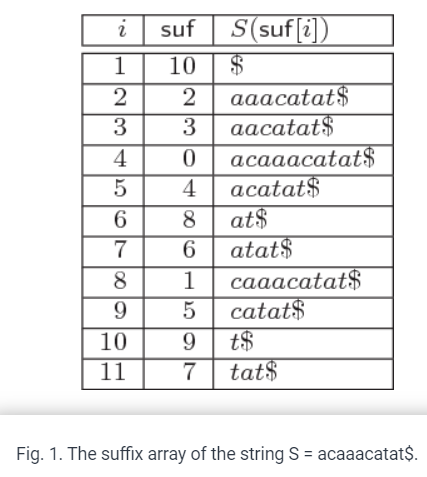
Parallel suffix sorting based on bucket pointer refinement
Suffix array is one of the most important data structures in bioinformatics. Much effort has been devoted to find efficient sequential algorithms for its construction, but little is done to introduce parallel construction algorithms. The bucket pointer refinement algorithm is one of the efficient suffix sorting algorithms that is tuned for genomic datasets. In this paper, we introduce a parallel version of this algorithm running on (shared memory) multicore computers. We present experimental results comparing our algorithms to other parallel algorithms running on similar architecture. Our
Modeling of ultrasound hyperthermia treatment of breast tumors
Ultrasound hyperthermia has become one of the new therapeutic modalities for breast cancer treatment, since ultrasound appears to selectively affect malignant cells without causing any deleterious effects to the surrounding normal tissues. The main objective of this study is to numerically simulate the interaction of therapeutic ultrasound with a multi- tissue type system, and to develop an analytical model for calculating the temperature rise in these tissues due to ultrasound. First, the Finite-Element Method has been used to compute the radiated power density produced by a circular

Multi-view human action recognition system employing 2DPCA
A novel algorithm for view-invariant human action recognition is presented. This approach is based on Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) applied directly on the Motion Energy Image (MEI) or the Motion History Image (MHI) in both the spatial domain and the transform domain. This method reduces the computational complexity by a factor of at least 66, achieving the highest recognition accuracy per camera, while maintaining minimum storage requirements, compared with the most recent reports in the field. Experimental results performed on the Weizmann action and the INIRIA IXMAS
Community assessment to advance computational prediction of cancer drug combinations in a pharmacogenomic screen
Chiral phase structure of the sixteen meson states in the SU(3) Polyakov linear-sigma model for finite temperature and chemical potential in a strong magnetic field
In characterizing the chiral phase-structure of pseudoscalar ( ), scalar ( ), vector ( ) and axial-vector ( t) meson states and their dependence on temperature, chemical potential, and magnetic field, we utilize the SU(3) Polyakov linear-sigma model (PLSM) in the mean-field approximation. We first determine the chiral (non)strange quark condensates, and , and the corresponding deconfinement order parameters, and , in thermal and dense (finite chemical potential) medium and finite magnetic field. The temperature and the chemical potential characteristics of nonet meson states normalized to the
Assessment of cardiac mass from tagged magnetic resonance images
Purpose: Tagged and cine magnetic resonance imaging (tMRI and cMRI) techniques are used for evaluating regional and global heart function, respectively. Measuring global function parameters directly from tMRI is challenging due to the obstruction of the anatomical structure by the tagging pattern. The purpose of this study was to develop a method for processing the tMRI images to improve the myocardium-blood contrast in order to estimate global function parameters from the processed images. Materials and methods: The developed method consists of two stages: (1) removing the tagging pattern
