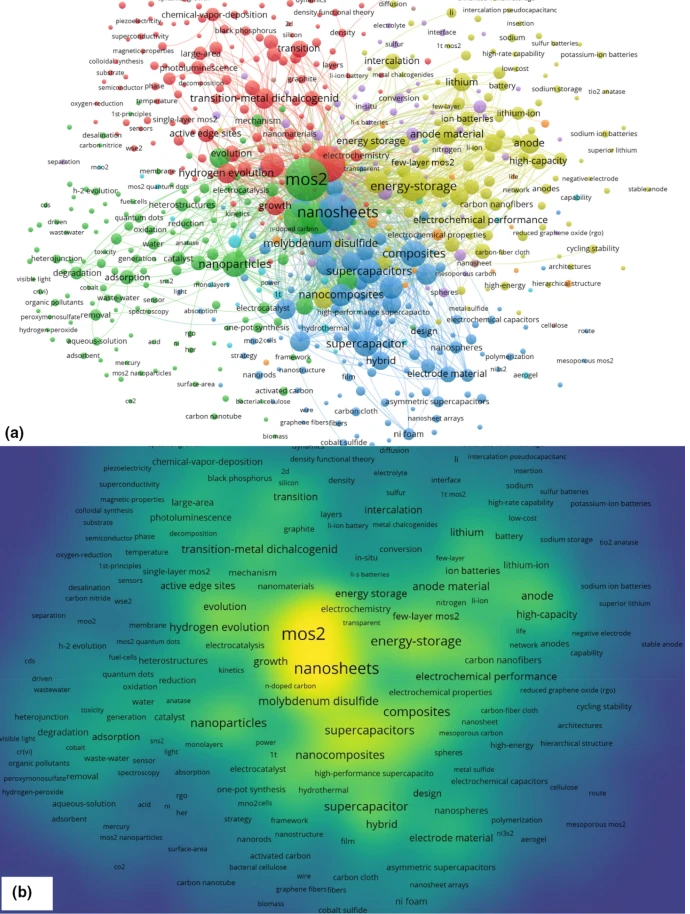
MoS2-based nanocomposites: synthesis, structure, and applications in water remediation and energy storage: a review
The world is currently facing critical water and energy issues due to the growing population and industrialization, calling for methods to obtain potable water, e.g., by photocatalysis, and to convert solar energy into fuels such as chemical or electrical energy, then storing this energy. Energy storage has been recently improved by using electrochemical capacitors and ion batteries. Research is actually focusing on the synthesis of materials and hybrids displaying improved electronic, physiochemical, electrical, and optical properties. Here, we review molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) materials and
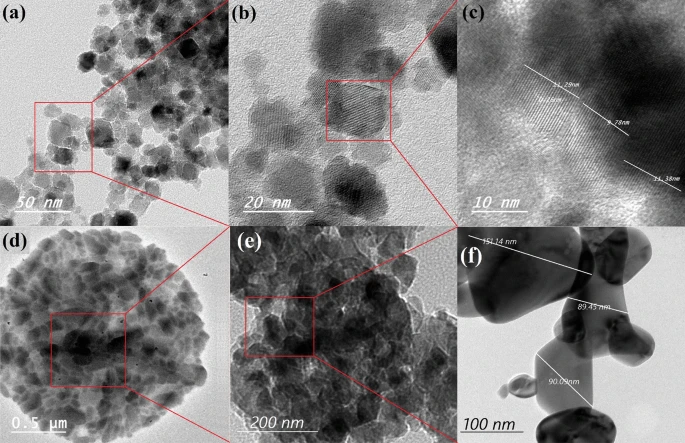
Novel (MnO2/Al) thermite colloid: an opportunity for energetic systems with enhanced performance
The current study highlights a sustainable fabrication of nanoscopic thermite (MnO2/Al) system, composed of MnO2 nanoparticles with an average particle size of about 20.8 nm prepared by a hydrothermal processing technique. In addition, it contains aluminium particles having a combustion heat of 32,000 J/g, which is very attractive for advanced energetic systems. Plate-like aluminium nanoparticles with an average particle size of 100 nm were developed by wet milling. Our results revealed aluminium optimum solid loading in tri-nitrotoulene (TNT), which was found to be 8.0 wt%. At this optimum
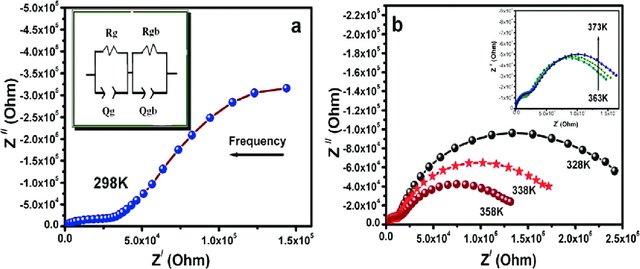
