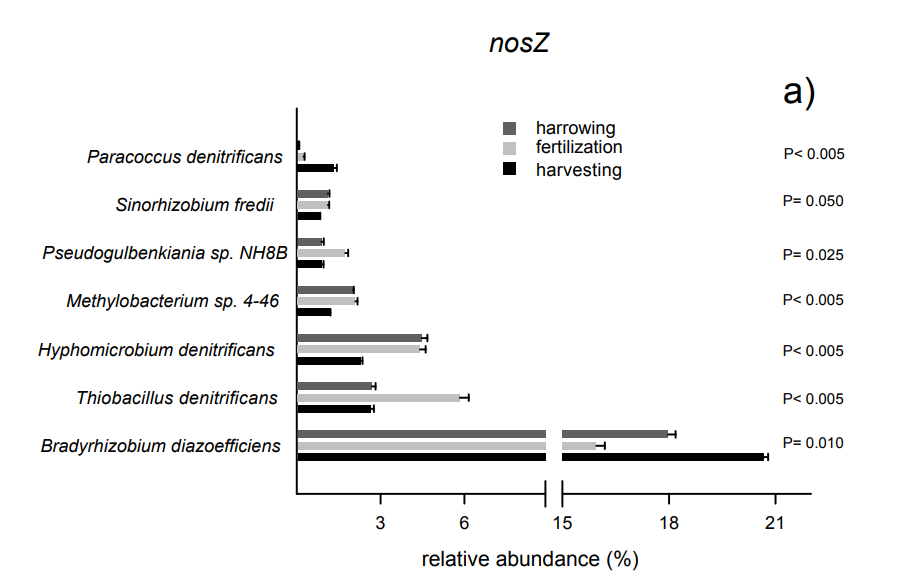
Biochar affects community composition of nitrous oxide reducers in a field experiment
N2O is a major greenhouse gas and the majority of anthropogenic N2O emissions originate from agriculturally managed soils. Therefore, developing N2O mitigation strategies is a key challenge for the agricultural sector and biochar soil treatment is one reported option. Biochar's capacity to increase soil pH and to foster activity of specialized N2O reducers has been proposed as possible mechanisms for N2O mitigation. An experiment was undertaken to investigate whether changes in the community composition of N2O reducers was observed under field conditions after biochar application. The study
Classification of Thyroid Carcinoma in Whole Slide Images Using Cascaded CNN
The objective of this research is to build a 'Whole Slide Images' classification system using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). This system is capable of classifying Thyroid tumors into three types: Follicular adenoma, follicular carcinoma, and papillary carcinoma. Furthermore, the cascaded CNN technique is additionally employed to classify the classified follicular carcinoma into four subclasses: follicular carcinoma, papillary follicular variant, well-differentiated follicular carcinoma, and Poorly-differentiated follicular carcinoma. Results of the proposed CNN architecture showed
Insilico Codon Bias Correction for Transgenic Biological Protein Sequences for Vaccine Production
Codon optimization is primarily used in enhancing the levels of protein expression in the host species. Each species has its own codon usage bias, which represents the codons abundance frequency in that species. Using the host usage profile contributes to personalize the synthesis of the DNA vaccines that can