In silico design and experimental validation of sirnas targeting conserved regions of multiple hepatitis c virus genotypes
RNA interference (RNAi) is a post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanism that mediates the sequence-specific degradation of targeted RNA and thus provides a tremendous opportunity for development of oligonucleotide-based drugs. Here, we report on the design and validation of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting highly conserved regions of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome. To aim for therapeutic applications by optimizing the RNAi efficacy and reducing potential side effects, we considered different factors such as target RNA variations, thermodynamics and accessibility of the siRNA
Myocardium segmentation in strain-encoded (SENC) magnetic resonance images using graph-cuts
Evaluation of cardiac functions using Strain Encoded (SENC) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is a powerful tool for imaging the deformation of left and right ventricles. However, automated analysis of SENC images is hindered due to the low signal-to-noise ratio SENC images. In this work, the authors propose a method to segment the left and right ventricles myocardium simultaneously in SENC-MR short-axis images. In addition, myocardium seed points are automatically selected using skeletonisation algorithm and used as hard constraints for the graph-cut optimization algorithm. The method is based
Myocardial segmentation using contour-constrained optical flow tracking
Despite the important role of object tracking using the Optical Flow (OF) in computer graphics applications, it has a limited role in segmenting speckle-free medical images such as magnetic resonance images of the heart. In this work, we propose a novel solution of the OF equation that allows incorporating additional constraints of the shape of the segmented object. We formulate a cost function that include the OF constraint in addition to myocardial contour properties such as smoothness and elasticity. The method is totally different from the common naïve combination of OF estimation within
Health Records Privacy Issues in Cloud Computing
Personal health record service avail patients to store and dominate their healthy information data through the cloud. Many users like medical doctors, health care providers and family members can access this data through the internet. However, there are privacy issues related to data exposure and data breaches, causing risk to patients' lives. Encryption techniques like public key encryption are applied but they are not efficient and very complex, in addition to scalability problems. In this paper, various multi-authority attributes based on encryption solutions features are discussed that

MC-GenomeKey: A multicloud system for the detection and annotation of genomic variants
Background: Next Generation Genome sequencing techniques became affordable for massive sequencing efforts devoted to clinical characterization of human diseases. However, the cost of providing cloud-based data analysis of the mounting datasets remains a concerning bottleneck for providing cost-effective clinical services. To address this computational problem, it is important to optimize the variant analysis workflow and the used analysis tools to reduce the overall computational processing time, and concomitantly reduce the processing cost. Furthermore, it is important to capitalize on the
The case for docker in multicloud enabled bioinformatics applications
The introduction of next generation sequencing technologies did not bring only huge amounts of biological data but also highly sophisticated and versatile analysis workflows and systems. These new challenges require reliable and fast deployment methods over high performance servers in the local infrastructure or in the cloud. The use of virtualization technology has provided an efficient solution to overcome the complexity of deployment procedures and to provide a safe personalized execution box. However, the performance of applications running in virtual machines is worse than that of those
Features selection for building an early diagnosis machine learning model for Parkinson's disease
In this work, different approaches were evaluated to optimize building machine learning classification models for the early diagnosis of the Parkinson disease. The goal was to sort the medical measurements and select the most relevant parameters to build a faster and more accurate model using feature selection techniques. Decreasing the number of features to build a model could lead to more efficient machine learning algorithm and help doctors to focus on what are the most important measurements to take into account. For feature selection we compared the Filter and Wrapper techniques. Then we
Controlled alternate quantum walks based privacy preserving healthcare images in Internet of Things
The development of quantum computers and quantum algorithms conveys a challenging scenario for several cryptographic protocols due to the mathematical scaffolding upon which those protocols have been built. Quantum walks constitute a universal quantum computational model which is widely used in various fields, including quantum algorithms and cryptography. Quantum walks can be utilized as a powerful tool for the development of modern chaos-based cryptographic applications due to their nonlinear dynamical behavior and high sensitivity to initial conditions. In this paper, we propose new
Extreme Points Derived Confidence Map as a Cue for Class-Agnostic Interactive Segmentation Using Deep Neural Network
To automate the process of segmenting an anatomy of interest, we can learn a model from previously annotated data. The learning-based approach uses annotations to train a model that tries to emulate the expert labeling on a new data set. While tremendous progress has been made using such approaches, labeling of medical images remains a time-consuming and expensive task. In this paper, we evaluate the utility of extreme points in learning to segment. Specifically, we propose a novel approach to compute a confidence map from extreme points that quantitatively encodes the priors derived from
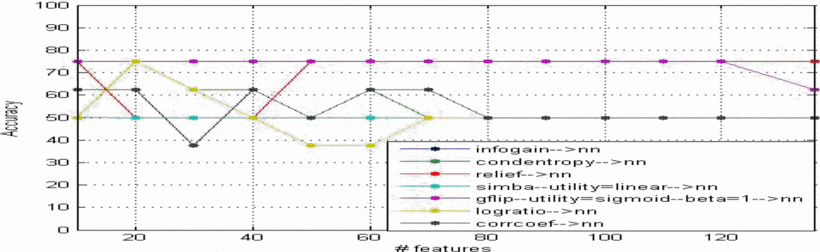
Feature selection in computer aided diagnostic system for microcalcification detection in digital mammograms
In this paper an approach is proposed to develop a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system that can be very helpful for radiologist in diagnosing microcalcifications' patterns in digitized mammograms earlier and faster than typical screening programs and showed the efficiency of feature selection on the CAD system. The proposed method has been implemented in four stages: (a) the region of interest (ROI) selection of 32x32 pixels size which identifies clusters of microcalcifications, (b) the feature extraction stage is based on the wavelet decomposition of locally processed image (region of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