Unveiling the Effect of Zn2+ Substitution in Enrichment of Structural, Magnetic, and Dielectric Properties of Cobalt Ferrite
This work reports the detailed structural characterization of Zn2+ ion-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (CFO NPs; Co1−xZnxFe2O4; x = 0.00, 0.25, 0.50, and 0.75), prepared using a facile sol–gel method. It correlates structural changes with magnetic and dielectric properties. The as-synthesized samples were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, BET surface area analyzer, energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), Mössbauer spectroscopy, and impedance analyzer. The pristine sample
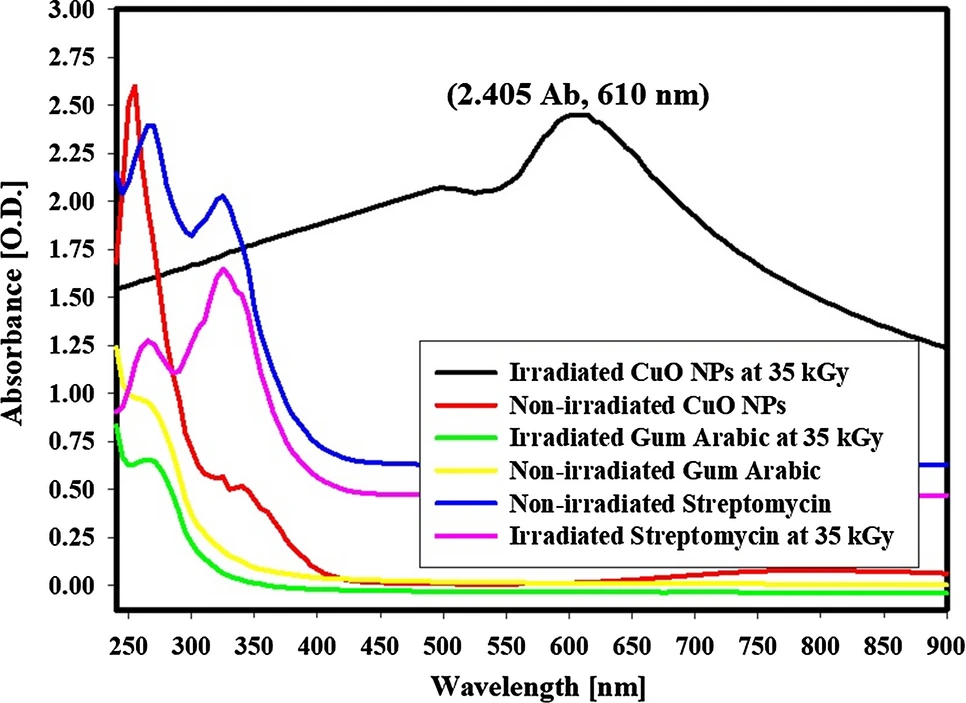
Protective Role of Copper Oxide-Streptomycin Nano-drug Against Potato Brown Rot Disease Caused by Ralstonia solanacearum
Potato plants can be infected by different bacterial diseases, among them, the potato brown rot disease, caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. The novelty of the present research is to assess the potential impact of the synthesized copper oxide NPs (CuO NPs)-streptomycin nano-drug synthesized by gamma irradiation for inducing the systemic resistance against potato brown rot disease. CuO NPs-streptomycin was completely-characterized by UV–Vis., XRD, FTIR, HRTEM, SEM, and EDX elemental analysis. In the greenhouse experiment, the efficiency of CuO NPs was tested after three times of application
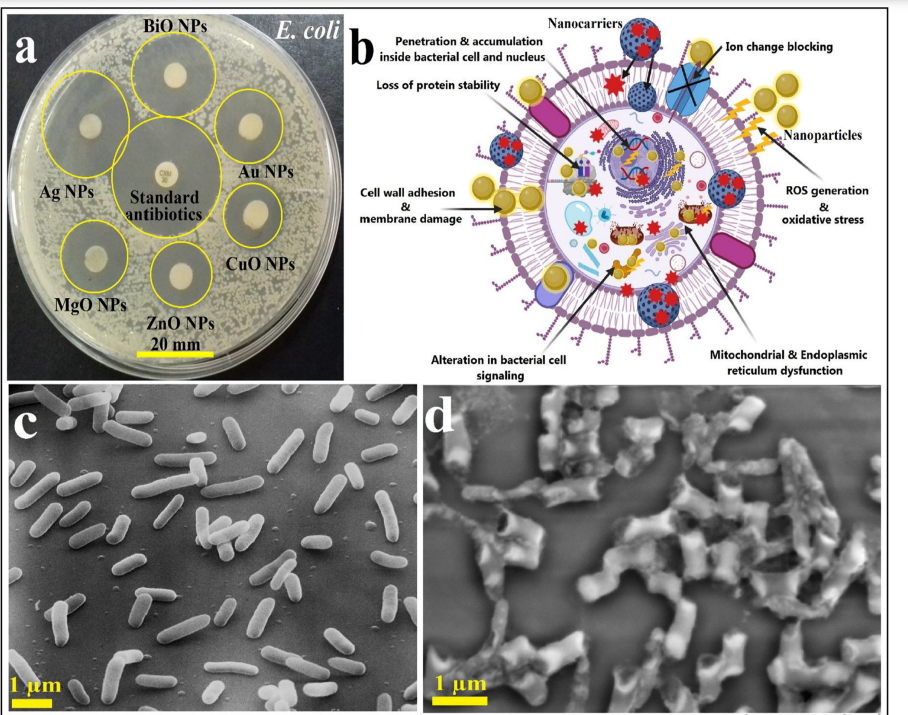
Engineered nanomaterials as fighters against SARS-CoV-2: The way to control and treat pandemics
