Full-duplex cooperative cognitive radio networks
In this paper, we study the impact of a full-duplex secondary node on a cognitive cooperative network with Multipacket Reception (MPR) capabilities at the receivers. Motivated by recent schemes that make full-duplex communication feasible, we study a model with one primary and one secondary transmitter-receiver pair, where the secondary transmitter is able to relay primary unsuccessful packets. Cooperation between primary and secondary users has been previously shown to be beneficial for the primary and the secondary users in terms of stable throughput. Our model assumes an imperfect full
A feedback-based access scheme for cognitive-relaying networks
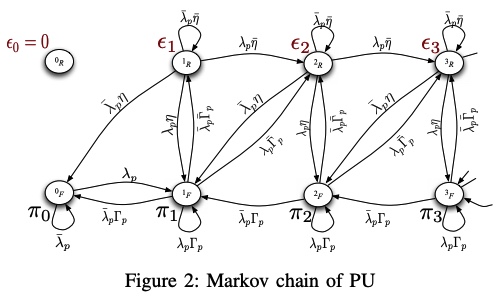
In this paper, we consider a cognitive relaying network in which the secondary user accesses the channel with a certain access probability that depends on the feedback information sent by the primary destination. In addition, the secondary user is granted relaying capabilities by which it can relay primary traffic that was unsuccessfully transmitted by the primary user. We show that this proposed scheme enhances the performance of the secondary user as well as the primary user, while the QoS requirements of the primary user is unviolated. The secondary user can avoid sure collisions with the
A feedback-based access scheme for cognitive radio systems
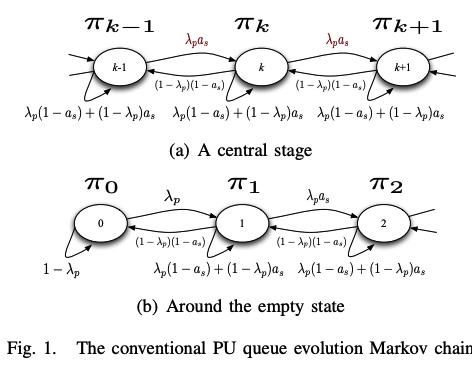
In this paper, we consider the design of access schemes for secondary users in cognitive radio systems based on the primary user feedback information. We consider a secondary user employing a random access scheme with an access probability that depends on the primary user feedback state. We show that the proposed scheme can enhance the system performance in terms of the secondary throughput and/or primary user delay while guaranteeing a certain quality of service (QoS) for the primary user; this is due to the fact that the proposed scheme avoids sure collisions between the primary and
A feedback-soft sensing-based access scheme for cognitive radio networks
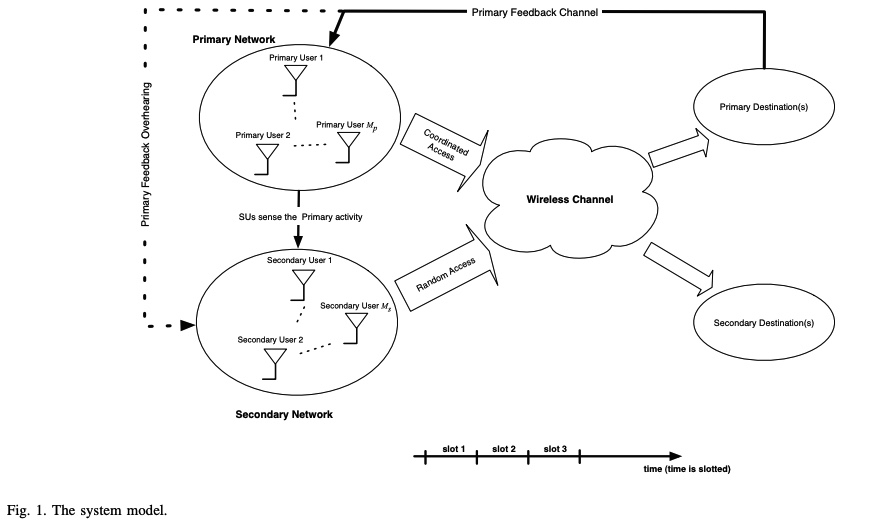
In this paper, we examine a cognitive spectrum access scheme in which secondary users exploit the primary feedback information. We consider an overlay secondary network employing a random access scheme in which secondary users access the channel by certain access probabilities that are functions of the spectrum sensing metric. In setting our problem, we assume that secondary users can eavesdrop on the primary link's feedback. We study the cognitive radio network from a queuing theory point of view. Access probabilities are determined by solving a secondary throughput maximization problem
Differential Evolution Mutations: Taxonomy, Comparison and Convergence Analysis
During last two decades, Differential Evolution (DE) proved to be one of the most popular and successful evolutionary algorithms for solving global optimization problems over continuous space. Proposing new mutation strategies to improve the optimization performance of (DE) is considered a significant research study. In DE, mutation operation plays a vital role in the performance of the algorithm. Therefore, in this paper, comprehensive analysis of the contributions on basic and novel mutation strategies that were proposed between 1995 and 2020 is presented. A new taxonomy based on the
Maximum throughput of a cooperative energy harvesting cognitive radio user