achieve highly active vectors the host cells. For optimizing protein expression levels in a particular host, the genetic code sequence needs correction of codon frequency bias to match the expression of host codon landscape rather than the donating organism profile. In this work, we have
In-Silico Comparative Analysis of Egyptian SARS CoV-2 with Other Populations: A Phylogeny and Mutation Analysis
In the current SARS-CoV2 pandemic, identification and differentiation between SARS-COV2 strains are vital to attain efficient therapeutic targeting, drug discovery and vaccination. In this study, we investigate how the viral genetic code mutated locally and what variations is the Egyptian population most susceptible to in comparison with different strains isolated from Asia, Europe and other countries in Africa. Our aim is to evaluate the significance of these variations and whether they constitute a change on the protein level and identify if any of these variations occurred in the conserved
Detection of Mammalian Coding Sequences Using a Hybrid Approach of Chaos Game Representation and Machine Learning
Mammalian protein-coding sequence detection provides a wide range of applications in biodiversity research, evolutionary studies, and understanding of genomic features. Representation of genomic sequences in Chaos Game Representation (CGR) helps reveal hidden features in DNA sequences due to its ability to represent sequences in both numerical and graphical levels. Machine learning approaches can automatically detect hidden patterns in CGR images by detecting and classifying protein-coding and noncoding patterns accurately. Here, we propose a pipeline that automatically detects coding (exons)
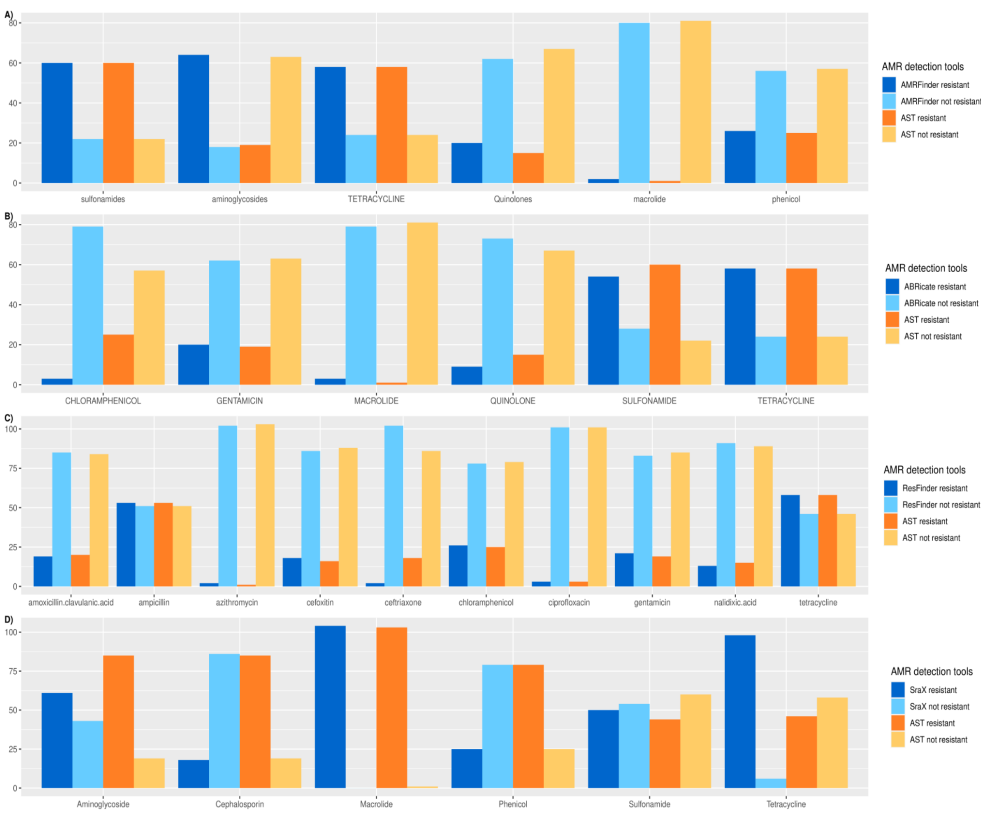
Benchmarking of Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Detection Tools in Assembled Bacterial Whole Genomes
