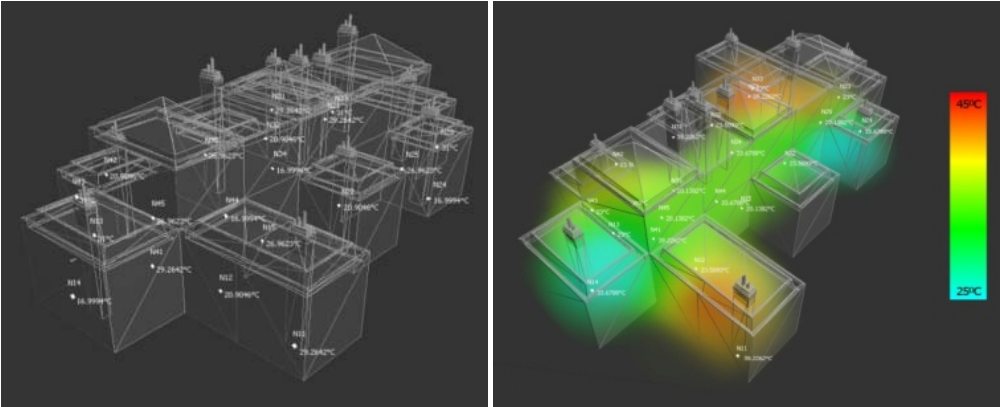
Monitoring and visualization of large WSN deployments
Recent developments in wireless sensor networks have ushered in novel ubiquitous computing applications based on distributed large-scale data acquisition and interactive interpretation. However, current WSNs suffer from lack of effective tools to support large network deployment and administration as well as unavailability of interactive visualization techniques required to explore and analyze captured sensing data, which is hindering the development of real-life WSN-based ubiquitous systems. Sensor Explorer addresses the above problems by providing modular efficient stream management engine

Ambient and wearable sensing for gait classification in pervasive healthcare environments
Pervasive healthcare environments provide an effective solution for monitoring the wellbeing of the elderly where the general trend of an increasingly ageing population has placed significant burdens on current healthcare systems. An important pervasive healthcare system functionality is patient motion analysis where gait information can be used to detect walking behavior abnormalities that may indicate the onset of adverse health problems, for quantifying post-operative recovery, and to observe the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The development of accurate motion analysis models
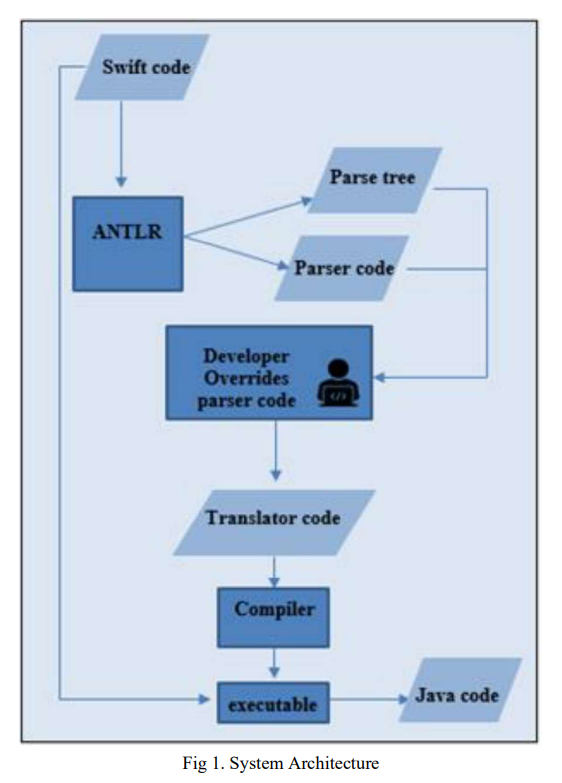
Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications code converter: Swift to java
Numerous commercial tools like Xamarin, React Native and PhoneGap utilize the concept of cross-platform mobile applications development that builds applications once and runs it everywhere opposed to native mobile app development that writes in a specific programming language for every platform. These commercial tools are not very efficient for native developers as mobile applications must be written in specific language and they need the usage of specific frameworks. In this paper, a suggested approach in TCAIOSC tool to convert mobile applications from Android to iOS is used to develop the
Named entity recognition of persons' names in Arabic tweets
The rise in Arabic usage within various socialmedia platforms, and notably in Twitter, has led to a growing interest in building ArabicNatural Language Processing (NLP) applications capable of dealing with informal colloquialArabic, as it is the most commonly used form of Arabic in social media. The uniquecharacteristics of the Arabic language make the extraction of Arabic named entities achallenging task, to which, the nature of tweets adds new dimensions. The majority ofprevious research done on Arabic NER focused on extracting entities from the formallanguage, namely Modern Standard Arabic
Health Records Privacy Issues in Cloud Computing
Personal health record service avail patients to store and dominate their healthy information data through the cloud. Many users like medical doctors, health care providers and family members can access this data through the internet. However, there are privacy issues related to data exposure and data breaches, causing risk to patients' lives. Encryption techniques like public key encryption are applied but they are not efficient and very complex, in addition to scalability problems. In this paper, various multi-authority attributes based on encryption solutions features are discussed that
Transform domain two dimensional and diagonal modular principal component analysis for facial recognition employing different windowing techniques