In this paper, we investigate the maximum throughput of a saturated rechargeable secondary user (SU) sharing the spectrum with a primary user (PU). The SU harvests energy packets (tokens) from the environment with a certain harvesting rate. All transmitters are assumed to have data buffers. In addition to its own traffic buffer, the SU has a buffer for storing the admitted primary packets for relaying; and a buffer for storing the energy tokens harvested from the environment. We propose a new cooperative cognitive relaying protocol that allows the SU to relay a fraction of the undelivered
Optimum Scheduling the Electric Distribution Substations with a Case Study: An Integer Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
This work is dedicated to the economic scheduling of the required electric stations in the upcoming 10-year long-term plan. The calculation of the required electric stations is carried out by estimating the yearly consumption of electricity over a long-time plan and then determining the required number of stations. The aim is to minimize the total establishing and operating costs of the stations based on a mathematical programming model with nonlinear objective function and integer decision variables. The introduced model is applied for a real practical case study to conclude the number of
Optimum distribution of protective materials for COVID−19 with a discrete binary gaining-sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm
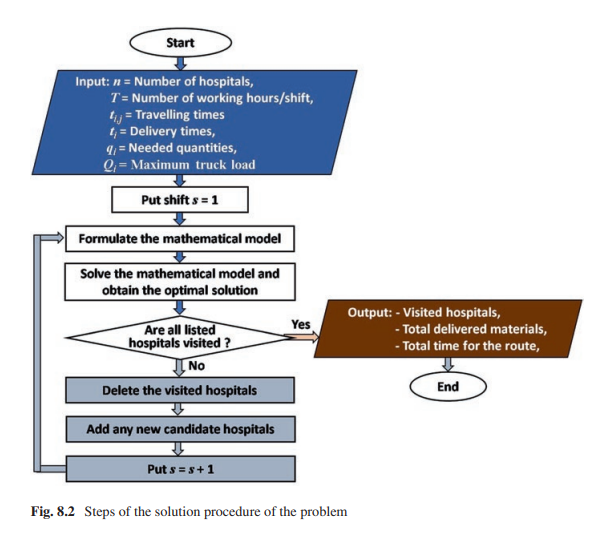
Many application problems are formulated as nonlinear binary programming models which are hard to be solved using exact algorithms especially in large dimensions. One of these practical applications is to optimally distribute protective materials for the newly emerged COVID-19. It is defined for a decision-maker who wants to choose a subset of candidate hospitals comprising the maximization of the distributed quantities of protective materials to a set of chosen hospitals within a specific time shift. A nonlinear binary mathematical programming model for the problem is introduced with a real
Optimum Location of Field Hospitals for COVID-19: A Nonlinear Binary Metaheuristic Algorithm
Determining the optimum location of facilities is critical in many fields, particularly in healthcare. This study proposes the application of a suitable location model for field hospitals during the novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The used model is the most appropriate among the threemost common locationmodels utilized to solve healthcare problems (the set covering model, the maximal covering model, and the P-median model). The proposed nonlinear binary constrained model is a slight modification of the maximal covering model with a set of nonlinear constraints. The model is used to
The deterministic capacity of relay networks with relay private messages
We study the capacity region of a deterministic 4-node network, where 3 nodes can only communicate via the fourth one. However, the fourth node is not merely a relay since it can exchange private messages with all other nodes. This situation resembles the case where a base station relays messages between users and delivers messages between the backbone system and the users. We assume an asymmetric scenario where the channel between any two nodes is not reciprocal. First, an upper bound on the capacity region is obtained based on the notion of single sided genie. Subsequently, we construct an
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