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the ten dangers threatening our world, according to the world health organization (WHO). Nowadays, there are plenty of electronic microbial genomics and metagenomics data records that represent host-associated microbiomes. These data introduce new insights and a comprehensive understanding of the current antibiotic resistance threats and the upcoming resistance outbreak. Many bioinformatics tools have been developed to detect the AMR genes based on different annotated databases of bacterial whole genome sequences (WGS). The number and structure of
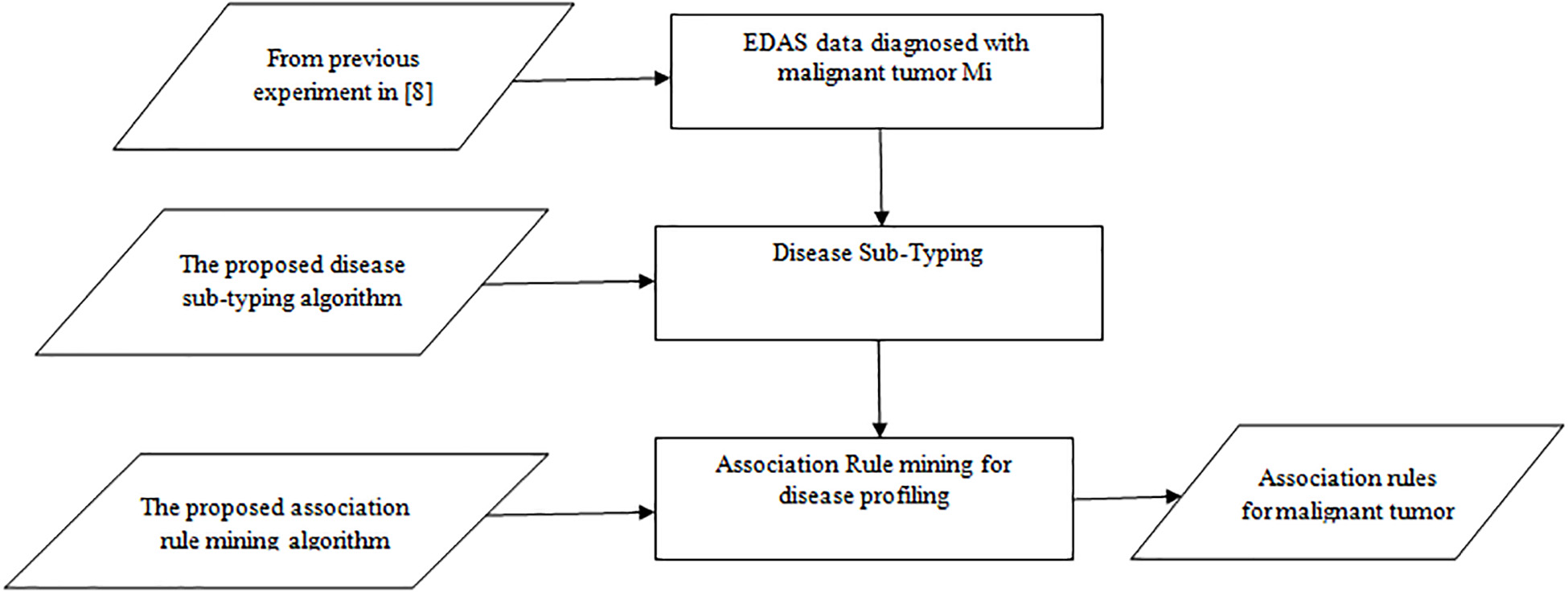
A Theoretical Approach for Correlating Proteins to Malignant Diseases
Malignant Tumors are developed over several years due to unknown biological factors. These biological factors induce changes in the body and consequently, they lead to Malignant Tumors. Some habits and behaviors initiate these biological factors. In effect, the immune system cannot recognize a Malignant Tumor as foreign tissue. In order to discover a fascinating pattern of these habits, behaviors, and diseases and to make effective decisions, different machine learning techniques should be used. This research attempts to find the association between normal proteins (environmental factors) and
Cardiac MRI steam images denoising using bayes classifier
Imaging of the heart anatomy and function using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an important diagnosis tool for heart diseases. Several techniques have been developed to increase the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) between myocardium and background. Recently, a technique that acquires cine cardiac images with black-blood contrast has been proposed. Although the technique produces cine sequence of high contrast, it suffers from elevated noise which limits the CNR. In this paper, we study the performance and efficiency of applying a Bayes classifier to remove background noise. Real MRI data is
