
Effect of solar canals on evaporation, water quality, and power production: An optimization study
Both energy and availability of water with good quality are essential for the well-being of humans. Thus, it is very important to study the parameters that would affect water quality, so as to come up with mitigation measures if water quality would be at risk or negatively affected. Moreover, it is very important to always search for new energy resources, especially if they are renewable. This research study is concerned with studying solar canals and their effect on evaporation and water quality variables of canals covered by solar cells, as well as the effect on power production. Both a
Predicting telecommunication tower costs using fuzzy subtractive clustering
This paper presents a fuzzy subtractive modelling technique to predict the weight of telecommunication towers which is used to estimate their respective costs. This is implemented through the utilization of data from previously installed telecommunication towers considering four input parameters: a) tower height; b) allowed tilt or deflection; c) antenna subjected area loading; and d) wind load. Telecommunication towers are classified according to designated code (TIA-222-F and TIA-222-G standards) and structures type (Self-Supporting Tower (SST) and Roof Top (RT)). As such, four fuzzy
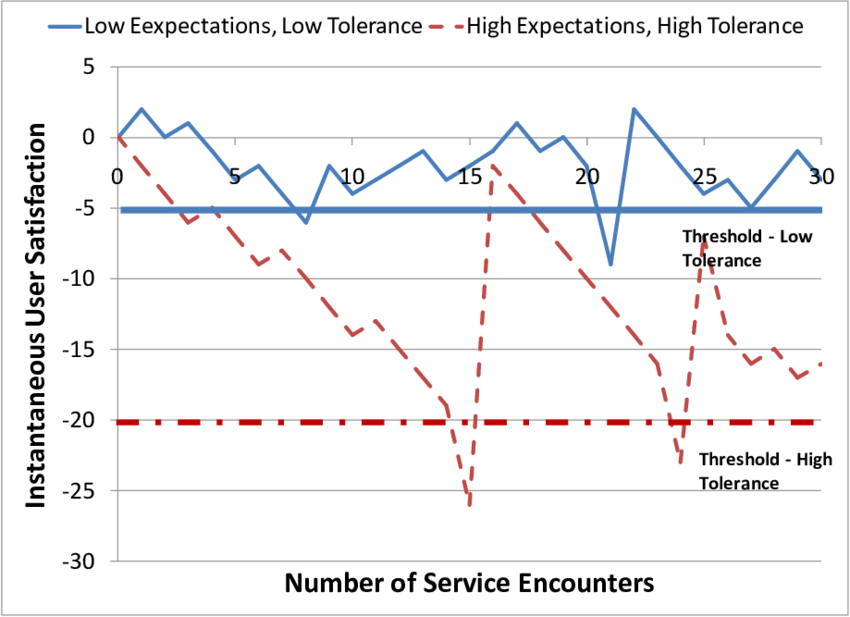
Modeling user behavior and infrastructure level of service: An agent-based simulation approach
Traditional modeling frameworks used for infrastructure asset management have suffered from two main shortcomings. Most approaches have focused their modeling efforts on the infrastructure asset itself, thereby ignoring the multitude of interactions that occur between other entities. In addition, an a-priori behavior of all elements in the modeling environment has always been assumed. This paper argues that these shortcomings have significantly limited the decision-making capabilities of infrastructure asset management systems by limiting their ability to simulate emergent behavior that is
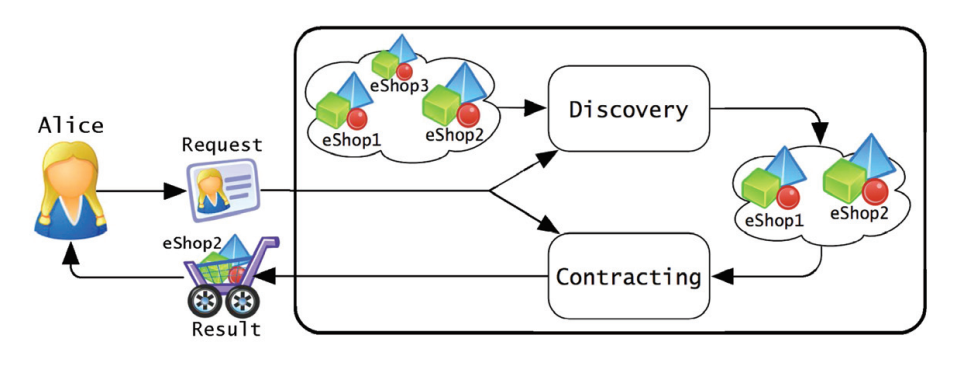
Knowledge management in contract administration: An ontological engineering approach
Knowledge has been identified to be a significant organizational resource, which if used effectively can provide competitive advantage. Construction contract administration is a complex, knowledge-intensive process that if properly managed can mitigate the contractor's risk exposure. Challenges in proper knowledge management of contract administration are due to: 1) Large amount of fragmented information that is required to manage a construction contract, 2) Information located in heterogeneous sources (Request For Information (RFIs), site notices, schedules, contracts, etc...), 3) Information
Discrete event simulation tool for earthmoving fleet selection
Earthmoving operations represent a sizable work in heavy civil engineering projects. Selecting optimum fleet configuration for an earthmoving operation is a very difficult process, especially when dealing with a multi loader type and multi truck type configurations. This paper presents a framework that can be used for the selection of optimum fleet for earthmoving operations. It enables the user to input the available loading and hauling equipment, then, it calculates the cost and total project time of each possible fleet combination, and finally it provides a list of the top-ten best fleet
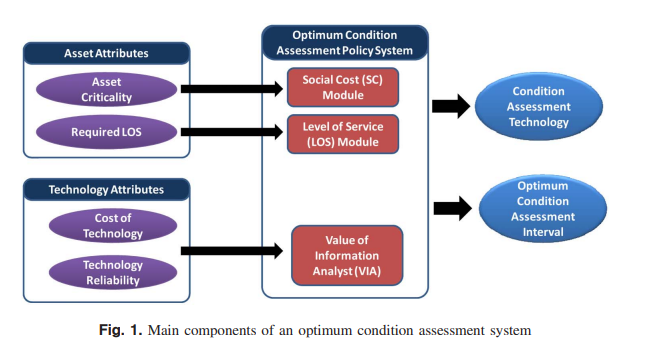
Optimizing inspection policies for buried municipal pipe infrastructure
