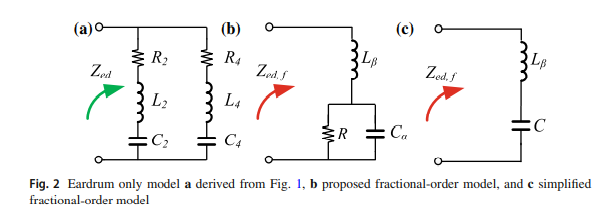
Design and Implementation of an Optimized Artificial Human Eardrum Model
This paper introduces a fractional-order eardrum Type-II model, which is derived using fractional calculus to reduce the number of elements compared to its integer-order counterpart. The proposed fractional-order model parameters are extracted and compared using five meta-heuristic optimization techniques. The CMOS implementation of the model is performed using the Design Kit of the Austria Mikro Systeme (AMS) 0.35 μ m CMOS process, while the simulations have been performed using the Cadence IC design suite. © 2019, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
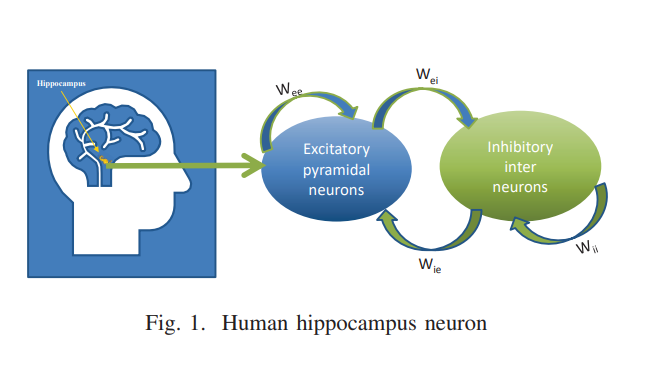
Generic FPGA Design of Spiking Neuron Model
This paper introduces a new representation of the human brain neuron cell response. Implementation of a single cell model of an excitatory and inhibitory neuron. The architecture is based on mimic the real reaction of the neuron cell. Excitatory and inhibitory are implemented in generic form for all neuron's behavior. The design is tested experimentally using FPGA. The designs have been realized, simulated using Xilinx ISE 14.7, and realized on Xilinx FPGA Virtex Artix-7 XC7A100T. The proposed realization shows good performance to be compatible with various applications. © 2020 IEEE.
Impact of oustaloup and matsuda approximations on fractional pid controller of pv panel
Due to the non-linear relation between current and voltage of the PV modules, DC/DC power electronic converters are used to adapt this non-linearity. Controllers are used to control the DC/DC converters in order that, they can take actions against changes in irradiance input levels, temperature input levels and load values. In this study, a standalone PV system that feeds a DC load is simulated. Integer order controller and fractional order controller are compared considering two scenarios. The first scenario is to change the irradiance levels while maintaining the load at a constant value. In

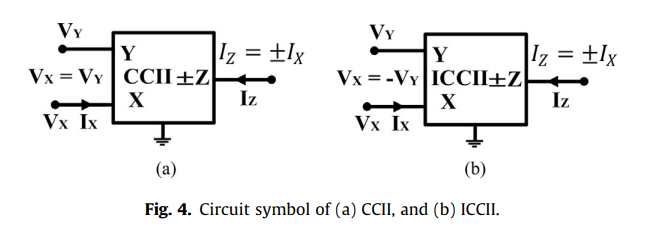
General fractional order mem-elements mutators
This paper proposes the realization of grounded and floating fractional order mem-elements (FOMEs) based on two- and three-port mutators, respectively. Three different topologies based on two-port mutators are implemented using the four members of the second-generation current conveyor (CCII) family which is useful to achieve several realizations for the same circuit. The Fractional Order Mem-capacitor (FOMC) and Fractional Order Mem-inductor (FOMI) are realized using different combinations of memristor and fractional order capacitor (FOC) plus resistors. In addition, the generalization of the
Generalized two-port network based fractional order filters
This paper proposes a general prototype fractional order filter based on a two-port network concept with four external impedances. Three induced classifications from the general prototype are extracted with one, two and three external impedances, achieving ten possible generalized topologies. The external impedances are fractional-order elements and resistors. There are forty-six filters divided into twenty-two and twenty-four different general fractional filters of order “α” and order “α + β”, respectively. The general transfer functions, the necessary network conditions, and the critical
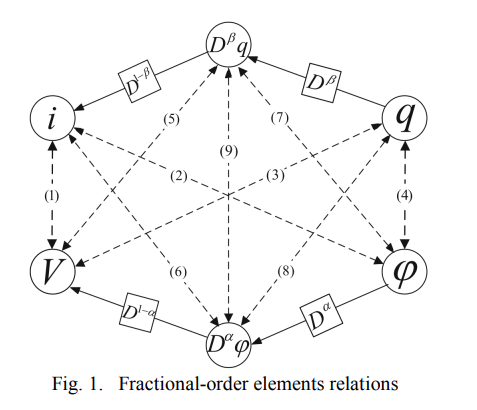
On the analysis of current-controlled fractional-order memristor emulator
In this paper, a current-controlled fractional-order memristor model and its emulator are proposed. The emulator is built using two second generation current conveyor (CCII) and fractional-order capacitor. It is shown that the effect of the fractional order is clearly noticeable in the circuit response. PSPICE simulations are introduced for different values of the fractional order showing noticeable variations of the pinched-loop hysteresis curves. The fractional order model shows wider frequency of operation and larger pinched loop hysteresis area than the integer one. © 2017 IEEE.