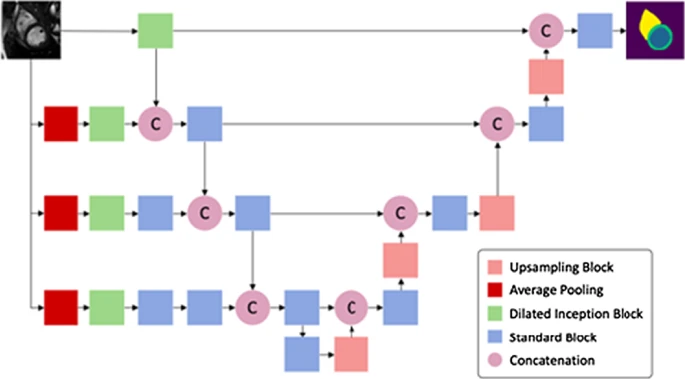
Multi-center, Multi-vendor, and Multi-disease Cardiac Image Segmentation Using Scale-Independent Multi-gate UNET
Heart segmentation in Cardiac MRI images is a fundamental step to quantify myocardium global function. In this paper, we introduce a pipeline for heart localization and segmentation that is fast and robust even in the apical slices that have small myocardium. Also, we propose an enhancement to the popular U-Net architecture for segmentation. The proposed method utilizes the aggregation of different feature scales from the image by using the inception block along with the multi-gate block that propagates the multi-scale context of the supplied data where the heart is subject to changes in scale
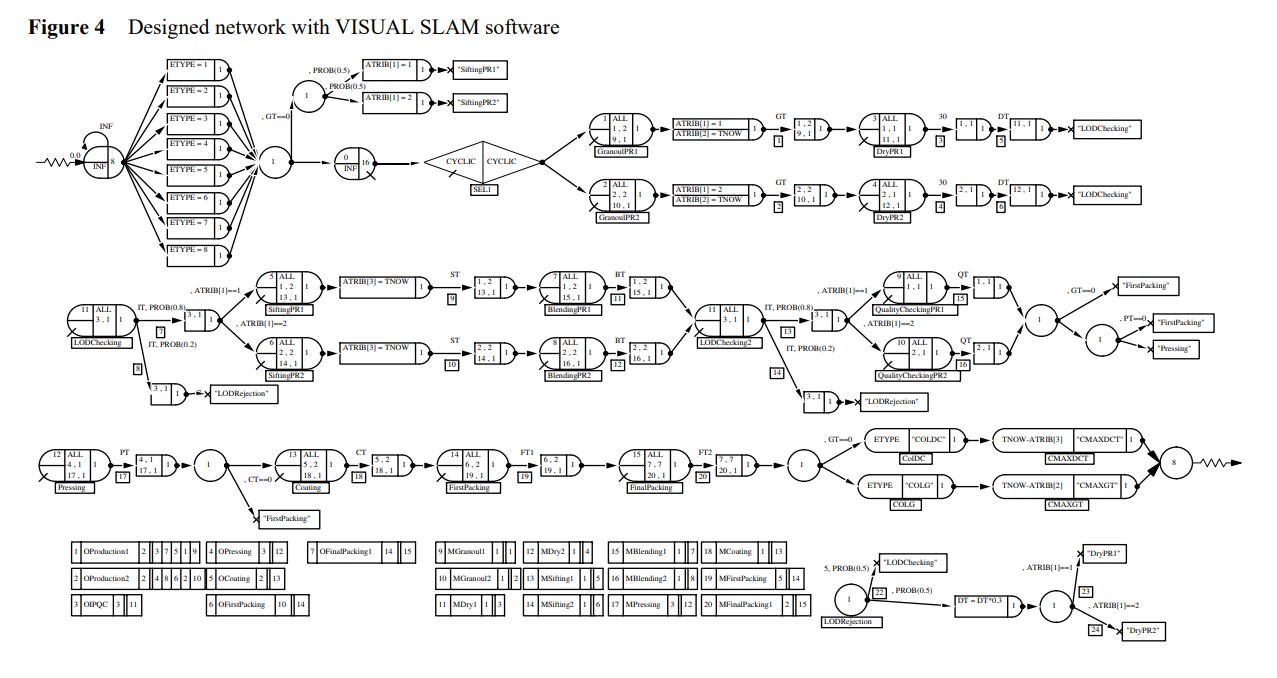
Performance optimisation of a pharmaceutical production line by integrated simulation and data envelopment analysis
It seems that the use of mathematical models is not suitable for pharmaceutical production line optimisation and the use of simulation leads to better outputs and provides more flexibility than mathematical models. Therefore, in this study, a novel methodology based on the integration of simulation and data envelopment analysis is developed for performance optimisation of a pharmaceutical production line. For this purpose, first, an actual pharmaceutical production line was simulated, verified and validated. Afterwards, Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) was developed for the scenario analysis
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