Condition assessment is an integral component in any infrastructure asset management system. Without condition information, asset managers lack the ability to make appropriate decisions regarding needed maintenance, rehabilitation, and replacement of infrastructure. Existing and emerging technologies for assessing the condition of water and sewer pipes provide a better picture of the state of these buried assets. Unfortunately, many of these technologies are costly and provide results that are not always highly reliable. This paper presents a methodology to assist asset managers in balancing
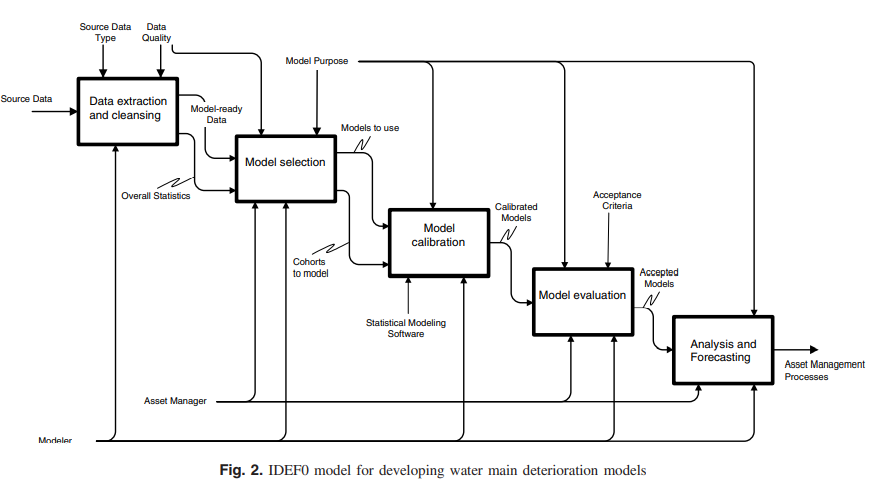
Comparison of statistical deterioration models for water distribution networks
The use of water main break history as a proxy for condition has become common practice because of the high costs associated with direct assessments. Statistical deterioration models predict future water main breaks on the basis of historical patterns. Many municipalities are beginning to understand the value of utilizing water pipe break histories to manage their noncritical distribution networks via deterioration models. This paper presents a generic IDEF0 process model for developing water main deterioration models. Two common statistical deterioration models for water pipes are compared
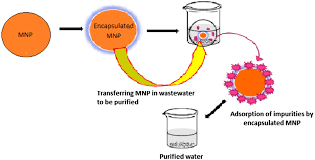
Engineered magnetic oxides nanoparticles as efficient sorbents for wastewater remediation: a review
The rapid urbanization and industrialization is causing worldwide water pollution, calling for advanced cleaning methods. For instance, pollutant adsorption on magnetic oxides is efficient and very practical due to the easy separation from solutions by an magnetic field. Here we review the synthesis and performance of magnetic oxides such as iron oxides, spinel ferrites, and perovskite oxides for water remediation. We present structural, optical, and magnetic properties. Magnetic oxides are also promising photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants. Antimicrobial activities and
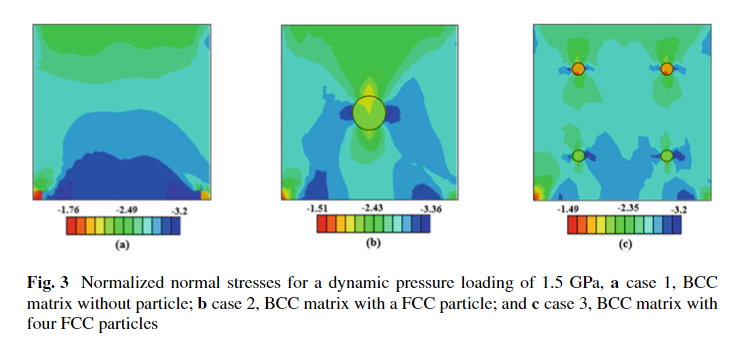
A 3D Multiple-Slip Crystal-Plasticity Model for Precipitate Hardening in Additively Manufactured High Strength Steels
Additive Manufacturing (AM) revolutionized the manufacturing of complex geometry products, especially in medical and aerospace fields. High-strength precipitate hardened (PH) stainless steels provide unique properties in term of strength and corrosion resistance for critical applications in both fields. In the current study, a 3D multiple-slip crystal-plasticity dislocation densities-based model is used to study the effect of copper precipitate hardening in high-strength stainless steels. The proposed approach accurately predicts the complex structure of martensite and properly represents the
Hybrid treatment system for real textile wastewater remediation based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes: Performance and economic evaluation
This research investigates the feasibility of using hybrid treatment system based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes for real textile wastewater treatment. Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) was used as a coagulant, Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) as adsorbent and Micro Zeolite (MZ) as filter media for the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), color, total nitrogen (TN) and turbidity from raw textile effluents. Batch and continuous feed scaling-up studies (full design and set-up studies) were conducted to evaluate the performance of the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
