Breadcrumb
Optimal Design of PID Controller for 2-DOF Drawing Robot Using Bat-Inspired Algorithm
Tuning process which is used to find the optimum values of the proportional integral derivative (PID) parameters, can be performed automatically using meta-heuristics algorithms such as BA (Bat Algorithm), PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization) and ABC (Artificial Bee Colony). This paper presented a theoretical and practical implementation of a drawing robot using BA to tune the PID controller governing the robotic arm which is a non linear system difficult to be controlled using classical control. In line with the above and in order to achieve this aim and meet high performance feedback and robust
PID Controller for 2-DOFs Twin Rotor MIMO System Tuned with Particle Swarm Optimization
This paper presents the modelling and control of a 2-DOFs Twin rotor multi input multi output (MIMO) system which is a laboratory setup resembling the dynamics of a helicopter. In this paper, the system modelling process is done using the common conventional mathematical model based on Euler-Lagrange method. The transfer functions of the model are used in the different tuning methods to reach the optimal PID gain values. The study uses conventional Proportional-Integral (PI) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers to obtain a robust controller for the system. Particle Swarm

Modeling of Nonlinear Enhanced Air Levitation System using NARX Neural Networks
the proposed paper aims to design and model an air levitation system, which is a highly nonlinear system because of its fast dynamics and low damping. The system is trained using a Nonlinear Autoregressive model with exogenous input (NARX model). An enhanced height measurement system, modified setup, and several training techniques have been used to overcome the restrictions that the non-linearity of the system imposes in the literature. The system mathematical model has been illustrated, followed by an identified model using NARX model trained on several input-output data from the physical
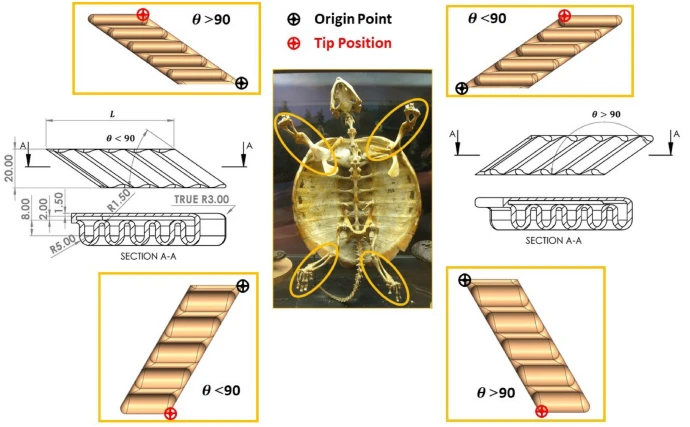
Modelling and implementation of soft bio-mimetic turtle using echo state network and soft pneumatic actuators
Advances of soft robotics enabled better mimicking of biological creatures and closer realization of animals’ motion in the robotics field. The biological creature’s movement has morphology and flexibility that is problematic deportation to a bio-inspired robot. This paper aims to study the ability to mimic turtle motion using a soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) as a turtle flipper limb. SPA’s behavior is simulated using finite element analysis to design turtle flipper at 22 different geometrical configurations, and the simulations are conducted on a large pressure range (0.11–0.4 Mpa). The
Tactile sensing biohybrid soft E-skin based on bioimpedance using aloe vera pulp tissues
Soft and flexible E-skin advances are a subset of soft robotics field where the soft morphology of human skin is mimicked. The number of prototypes that conformed the use of biological tissues within the structure of soft robots—to develop “Biohybrid Soft Robots”—has increased in the last decade. However, no research was conducted to realize Biohybrid E-skin. In this paper, a novel biohybrid E-skin that provides tactile sensing is developed. The biohybrid E-skin highly mimics the human skin softness and morphology and can sense forces as low as 0.01 newton. The tactile sensing feature is
