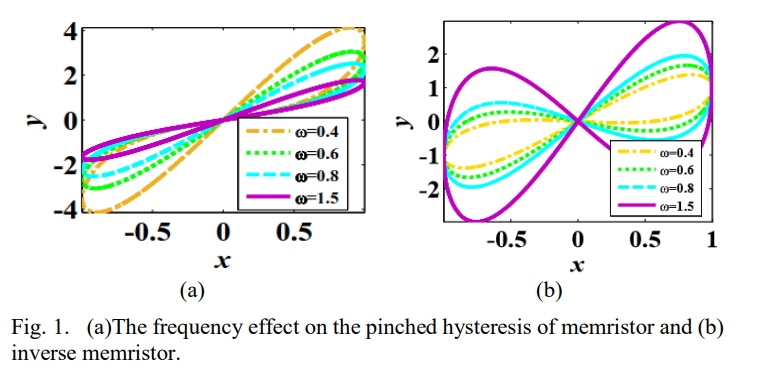
Inverse memrsitor emulator active Realizations
The paper aims to propose three different inverse memristor emulators based on serveral active blocks. One of the presented emulator realizes employing second generation current conveyor (CCII) andcanalog voltage multiplier with passive elements. The other two introduced emulators are designed using cureent feedback operational amplifier (CFOA) with two switches or two BJT transistor. One of the proposed emulators has the advantages that it switches between the inverse and memristor at the same time but in different frequency with less number of components. The introduced circuitry are
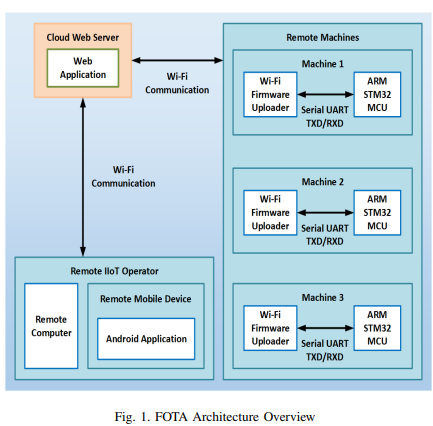
A Scalable Firmware-Over-The-Air Architecture suitable for Industrial IoT Applications
This paper proposes a reliable and scalable architecture for firmware-over-the-air updates, which provides remote cloud real-time distribution of new firmware versions on industrial machines in an efficient simultaneous manner. The architecture comprises remotely interconnected software and hardware systems for handling the procedures of firmware distribution over a wireless network. The main contributions are developing a special boot-loader for ARM micro-controllers and an Android application for performing FOTA updates. A simulation is performed using Web and Android applications showing
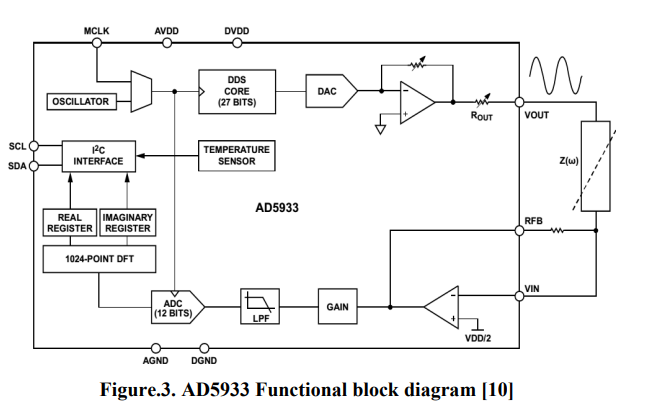
Aging effect on apples bio-impedance using AD5933
In this paper, the effect of the fruits aging on bio-impedance is experimentally studied. Bio-impedance analysis, as accurate and fast method is used to investigate and monitor group of apples properties during aging. This method provides an alternative method for investigating apples physical properties that are highly related to chemical properties. AD5933 impedance analyzer chip within the frequency range (5 KHz-100 KHz) and NI-ELVIS board within the frequency range (300 Hz-5 KHz) are used to investigate the changes in apple's properties during aging. According to experimental results, the
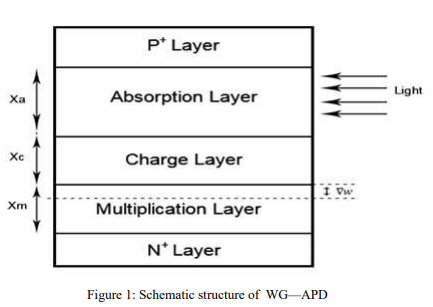
A Stochastic Modeling of the Gain in Waveguide Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs)
Waveguide photodetectors are considered as a promising candidate for high speed photodetection where the tradeoff between the transit time bandwidth and the quantum efficiency is overcome as the incident optical signal and the photogenerated carriers move in perpendicular directions. In WG-Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs), the avalanche multiplication gain enhances the photocurrent of the photodiodes. In these photodiodes, the inaccuracies in the ionizations coefficients of the photogenerated electrons and holes and in the dimensions of the multiplication layer affect the multiplication gain
Improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator
This paper presents an improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator which offers higher frequency and wider tunning range than the existing reactance-less oscillators. It also has the capability of operating on two positive supplies or alternatively a positive and negative supply. Furthermore, it has the advantage that it can be fully integrated on-chip providing an area-efficient solution. On the other hand, The oscillation concept is discussed then a complete mathematical analysis of the proposed oscillator is introduced. Furthermore, the power consumption of the new relaxation circuit is