Spatial domain facial recognition Modular IMage Principal Component Analysis (MIMPCA) has an improved recognition rate compared to the conventional PCA. In the MPCA, face images are divided into smaller sub-images and the PCA approach is applied to each of these sub-images. In this work, the Transform Domain implementation of MPCA is presented. The facial image has two representations. The Two Dimensional MPCA (TD-2D-MPCA) and the Diagonal matrix MPCA (TD-Dia-MPCA). The sub-images are processed using both non-overlapping and overlapping windows. All the test results, for noise free and noisy
Towards Efficient Online Topic Detection through Automated Bursty Feature Detection from Arabic Twitter Streams
Detecting trending topics or events from Twitter is an active research area. The first step in detecting such topics focuses on efficiently capturing textual features that exhibit an unusual high rate of appearance during a specific timeframe. Previous work in this area has resulted in coining the term "detecting bursty features" to refer to this step. In this paper, TFIDF, entropy, and stream chunking are adapted to investigate a new technique for detecting bursty features from an Arabic Twitter stream. Experimental results comparing bursty features extracted from Twitter streams, to Twitter
Streaming support for data intensive cloud-based sequence analysis
Cloud computing provides a promising solution to the genomics data deluge problem resulting from the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology. Based on the concepts of "resources-on-demand" and "pay-as-you-go", scientists with no or limited infrastructure can have access to scalable and cost-effective computational resources. However, the large size of NGS data causes a significant data transfer latency from the client's site to the cloud, which presents a bottleneck for using cloud computing services. In this paper, we provide a streaming-based scheme to overcome this problem
Myocardial segmentation using contour-constrained optical flow tracking
Despite the important role of object tracking using the Optical Flow (OF) in computer graphics applications, it has a limited role in segmenting speckle-free medical images such as magnetic resonance images of the heart. In this work, we propose a novel solution of the OF equation that allows incorporating additional constraints of the shape of the segmented object. We formulate a cost function that include the OF constraint in addition to myocardial contour properties such as smoothness and elasticity. The method is totally different from the common naïve combination of OF estimation within
Myocardium segmentation in strain-encoded (SENC) magnetic resonance images using graph-cuts
Evaluation of cardiac functions using Strain Encoded (SENC) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is a powerful tool for imaging the deformation of left and right ventricles. However, automated analysis of SENC images is hindered due to the low signal-to-noise ratio SENC images. In this work, the authors propose a method to segment the left and right ventricles myocardium simultaneously in SENC-MR short-axis images. In addition, myocardium seed points are automatically selected using skeletonisation algorithm and used as hard constraints for the graph-cut optimization algorithm. The method is based
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 25
- Next page ››