Two-Degree of Freedom Proportional Integral Derivative (2-DOF PID) Controller for Robotic Infusion Stand
Infusion Stand is one of the medical supportive tools in the field of biomedical that assist in holding and carrying medications to patients via intravenous injections. Mobilization of Infusion Stand from a place to another place is necessary not only for the patients itself but also for the nurses. Therefore, this leads to not only uneasiness but also inconvenience for both parties. Therefore, to improve the existing situation and current Infusion Stand in the market, a proposal to design and implement a prototypic Robotic Infusion Stand is submitted. In this paper, 2-Degree of Freedom
Gripping Force Modeling of a Variable Inclined Air Pillow Soft Pneumatic Actuator
Soft pneumatic actuators grasping tasks is one of the essential rules in robot manipulation methods. The grasping forces can be adapted to handle delicate and hard objects without leaving any damages on the object surfaces. This paper investigates the influence of the inclination angle of the soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) on its gripping force at its end tip. A range of inclination angles for SPA is analyzed using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to estimate the gripping force at the end tip regarding SPA inner faces pressure. FEA study is conducted based on Hyperelastic material modeling
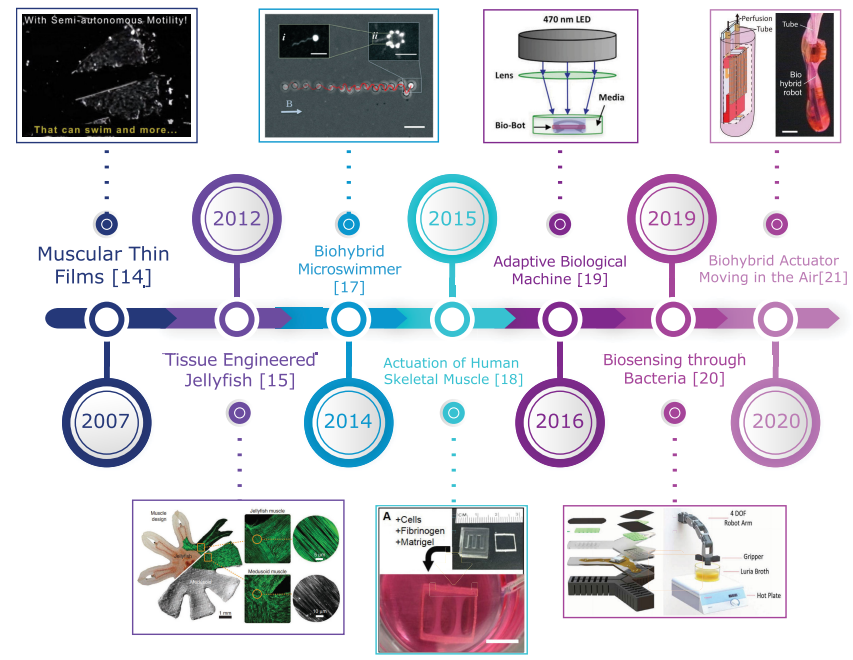
Biohybrid soft robots, E-skin, and bioimpedance potential to build up their applications: A review
Soft Robotics is a new approach towards better human-robot interaction and biomimicry in the robotics field. Its integration with biological materials (Biohybrid soft robotics) is one of the topics being focused on in the soft robotics research in the last fifteen years. The motive for this approach is to combine the best of biological and artificial systems. In this article, Biohybrid soft robots and Electronic Skin (E-skin), which is considered one of the advances of soft robotics, are reviewed. Their most significant milestones and the highlights of their most researched applications are
Improved Production Key Performance Indicators (KPI’s) Using Intelligent-Manufacturing Execution Systems (I-MES)
The aim of this research is to reduce the gap between manufacture expertise and management expertise by using modern technology like Manufacturing Execution System (MES) via Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machin Learning (ML). A design of MES has been proposed and implemented on El-Araby Plastic Injection Molding (PIM) factory. This work is based on the International Society of Automation Standard (ISA-S95). A fully automated data management system has been designed and implemented to control data follow between shop floor e.g. (machines and operators) and management floor e.g. (production
Implementation of PID Controller with PSO Tuning for Autonomous Vehicle
In the use of automatic control and its optimization methods, this research discusses how Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller is used to provide a smooth auto-parking for an electrical autonomous car. Different tuning methods are shown, discussed, and applied to the system looking forward to enhancing its performance. Time domain specifications are used as a criterion of comparison between tuning methods in order to select the best tuning method to the system with a proper cost function. Results show that Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) method gives the best results according
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
