
Water Importance and Pollution Sources—Recommended Limits of Pollutants
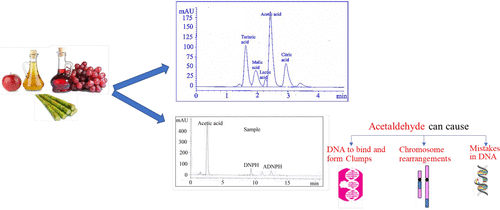
Detection and Identification of Adulteration in Vinegar Samples Based on Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic (RP-HPLC) Strategies
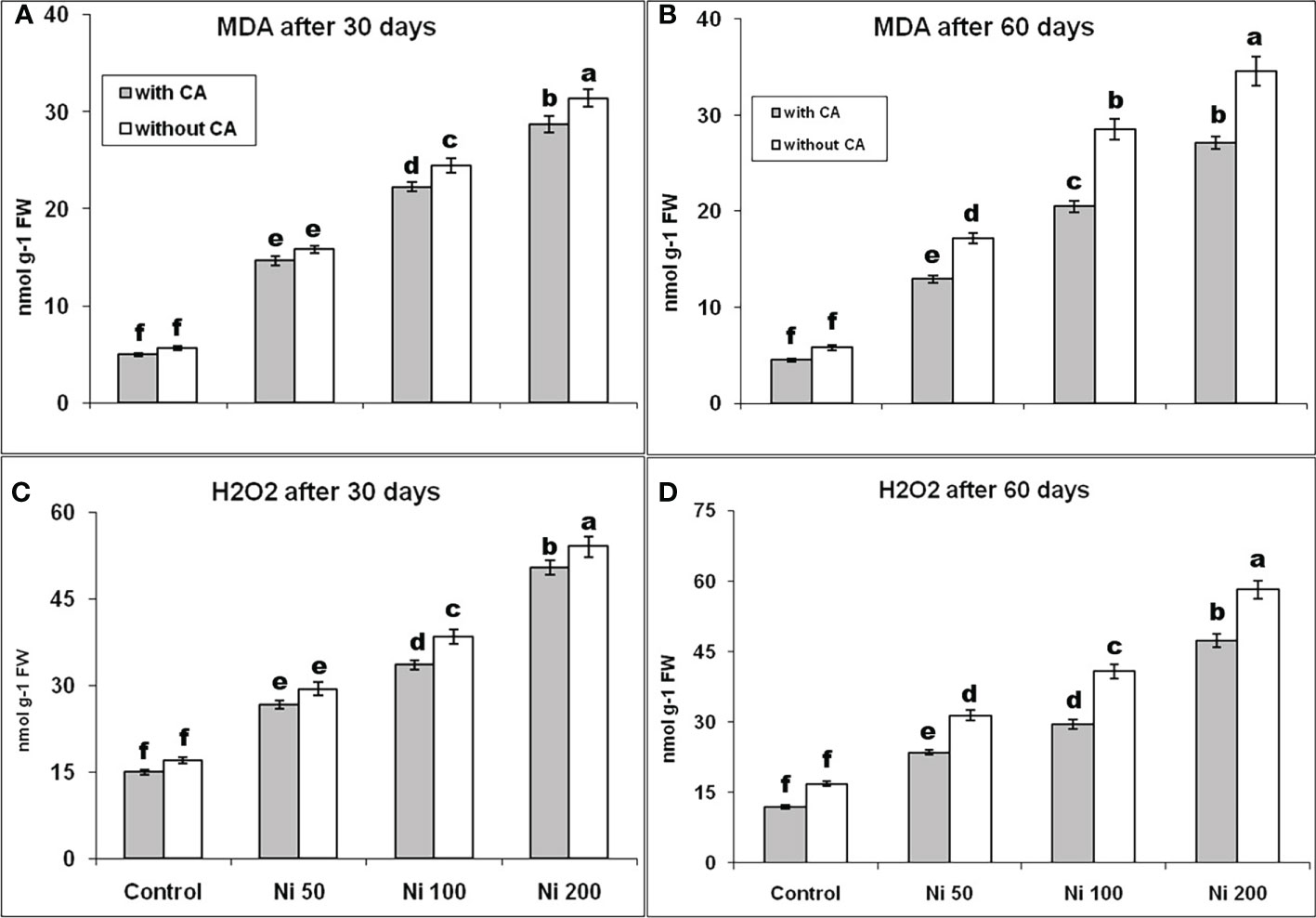
Citric acid assisted phytoextraction of nickle from soil helps to tolerate oxidative stress and expression profile of NRAMP genes in sunflower at different growth stages
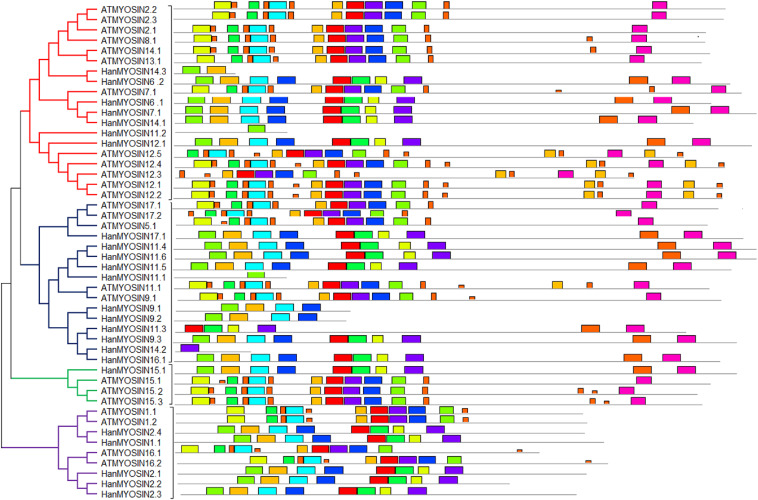
Genome-wide comparison and identification of myosin gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana and Helianthus annuus
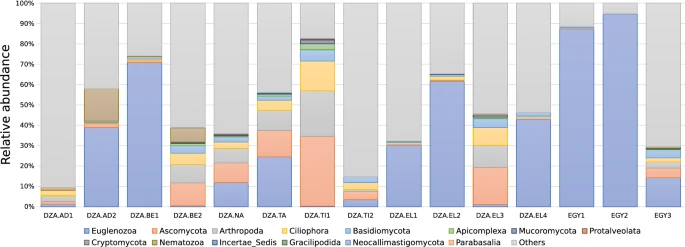
Biochemical and genotyping analyses of camels (Camelus dromedaries) trypanosomiasis in North Africa
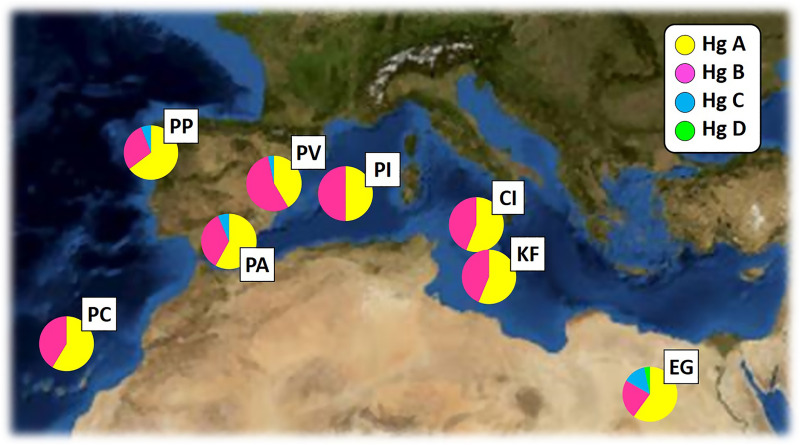
Phylogeographic and population genetic structure of hound-like native dogs of the Mediterranean Basin
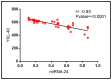
Can Micro RNA-24 Affect the Cardiovascular Morbidity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Targeting YKL-40?
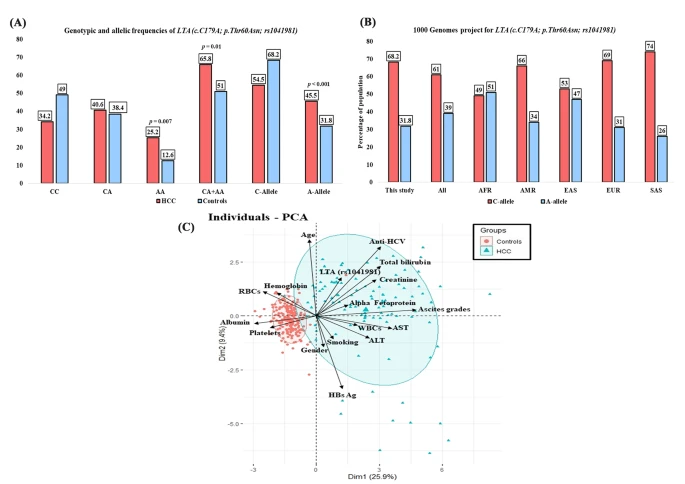
Prognostic significance of the genetic variant of lymphotoxin alpha (p.Thr60Asn) in egyptian patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
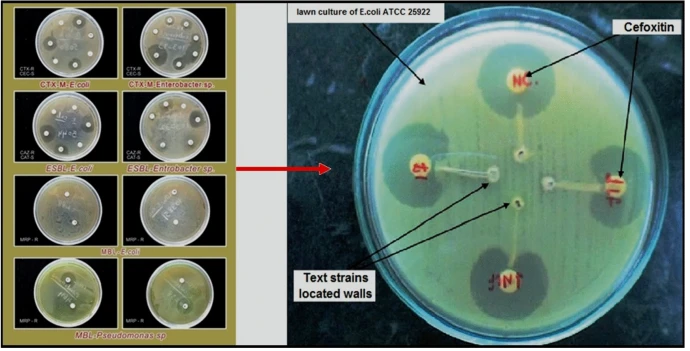
Molecular identification of extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs)-producing strains in clinical specimens from Tiruchirappalli, India
