Assessment of cardiac mass from tagged magnetic resonance images
Purpose: Tagged and cine magnetic resonance imaging (tMRI and cMRI) techniques are used for evaluating regional and global heart function, respectively. Measuring global function parameters directly from tMRI is challenging due to the obstruction of the anatomical structure by the tagging pattern. The purpose of this study was to develop a method for processing the tMRI images to improve the myocardium-blood contrast in order to estimate global function parameters from the processed images. Materials and methods: The developed method consists of two stages: (1) removing the tagging pattern
Chiral phase structure of the sixteen meson states in the SU(3) Polyakov linear-sigma model for finite temperature and chemical potential in a strong magnetic field
In characterizing the chiral phase-structure of pseudoscalar ( ), scalar ( ), vector ( ) and axial-vector ( t) meson states and their dependence on temperature, chemical potential, and magnetic field, we utilize the SU(3) Polyakov linear-sigma model (PLSM) in the mean-field approximation. We first determine the chiral (non)strange quark condensates, and , and the corresponding deconfinement order parameters, and , in thermal and dense (finite chemical potential) medium and finite magnetic field. The temperature and the chemical potential characteristics of nonet meson states normalized to the
Community assessment to advance computational prediction of cancer drug combinations in a pharmacogenomic screen
CoCoNUT: An efficient system for the comparison and analysis of genomes
Background: Comparative genomics is the analysis and comparison of genomes from different species. This area of research is driven by the large number of sequenced genomes and heavily relies on efficient algorithms and software to perform pairwise and multiple genome comparisons. Results: Most of the software tools available are tailored for one specific task. In contrast, we have developed a novel system CoCoNUT (Computational Comparative geNomics Utility Toolkit) that allows solving several different tasks in a unified framework: (1) finding regions of high similarity among multiple genomic
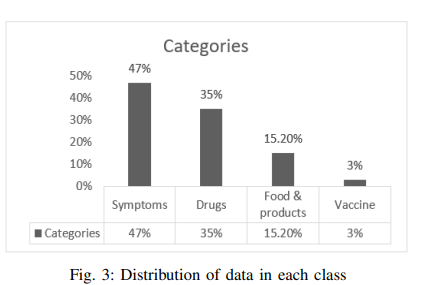
Intelligent Arabic-Based Healthcare Assistant
Text classification has been one of the most common natural language processing (NLP) objectives in recent years. Compared to other languages, this mission with Arabic is relatively restricted and in its early stages, and this combination in the medical application area is rare. This paper builds an Arabic health care assistant, specifically a pediatrician that supports Arabic dialects, especially Egyptian accents. The proposed application is a chatbot based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) models after experimenting with Two Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) models
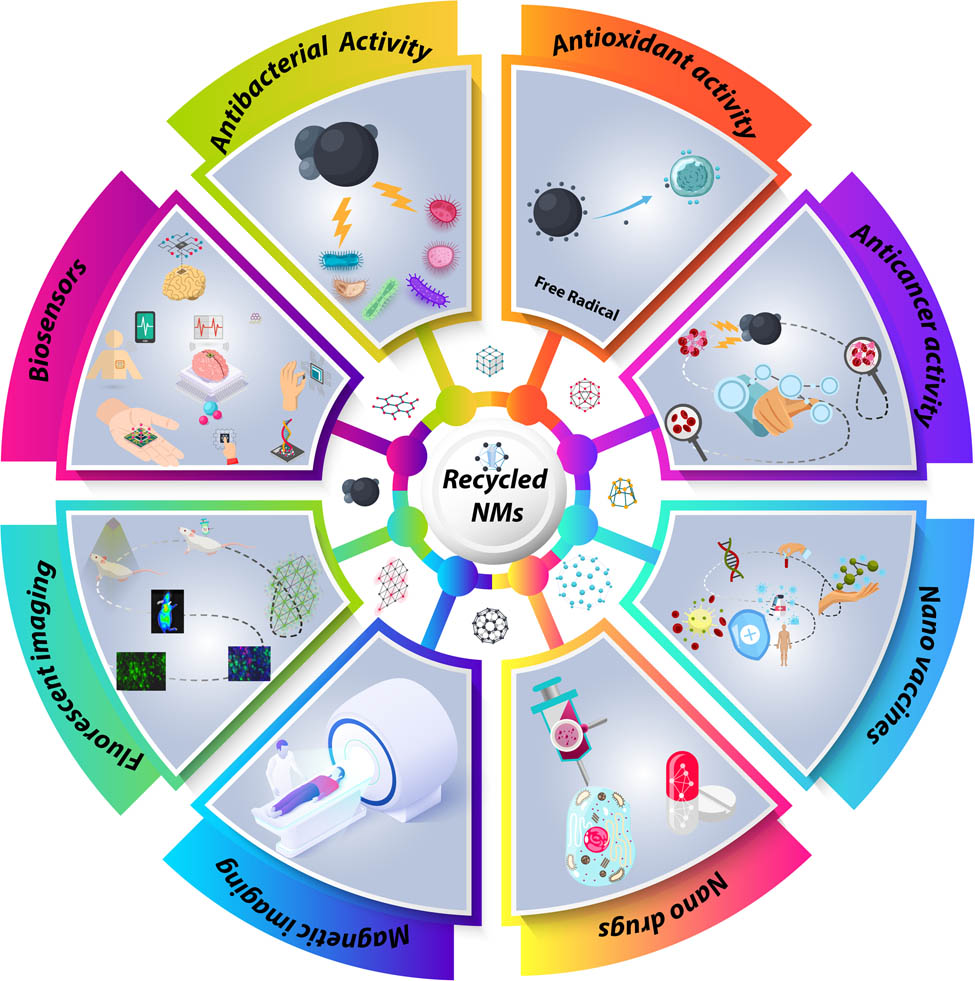