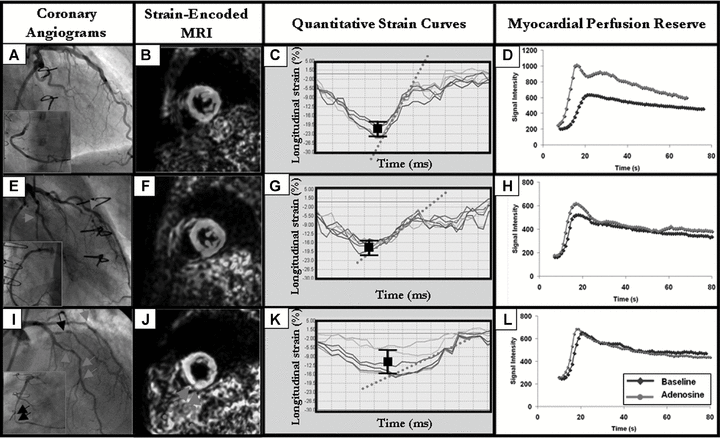
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance for the evaluation of chronic allograft vasculopathy in transplant recipients
The aim of our study was to investigate the ability of Strain-Encoded magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) in heart transplantation (HTx)-recipients. In consecutive subjects (n = 69), who underwent cardiac catheterization, MRI was performed for quantification of myocardial strain and perfusion reserve. Based on angiographic findings subjects were classified: group A including patients with normal vessels; group B, patients with stenosis
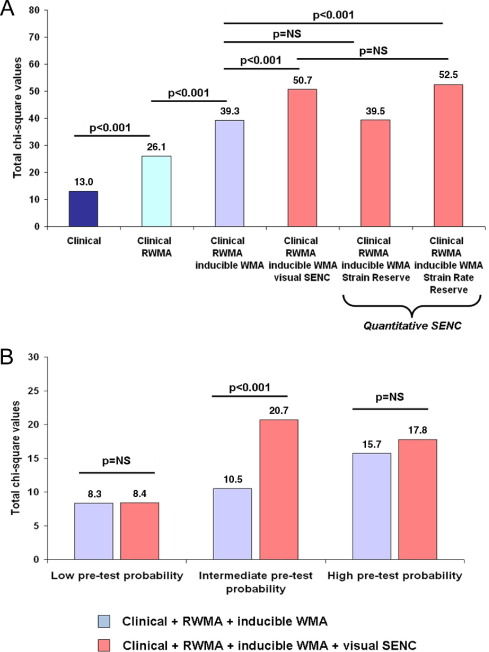
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance during high-dose dobutamine stress testing for the estimation of cardiac outcomes: Comparison to Clinical Parameters and Conventional Wall Motion Readings
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the prognostic value of strain-encoded magnetic resonance imaging (SENC) during high-dose dobutamine stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (DS-MRI) compared with conventional wall motion readings. Background: Detection of inducible ischemia by DS-MRI on the basis of assessing cine images is subjective and depends on the experience of the readers, which may influence not only the diagnostic classification but also the risk stratification of patients with ischemic heart disease. Methods: In all, 320 consecutive patients with suspected or
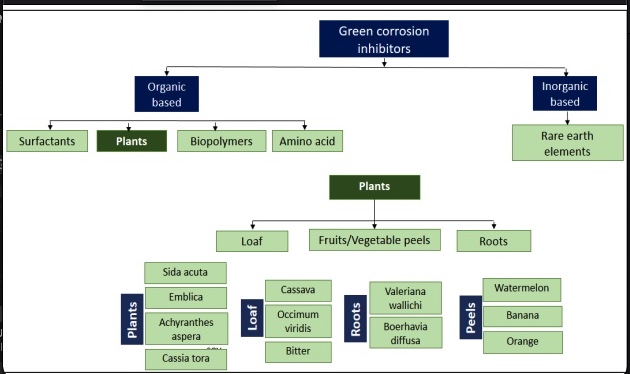
A critical review on green corrosion inhibitors based on plant extracts: Advances and potential presence in the market
Corrosion occurs in all sectors including oil pipelines, drinking water and sewerage in the majority of cases linked to corrosion of steel. Good corrosion management includes optimising corrosion control actions and minimising lifecycle corrosion costs whilst meeting environmental goals. The toxicity of commonly used synthetic inhibitors are the subject of recent legislations (REACH and PARCOM) have led to search on more eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors. Extensive research is conducted to assess the corrosion inhibition rate of diverse green inhibitors. However, it was not adequately
Comparison study of digital forensics analysis techniques
Recently, digital forensics analysis got a great attention in IT security. This is especially after cyber incidents are getting new form of organized crime which introduced Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), and hacking Kill Chain definitions. The threat intense rises when it is affecting the healthcare organization where it will be life-threatening. Handling such incidents is a great challenge for handlers to uncover the attack steps. With various sources of evidential data that require analysis, one analysis technique can be more beneficial than another, comparing to the time and resources
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