Worldwide, the phenomenal antimicrobial resistance with its consequences of fatal diseases has been alerted; it is because the morbidity and mortality at a shocking rate. Therefore, there is an urgent quest of innovative antimicrobials agents; it is that communicable disease is a worldwide trouble as of the growth and wideness of drug-resistant pathogens. As for the aim of the research, it is widely investigative to the prevalence of Gram-negative pathogens of E. coli and K. pneumoniae in different age groups, gender along with the identification of ESBL-producing pathogens and antimicrobial
Nanomaterial-based drug delivery systems as promising carriers for patients with COVID-19
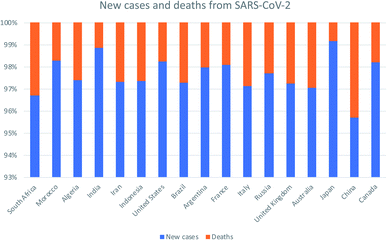
Once the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 outbreak to be pandemic, massive efforts have been launched by researchers around the globe to combat this emerging infectious disease. Here we review the most recent data on the novel SARS-CoV-2 pathogen. We analyzed its etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and current medications. After that, we summarized the promising drug delivery application of nanomaterial-based systems. Their preparation routes, unique advantages over the traditional drug delivery routes and their toxicity though risk analysis were also covered
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