In this editorial trend, we aim to collect and present recently available data about the characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 virus, severity, infection, replication, diagnosis, and current medications. In addition, we propose the role of nanomaterials in controlling and treating COVID-19 through their antiviral and antibacterial potential with suggested action mechanisms indicating the capability of interaction between these nanomaterials and SARS-CoV-2. These nanomaterials might be among the possible and most effective cures against coronavirus. © 2020, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of
Microbial acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s therapy: recent trends on extraction, detection, irradiation-assisted production improvement and nano-structured drug delivery
Abstract: Neurodegenerative disorders especially Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are significantly threatening the public health. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors are compounds of great interest which can be used as effective agents for the symptomatic treatment of AD. Although plants are considered the largest source for these types of inhibitors, the microbial production of AChE inhibitors represents an efficient, easily manipulated, eco-friendly, cost-effective, and alternative approach. This review highlights the recent advances on the microbial production of AChE inhibitors and summarizes
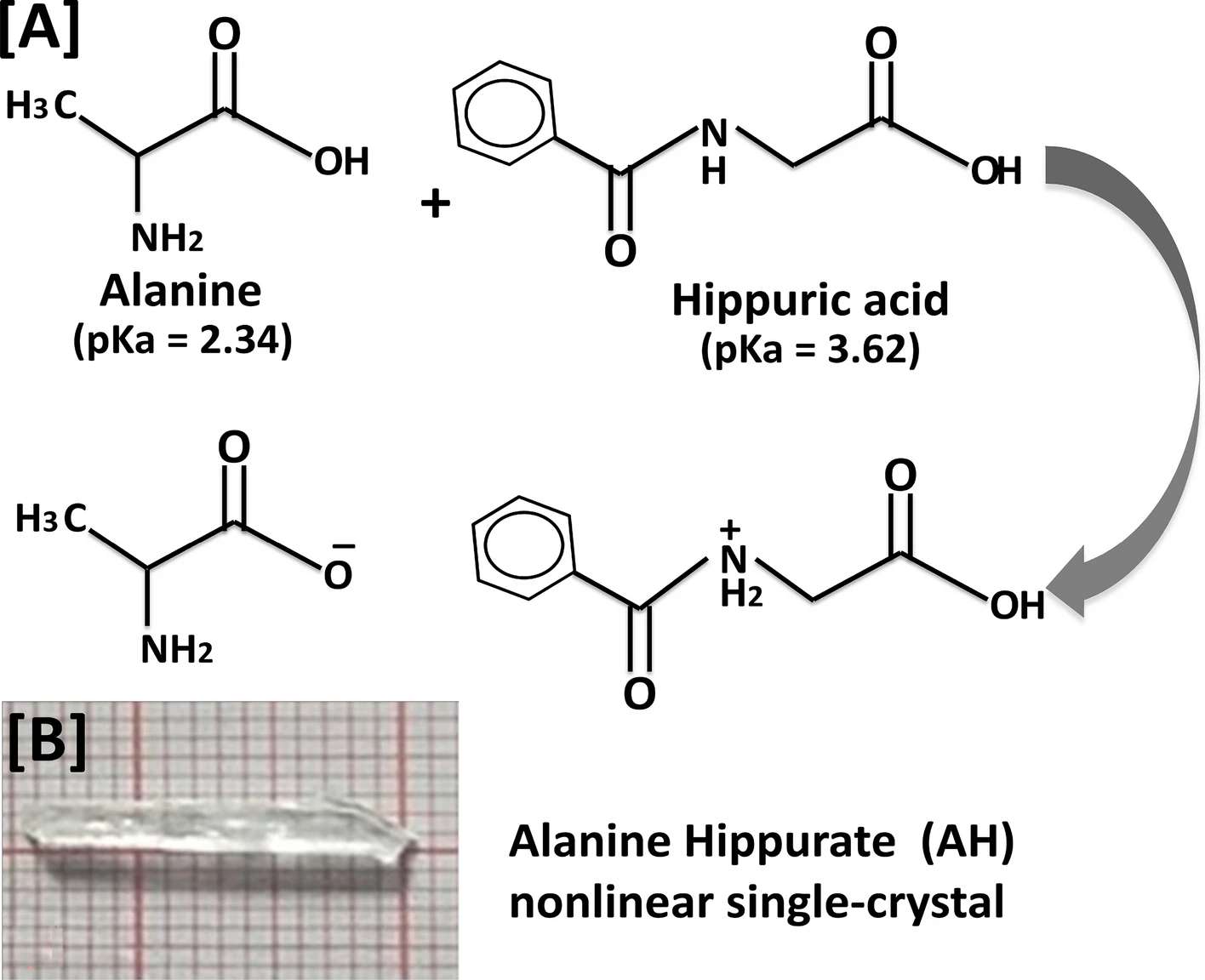