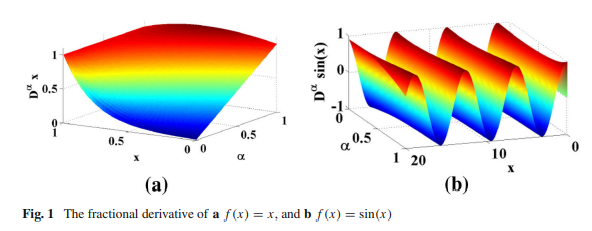
On The Optimization of Fractional Order Low-Pass Filters
This paper presents three different optimization cases for normalized fractional order low-pass filters (LPFs) with numerical, circuit and experimental results. A multi-objective optimization technique is used for controlling some filter specifications, which are the transition bandwidth, the stop band frequency gain and the maximum allowable peak in the filter pass band. The extra degree of freedom provided by the fractional order parameter allows the full manipulation of the filter specifications to obtain the desired response required by any application. The proposed mathematical model is
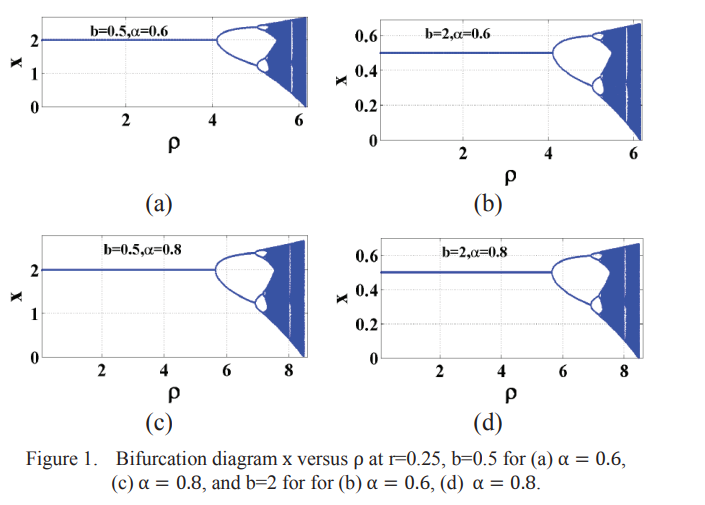
Generalized fractional logistic map suitable for data encryption
This paper presents a generalized form of the fractional logistic map. Two general parameters a and b are added to the classical fractional logistic equation. The effect of such parameters on the map is studied explicitly, in combination with the fractional order parameter α, which offers an extra degree of freedom increasing the design flexibility and adding more controllability on the design. The vertical and the zooming map are two special maps that arise as a result of the added parameters. Moreover, different design problems are offered in this work, as a resultant of the control of all
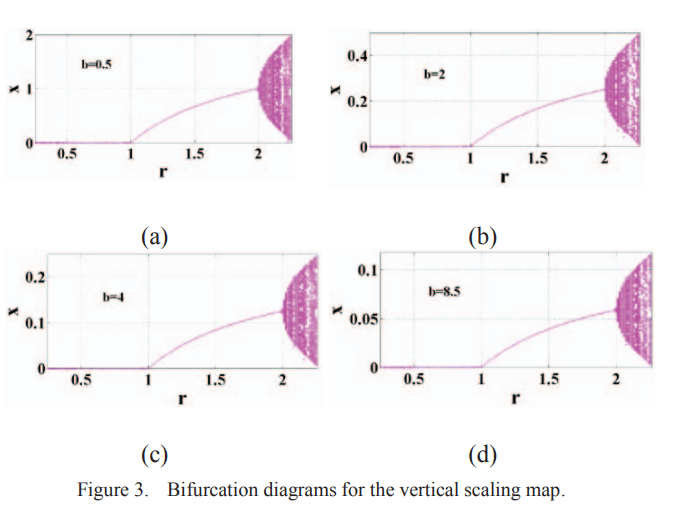
Generalized delayed logistic map suitable for pseudo-random number generation
This paper presents the generalization of a delayed version of the logistic map. The effect of the added two general parameters is studied, which offers the option of having three different maps. The dynamic behavior of the vertical, zooming and the general map is analyzed. The study of the fixed points, stability ranges and bifurcation diagram of the delayed logistic map at hand is detailed in this work. The flow of the system behavior from stability to chaos is also presented with its transient response as well as its phase plane portraits. Moreover, using the general parameters, the option
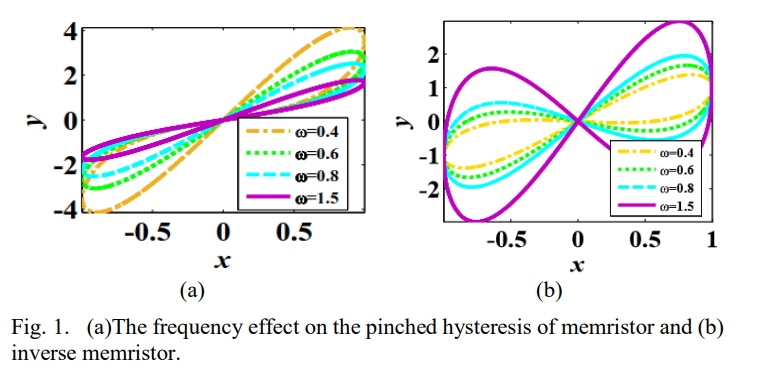
Inverse memrsitor emulator active Realizations
The paper aims to propose three different inverse memristor emulators based on serveral active blocks. One of the presented emulator realizes employing second generation current conveyor (CCII) andcanalog voltage multiplier with passive elements. The other two introduced emulators are designed using cureent feedback operational amplifier (CFOA) with two switches or two BJT transistor. One of the proposed emulators has the advantages that it switches between the inverse and memristor at the same time but in different frequency with less number of components. The introduced circuitry are
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
