Combined effect of wind speed and covering irrigation canals on water quality parameters
Wind has a considerable effect on many water quality parameters. Some of the parameters are directly affected by the wind, while others are influenced by other physical water parameters like the velocity, temperature. etc. that are affected by wind and hence transfer their effect to water quality parameters. As the wind has an effect on water quality parameters, also covering waterways has a great effect on the water quality of those covered waterways. This is because covering a waterway alters the concentrations of its water quality parameters. This research is concerned with studying the
Combined effect of wind speed and covering irrigation canals on water quality parameters
Wind has a considerable effect on many water quality parameters. Some of the parameters are directly affected by the wind, while others are influenced by other physical water parameters like the velocity, temperature. etc.That are affected by wind and hence transfer their effect to water quality parameters. As the wind has an effect on water quality parameters, also covering waterways has a great effect on the water quality of those covered waterways. This is because covering a waterway alters the concentrations of its water quality parameters. This research is concerned with studying the
Towards optimum condition assessment policies for water and sewer networks
With ageing water and sewer infrastructure in North America, assessing the condition of these assets has received increased attention in the past few years. Condition assessment is an integral component in any asset management program. Determining the condition of buried infrastructure tends to be more cumbersome, costly and error-prone compared to other surface infrastructure like roads and buildings. For sewers, CCTV is considered the industry standard for condition assessment technologies. For pressurized water pipelines, technologies tend to be more costly and uncertain (e.g
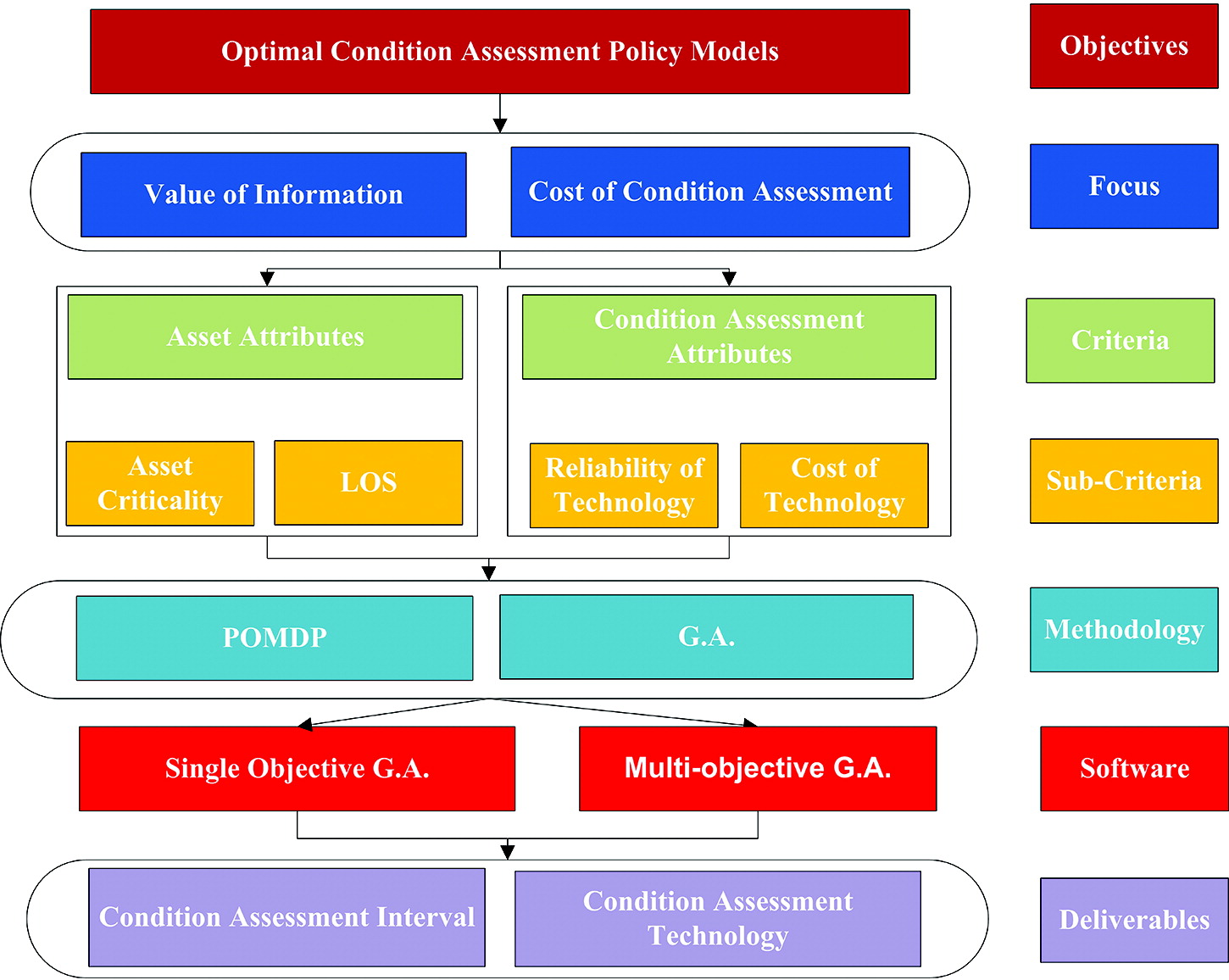
Multiobjective genetic algorithm to allocate budgetary resources for condition assessment of water and sewer networks
This paper presents a framework for optimizing condition assessment policies by balancing the revealed value of information with the cost of obtaining such information. The computational platform is based on augmenting the asset condition state with an expected level of accuracy. Inaccuracies due to condition assessment reliability are evaluated using the partially observable Markov decision process. The single objective genetic algorithm is used to select the most cost-effective assets to assess considering information inaccuracy under a fixed budget. The model is extended using
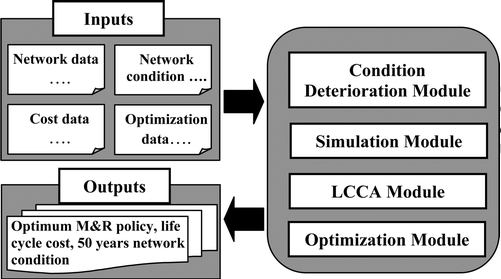
Multiobjective optimisation algorithm for sewer network rehabilitation
Understanding of deterioration mechanisms in sewers helps asset managers in developing prediction models for estimating whether or not sewer collapse is likely. Effective utilisation of deterioration prediction models along with the development and use of life cycle maintenance cost analysis contribute to reducing operation and maintenance costs in sewer systems. This article presents a model for life-cycle maintenance planning of deteriorating sewer network as a multi-objective optimisation problem that treats the sewer network condition and service life as well as life-cycle maintenance cost
