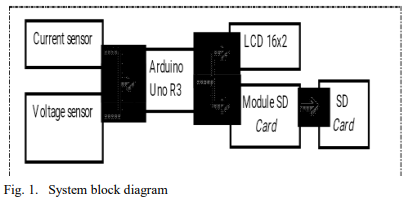
Design and analysis of DC electrical voltage-current data logger device implemented on wind turbine control system
DC electrical voltage-current measuring instrument and data are an instrument used to measure the current and voltage generated by wind turbines and record the measurement results. The function of this instrument is to activate the dummy load on the wind turbine control system to reduce the voltage that exceeds the safe limit when saving electrical energy. The research aimed to manufacture and analyze DC electrical voltage - current measuring instrument using the Arduino Uno based data logger, capable of measuring the DC and voltage generated by Hybrid Power Plants (PLTH) and use the metrology
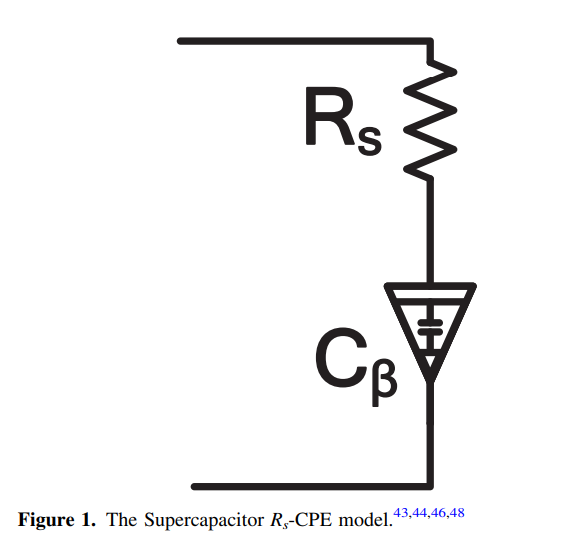
Optimal Charging and Discharging of Supercapacitors
In this paper, we discuss the optimal charging and discharging of supercapacitors to maximize the delivered energy by deploying the fractional and multivariate calculus of variations. We prove mathematically that the constant current is the optimal charging and discharging method under R s -CPE model of supercapacitors. The charging and round-trip efficiencies have been mathematically analyzed for constant current charging and discharging. © 2020 The Electrochemical Society ("ECS"). Published on behalf of ECS by IOP Publishing Limited.
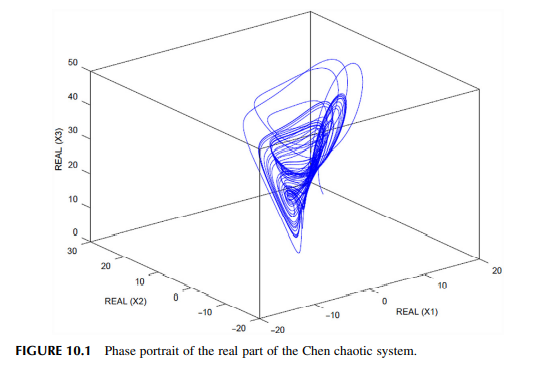
Sliding mode stabilization and synchronization of fractional order complex chaotic and hyperchaotic systems
This chapter is intended to design and analyze several sliding mode techniques for the stabilization and synchronization of fractional order complex chaotic and hyperchaotic systems. Considering that chaos is a hot topic nowadays due to the vast number of real physical systems such as mechanical, electrical, and chemical systems in which this phenomenon is found; this book chapter will provide novel sliding mode approaches for the stabilization and synchronization of chaotic and hyperchaotic systems. Fractional order chaotic and hyperchaotic systems have been proved to be difficult to
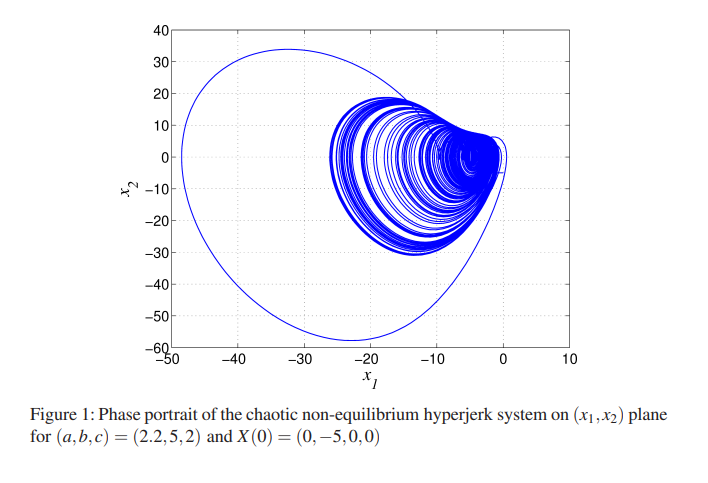
A 4-D chaotic hyperjerk system with a hidden attractor, adaptive backstepping control and circuit design
