Feature selection in computer aided diagnostic system for microcalcification detection in digital mammograms
In this paper an approach is proposed to develop a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system that can be very helpful for radiologist in diagnosing microcalcifications' patterns in digitized mammograms earlier and faster than typical screening programs and showed the efficiency of feature selection on the CAD system. The proposed method has been implemented in four stages: (a) the region of interest (ROI) selection of 32x32 pixels size which identifies clusters of microcalcifications, (b) the feature extraction stage is based on the wavelet decomposition of locally processed image (region of
Extreme Points Derived Confidence Map as a Cue for Class-Agnostic Interactive Segmentation Using Deep Neural Network
To automate the process of segmenting an anatomy of interest, we can learn a model from previously annotated data. The learning-based approach uses annotations to train a model that tries to emulate the expert labeling on a new data set. While tremendous progress has been made using such approaches, labeling of medical images remains a time-consuming and expensive task. In this paper, we evaluate the utility of extreme points in learning to segment. Specifically, we propose a novel approach to compute a confidence map from extreme points that quantitatively encodes the priors derived from
Controlled alternate quantum walks based privacy preserving healthcare images in Internet of Things
The development of quantum computers and quantum algorithms conveys a challenging scenario for several cryptographic protocols due to the mathematical scaffolding upon which those protocols have been built. Quantum walks constitute a universal quantum computational model which is widely used in various fields, including quantum algorithms and cryptography. Quantum walks can be utilized as a powerful tool for the development of modern chaos-based cryptographic applications due to their nonlinear dynamical behavior and high sensitivity to initial conditions. In this paper, we propose new
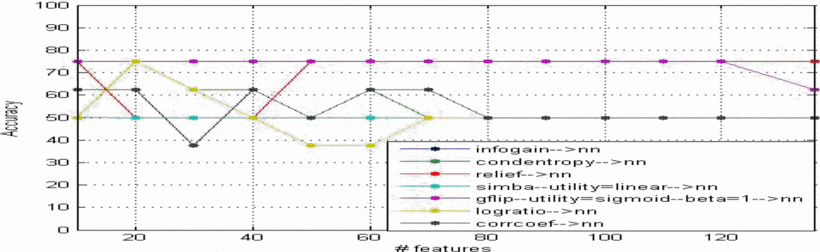
Features selection for building an early diagnosis machine learning model for Parkinson's disease
In this work, different approaches were evaluated to optimize building machine learning classification models for the early diagnosis of the Parkinson disease. The goal was to sort the medical measurements and select the most relevant parameters to build a faster and more accurate model using feature selection techniques. Decreasing the number of features to build a model could lead to more efficient machine learning algorithm and help doctors to focus on what are the most important measurements to take into account. For feature selection we compared the Filter and Wrapper techniques. Then we

MC-GenomeKey: A multicloud system for the detection and annotation of genomic variants
Background: Next Generation Genome sequencing techniques became affordable for massive sequencing efforts devoted to clinical characterization of human diseases. However, the cost of providing cloud-based data analysis of the mounting datasets remains a concerning bottleneck for providing cost-effective clinical services. To address this computational problem, it is important to optimize the variant analysis workflow and the used analysis tools to reduce the overall computational processing time, and concomitantly reduce the processing cost. Furthermore, it is important to capitalize on the
Health Records Privacy Issues in Cloud Computing
Personal health record service avail patients to store and dominate their healthy information data through the cloud. Many users like medical doctors, health care providers and family members can access this data through the internet. However, there are privacy issues related to data exposure and data breaches, causing risk to patients' lives. Encryption techniques like public key encryption are applied but they are not efficient and very complex, in addition to scalability problems. In this paper, various multi-authority attributes based on encryption solutions features are discussed that
Transform domain two dimensional and diagonal modular principal component analysis for facial recognition employing different windowing techniques
Spatial domain facial recognition Modular IMage Principal Component Analysis (MIMPCA) has an improved recognition rate compared to the conventional PCA. In the MPCA, face images are divided into smaller sub-images and the PCA approach is applied to each of these sub-images. In this work, the Transform Domain implementation of MPCA is presented. The facial image has two representations. The Two Dimensional MPCA (TD-2D-MPCA) and the Diagonal matrix MPCA (TD-Dia-MPCA). The sub-images are processed using both non-overlapping and overlapping windows. All the test results, for noise free and noisy
Towards Efficient Online Topic Detection through Automated Bursty Feature Detection from Arabic Twitter Streams
Detecting trending topics or events from Twitter is an active research area. The first step in detecting such topics focuses on efficiently capturing textual features that exhibit an unusual high rate of appearance during a specific timeframe. Previous work in this area has resulted in coining the term "detecting bursty features" to refer to this step. In this paper, TFIDF, entropy, and stream chunking are adapted to investigate a new technique for detecting bursty features from an Arabic Twitter stream. Experimental results comparing bursty features extracted from Twitter streams, to Twitter
Streaming support for data intensive cloud-based sequence analysis
Cloud computing provides a promising solution to the genomics data deluge problem resulting from the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology. Based on the concepts of "resources-on-demand" and "pay-as-you-go", scientists with no or limited infrastructure can have access to scalable and cost-effective computational resources. However, the large size of NGS data causes a significant data transfer latency from the client's site to the cloud, which presents a bottleneck for using cloud computing services. In this paper, we provide a streaming-based scheme to overcome this problem
Named entity recognition of persons' names in Arabic tweets
The rise in Arabic usage within various socialmedia platforms, and notably in Twitter, has led to a growing interest in building ArabicNatural Language Processing (NLP) applications capable of dealing with informal colloquialArabic, as it is the most commonly used form of Arabic in social media. The uniquecharacteristics of the Arabic language make the extraction of Arabic named entities achallenging task, to which, the nature of tweets adds new dimensions. The majority ofprevious research done on Arabic NER focused on extracting entities from the formallanguage, namely Modern Standard Arabic
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››
