Replay attack on lightweight CAN authentication protocol
Day after day, users' expectations of tomorrow vehicles' features are increasing. Although the industry's prime goal is users' satisfaction, many unsolved problems are still present. Amongst the major challenges are the huge interconnections and dependability within the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) used inside vehicles. Five years ago, the number of ECUs within a vehicle was about 70 ECUs. This number has doubled nowadays, and it is expected to double again in the near future. This adds challenges to both of network management and network security. The purpose of this paper is to enhance the
Fractional Order Sliding Mode PID Controller/Observer for Continuous Nonlinear Switched Systems with PSO Parameter Tuning
In this article a fractional order sliding mode PID controller and observer for the stabilization of continuous nonlinear switched systems is proposed. The design of the controller and observer is done following the separation principle, this means that the observer and controller are designed in a separate fashion, so a hybrid controller is implemented by designing the sliding mode controller part using an integral sliding mode surface along with a PIλDμ controller part which is the fractional order PID controller that is implemented to stabilizes the system. For the observer part, an
Fractional Order Two Degree of Freedom PID Controller for a Robotic Manipulator with a Fuzzy Type-2 Compensator
In this paper a novel strategy for the position control and trajectory tracking of robotic manipulators is proposed. This strategy consists of an independent two degree of freedom PID controller for a two links robotic arm. Due to the capability of two degree of freedom PID controllers to deal with disturbances, each link is controlled independently considering that the disturbance does not affect the system performance due to the robustness of the closed loop system. Then, a fuzzy type-2 centralized compensator is implemented to drive the orientation variables with the desired trajectory in
Memristor-based quinary half adder