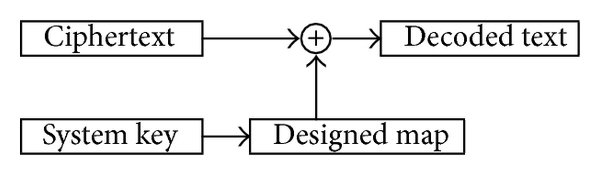
Design of Positive, Negative, and Alternating Sign Generalized Logistic Maps
The discrete logistic map is one of the most famous discrete chaotic maps which has widely spread applications. This paper investigates a set of four generalized logistic maps where the conventional map is a special case. The proposed maps have extra degrees of freedom which provide different chaotic characteristics and increase the design flexibility required for many applications such as quantitative financial modeling. Based on the maximum chaotic range of the output, the proposed maps can be classified as positive logistic map, mostly positive logistic map, negative logistic map, and
Trajectory control and image encryption using affine transformation of lorenz system
This paper presents a generalization of chaotic systems using two-dimensional affine transformations with six introduced parameters to achieve scaling, reflection, rotation, translation and/or shearing. Hence, the location of the strange attractor in space can be controlled without changing its chaotic dynamics. In addition, the embedded parameters enhance the randomness and sensitivity of the system and control its response. This approach overpasses performing the transformations as post-processing stages by applying them on the resulting time series. Trajectory control through dynamic
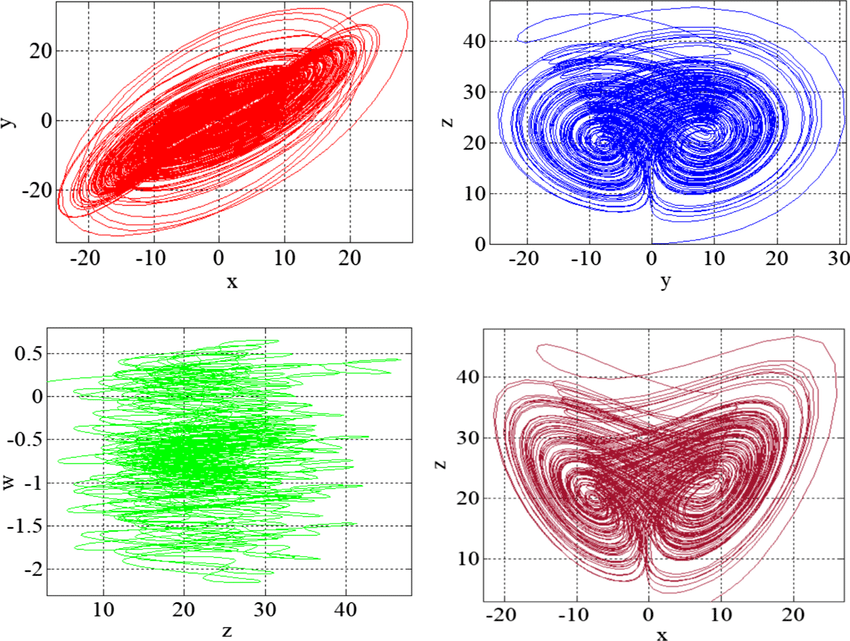
New hybrid synchronisation schemes based on coexistence of various types of synchronisation between master-slave hyperchaotic systems
In this paper, we present new approaches to study the co-existence of some types of synchronisation between hyperchaotic dynamical systems. The paper first analyses, based on stability theory of linear continuous-Time systems, the co-existence of the projective synchronisation (PS), the function projective synchronisation (FPS), the full state hybrid function projective synchronisation (FSHFPS) and the generalised synchronisation (GS) between general master and slave hyperchaotic systems. Successively, using Lyapunov stability theory, the coexistence of three different synchronisation types is
High Speed, Approximate Arithmetic Based Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms have been widely used in many applications especially for image recognition. However, the growth in CNN-based image recognition applications raised challenge in executing millions of Multiply and Accumulate (MAC) operations in the state-of-The-Art CNNs. Therefore, GPUs, FPGAs, and ASICs are the feasible solutions for balancing processing speed and power consumption. In this paper, we propose an efficient hardware architecture for CNN that provides high speed, low power, and small area targeting ASIC implementation
FPGA-Based Memristor Emulator Circuit for Binary Convolutional Neural Networks
Binary convolutional neural networks (BCNN) have been proposed in the literature for resource-constrained IoTs nodes and mobile computing devices. Such computing platforms have strict constraints on the power budget, system performance, processing and memory capabilities. Nonetheless, the platforms are still required to efficiently perform classification and matching tasks needed in various applications. The memristor device has shown promising results when utilized for in-memory computing architectures, due to its ability to perform storage and computation using the same physical element
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