Fabrication, Characterization and Optical Investigation of Semi-organic Nonlinear Alanine Hippurate Single Crystals
In the present work, a single crystal of alanine and hippuric acid was prepared through the slow growth dynamics of sample evaporation. The crystallinity, structure, and cell parameters of the produced single crystals were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. While, frequency shifting and the various functional groups of alanine with hippuric acid were investigated by FTIR and FT-Raman studies. In addition, grain size and the morphological shape of alanine hippurate (AH) single crystals were examined by FE-SEM analysis. Transmission of light through the grown material was defined by
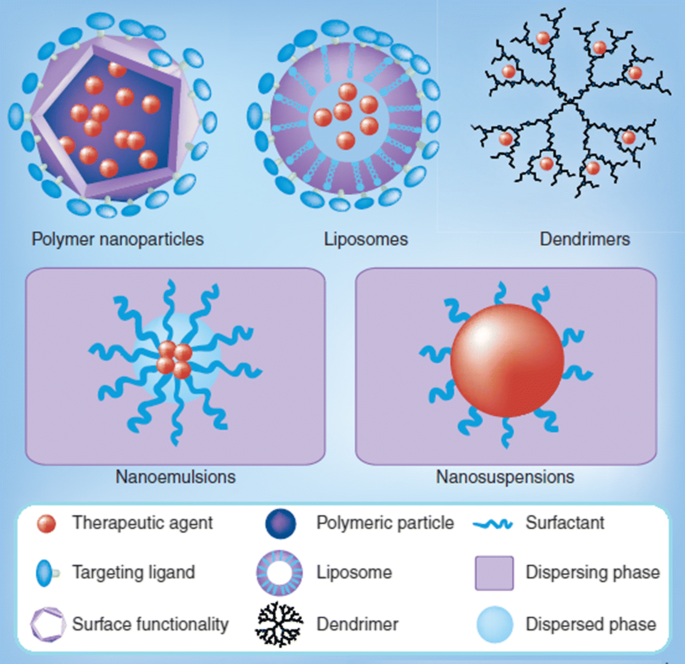
Engineered Nanomaterials as Potential Candidates for HIV Treatment: Between Opportunities and Challenges
Nanomaterials have received considerable attention due to their unique properties; they have high surface area compared to volume ratio, giving them superior chemical, optical and thermal characteristics. Nanomaterials have also both diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In this mini review, we are highlighting valuable data about human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), its relationship with cancer and its potential treatment with some nanomaterials such as silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs). © 2019, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
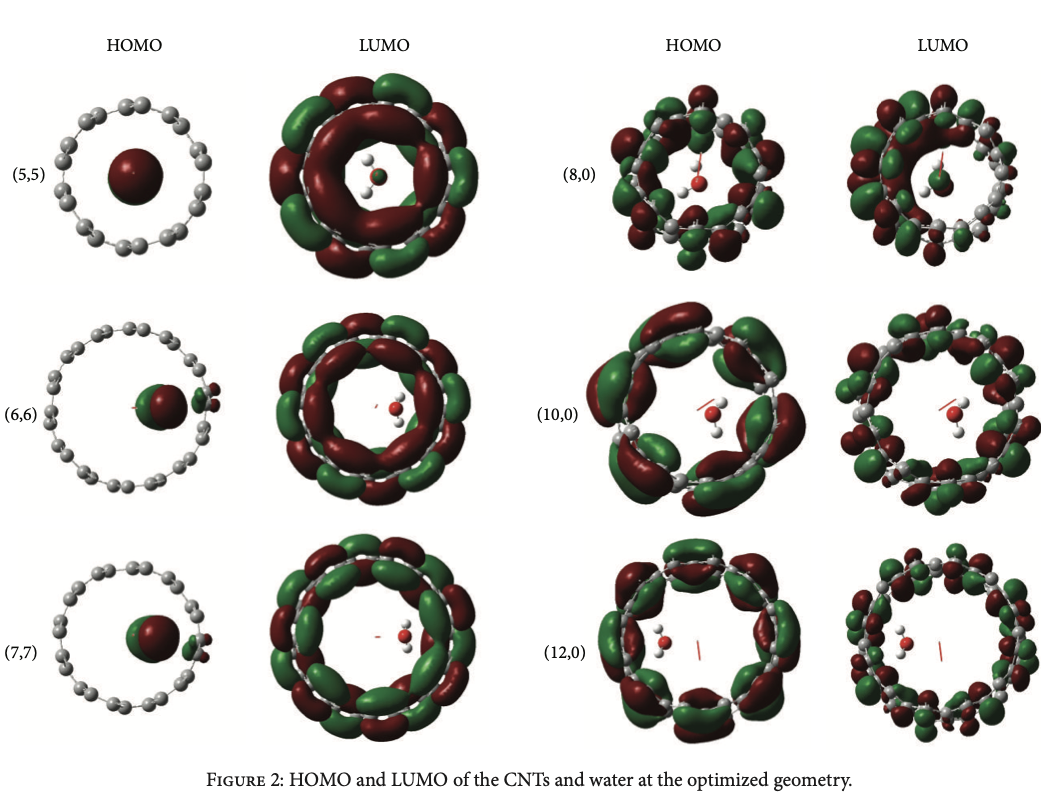
Ab initio density functional theory investigation of the interaction between carbon nanotubes and water molecules during water desalination Process
Density functional theory calculations using B3LYP/3-21G level of theory have been implemented on 6 carbon nanotubes (CNTs) structures (3 zigzag and 3 armchair CNTs) to study the energetics of the reverse osmosis during water desalination process. Calculations of the band gap, interaction energy, highest occupied molecular orbital, lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, electronegativity, hardness, and pressure of the system are discussed. The calculations showed that the water molecule that exists inside the CNT is about 2-3 Å away from its wall. The calculations have proven that the zigzag
Merits of photocatalytic and antimicrobial applications of gamma-irradiated Co: XNi1- xFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; X = 0.9 nanocomposite for pyridine removal and pathogenic bacteria/fungi disinfection: Implication for wastewater treatment
In this paper, we report a layer-by-layer approach for the preparation of a concentric recyclable composite (CoxNi1-xFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; x = 0.9) designed for wastewater treatment. The prepared composite was investigated by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) supported with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy to analyze crystallinity, average particle size, morphology and elemental composition, respectively. The antimicrobial activities of the prepared composite have been investigated against multi-drug
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››