This paper theorizes the possibilities of generalizing a memristor based ternary adder circuit, to a memristor based multi-valued logic adder. The proposition tries to achieve the theoretical advantages of processing different numbering systems, increasing the density, and decreasing the processing time, by utilizing the memristor properties and dynamics. This is done using a memristor cell based circuit structure. The memristor is quantized to more levels in order to accommodate more values of logic being processed. Quinary numbering system is used to demonstrate the generalization, then a
Synchronization between a Novel Integer-Order Hyperchaotic System and a Fractional-Order Hyperchaotic System Using Tracking Control
This manuscript investigates the synchronization between a novel integer order hyperchaotic system and a fractional order hyperchaotic system. The controllers are constructed using the technique of tracking controller and the stability theory of the linear fractional order system. Chaotic analysis of the introduced novel integer order hyperchaotic system is also investigated. The Lyapunov exponent, bifurcation diagram, Poincare section, Kaplan-Yorke dimension, equilibria and phase portraits are given to justify the chaotic nature of the system. Theoretical results are supported with the
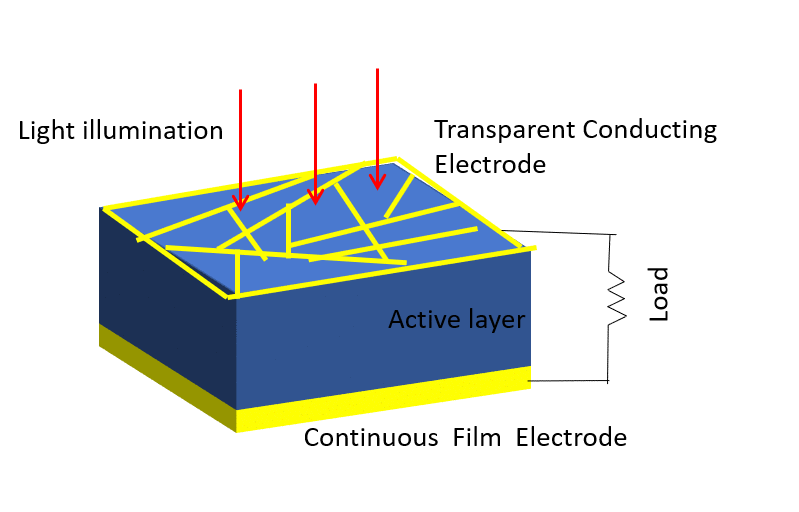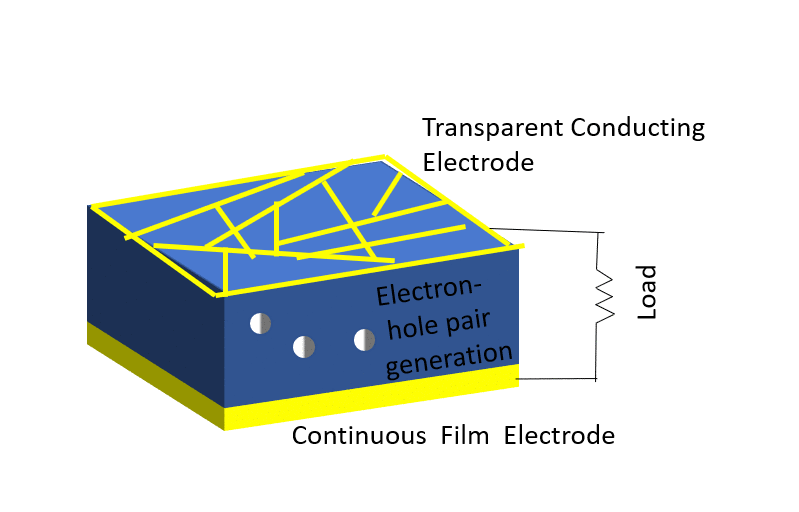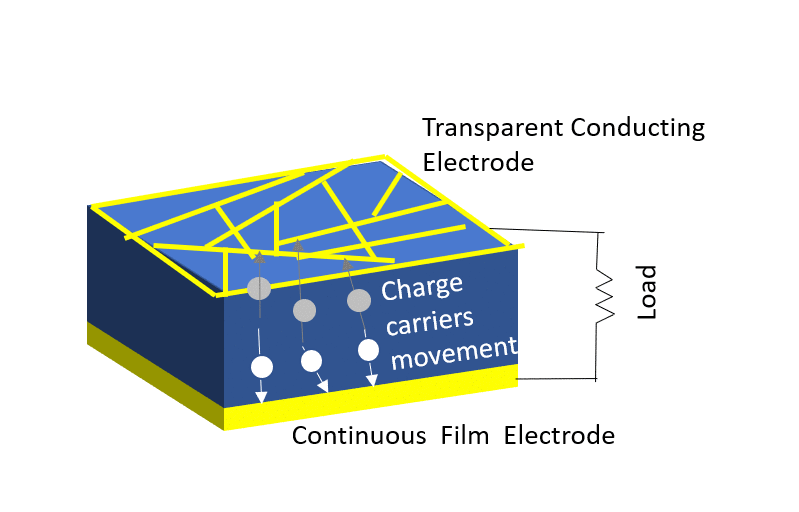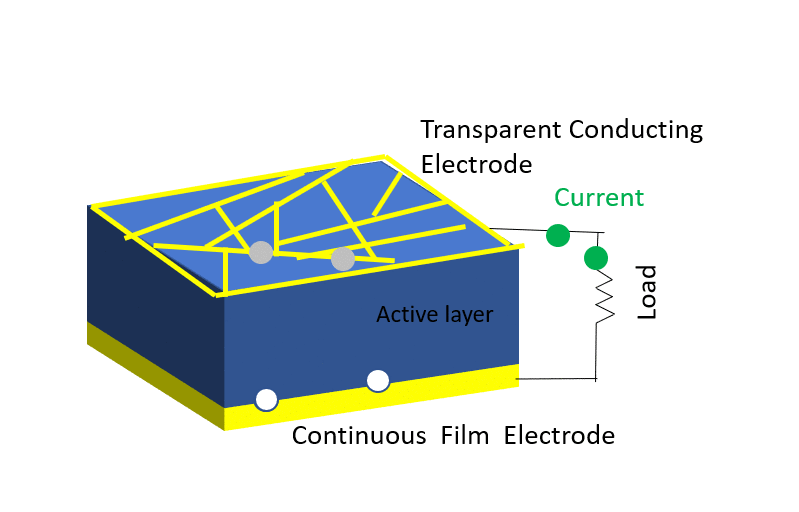
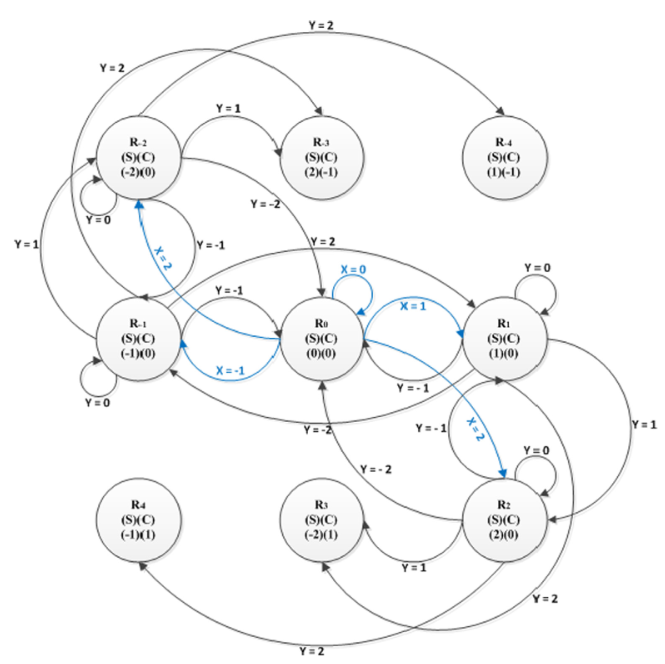
Investigation of properties limiting efficiency in Cu2ZnSnSe4-based solar cells
We have investigated different nonidealities in Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cells with 9.7% conversion efficiency, in order to determine what is limiting the efficiency of these devices. Several nonidealities could be observed. A barrier of about 300 meV is present for electron flow at the absorber-buffer heterojunction leading to a strong crossover behavior between dark and illuminated current-voltage curves. In addition, a barrier of about 130 meV is present at the Mo-absorber contact, which could be reduced to 15 meV by inclusion of a TiN interlayer. Admittance spectroscopy results on the
Cole-Cole Bio-Impedance Parameters Extraction from a Single Time-Domain Measurement
We show that the four parameters of a single-dispersion Cole-Cole bio-impedance model can be extracted from an one time-domain measurement with a fixed frequency. In particular, a periodic triangle waveform current excitation signal is injected into the biological sample under study while measuring the voltage developed across this sample in a galvanostatic measurement setup. The voltage response due to this triangle-wave excitation is firstly analytically derived in closed form. After that the Flower Pollination optimization Algorithm (FPA) is applied to extract the unknown model parameters