Comparative Studies of Using Nano Zerovalent Iron, Activated Carbon, and Green Synthesized Nano Zerovalent Iron for Textile Wastewater Color Removal Using Artificial Intelligence, Regression Analysis, Adsorption Isotherm, and Kinetic Studies
Daily, a big extent of colored, partially treated textile effluents drained into the sanitation systems causing serious environmental concerns. Therefore, the decolorization treatment process of wastewater is crucial to improve effluent quality. In the present study, 3 different sorbent materials, nano zerovalent iron (nZVI), activated carbon (AC), and green-synthesized nano zerovalent iron (GT-nZVI), have been prepared for raw textile wastewater decolourization. The prepared nanomaterials were characterized via X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy
Characterization of defects in 9.7% efficient Cu2ZnSnSe 4-CdS-ZnO solar cells
We have fabricated Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cells with a total area efficiency of 9.7%. The absorber layer was fabricated by selenization of sputtered Cu10Sn90, Zn, and Cu multilayers. A large ideality factor of the order of 3 is observed in both illuminated and dark IV-curves, which seems to point in the direction of complex recombination mechanisms such as recombination through fluctuating potentials in the conduction and valence bands of the solar cell structure. A potential barrier of about 135 meV in the device seems to be responsible for an exponential increase of the series resistance
Comparison and analysis of water main performance models
Evaluating the condition state of infrastructure assets is one of the most integral pieces of information to the asset manager. Water infrastructure poses specific challenges compared to sewer infrastructure where techniques like CCTV are now being consistently used to assess condition. The number of water main breaks is commonly used as a proxy for water main condition. Statistical water main performance models rely on using past breakage patterns and rates to predict future performance of the water main network. Performance models can be broadly classified into two groups. Rate-of-failure
Frequency survey simulation for developing novel radio frequency energy harvesting model
Renewable Energy sources are the center of attraction for research and development all over the world nowadays, the demand of a lasting cheap source of energy that is environmental friendly, is the main challenge recently. Energy Harvesting is a new technology that is going to make a revolution in the coming decade. Energy Harvesting is a technique to provide alternative sources of energy that are environmental friendly and low in cost. Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting is one of the methods to provide electrical energy from the ambient Radio Frequency waves that already exists in the
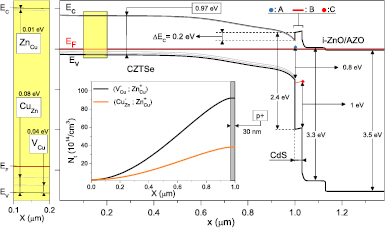
Modelling of Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO thin film solar cell
We present a device model for the Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cell with a total area efficiency of 9.7% reported in 2013 (Brammertz et al 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 163904). The simulations were performed using SCAPS program. In the device model, we reproduce rigorously the full range of layers and device properties estimated experientially using various characterization techniques. We include in the device model barriers at the back contact and the absorber/buffer interfaces, the photo-doped CdS buffer layer and defect states at the CdS/ZnO interface. A perfect match with the electrical
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