Recent advances in waste-recycled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Waste-to-wealth
Global overpopulation, industrial expansion, and urbanization have generated massive amounts of wastes. This is considered as a significant worldwide challenge that requires an urgent solution. Additionally, remarkable advances in the field of biomedicine have impacted the entire spectrum of healthcare and medicine. This has paved the way for further refining of the outcomes of biomedical strategies toward early detection and treatment of different diseases. Various nanomaterials (NMs) have been dedicated to different biomedical applications including drug delivery, vaccinations, imaging
Detection of cardiac function abnormality from MRI images using normalized wall thickness temporal patterns
Purpose. To develop a method for identifying abnormal myocardial function based on studying the normalized wall motion pattern during the cardiac cycle. Methods. The temporal pattern of the normalized myocardial wall thickness is used as a feature vector to assess the cardiac wall motion abnormality. Principal component analysis is used to reduce the feature dimensionality and the maximum likelihood method is used to differentiate between normal and abnormal features. The proposed method was applied on a dataset of 27 cases from normal subjects and patients. Results. The developed method
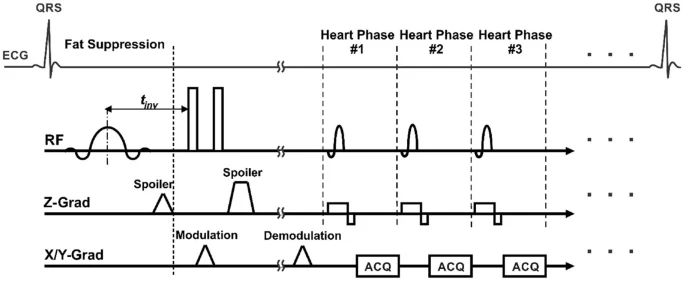
An efficient fat suppression technique for stimulated-echo based CMR
[No abstract available]
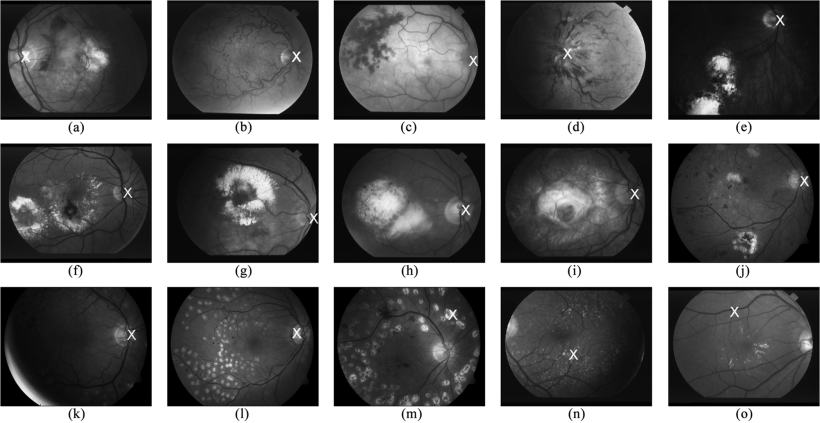
Fast localization of the optic disc using projection of image features
Optic Disc (OD) localization is an important pre-processing step that significantly simplifies subsequent segmentation of the OD and other retinal structures. Current OD localization techniques suffer from impractically-high computation times (few minutes per image). In this work, we present a fast technique that requires less than a second to localize the OD. The technique is based upon obtaining two projections of certain image features that encode the x- and y- coordinates of the OD. The resulting 1-D projections are then searched to determine the location of the OD. This avoids searching
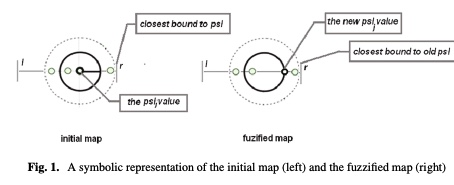
A fuzzy approach of sensitivity for multiple colonies on ant colony optimization
In order to solve combinatorial optimization problem are used mainly hybrid heuristics. Inspired from nature, both genetic and ant colony algorithms could be used in a hybrid model by using their benefits. The paper introduces a new model of Ant Colony Optimization using multiple colonies with different level of sensitivity to the ant’s pheromone. The colonies react different to the changing environment, based on their level of sensitivity and thus the exploration of the solution space is extended. Several discussion follows about the fuzziness degree of sensitivity and its influence on the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