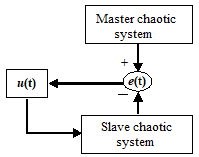
Multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems
This paper investigates the multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems in which state variables of a master system are synchronized with different state variables of a slave system using the sliding mode control technique. To design the appropriate controllers via sliding mode control for different switches, Lyapunov stability theory is taken into account. Theoretical results are applied by considering two non-identical chaotic systems where one is considered as master system and another is considered as slave system. Numerical simulations are performed to
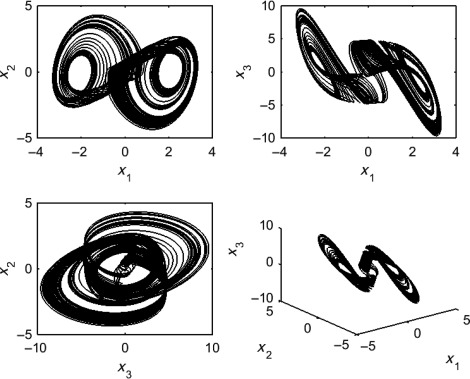
Multiswitching synchronization of commensurate fractional order hyperchaotic systems via active control
In this chapter, the multiswitching synchronization scheme has been investigated for a class of nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems. The multiswitching complete synchronization scheme has been examined such that the state variables of the slave system synchronize with different state variables of the master system. For the synchronization of two nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems suitable controllers have been designed using active control technique. The stability of fractional order chaotic systems has been used to stabilize the error dynamical system. Two
New Control Schemes for Fractional Chaos Synchronization
Chaos theory deals with the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. Chaotic systems are characterized by the property that small changes in the initial conditions result in widely diverging responses. In this paper, new control schemes of synchronization for different arbitrary incommensurate and commensurate fractional order chaotic systems are presented. Synchronization stability, based on stability of linear fractional-order systems and fractional Lyapunov stability, is proved theoretically. Numerical examples are given to show the effectiveness of the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››