A novel 4-D chaotic hyperjerk system with four quadratic nonlinearities is presented in this work. It is interesting that the hyperjerk system has no equilibrium. A chaotic attractor is said to be a hidden attractor when its basin of attraction has no intersection with small neighborhoods of equilibrium points of the system. Thus, our new non-equilibrium hyperjerk system possesses a hidden attractor. Chaos in the system has been observed in phase portraits and verified by positive Lyapunov exponents. Adaptive backstepping controller is designed for the global chaos control of the non
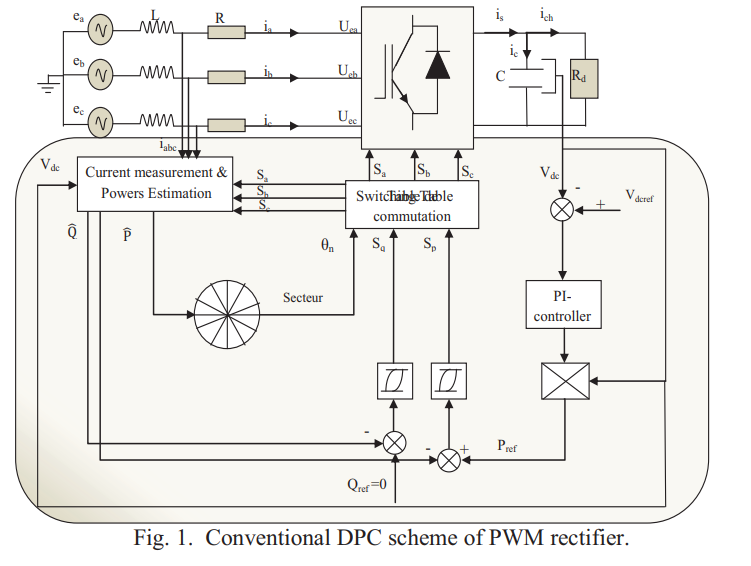
Direct Power Control of a three-phase PWM-Rectifier based on Petri nets for the selection of Switching States
This article proposes a new simple scheme for direct power control of a PWM rectifier without a switch table and voltage sensor. The selection of the switching state of the converter is based on the transition of a Petri net, using the instantaneous active and reactive power tracking errors and the angular position of the network line voltage estimated as variables of Controller input based on Petri nets. Simulation and experimental results demonstrated better performance and verified the validity of the new command with the Petri nets applied to the bridge rectifier connected to the
In-Silico Comparative Analysis of Egyptian SARS CoV-2 with Other Populations: A Phylogeny and Mutation Analysis
In the current SARS-CoV2 pandemic, identification and differentiation between SARS-COV2 strains are vital to attain efficient therapeutic targeting, drug discovery and vaccination. In this study, we investigate how the viral genetic code mutated locally and what variations is the Egyptian population most susceptible to in comparison with different strains isolated from Asia, Europe and other countries in Africa. Our aim is to evaluate the significance of these variations and whether they constitute a change on the protein level and identify if any of these variations occurred in the conserved
Honey Badger Algorithm: New metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems
Recently, the numerical optimization field has attracted the research community to propose and develop various metaheuristic optimization algorithms. This paper presents a new metaheuristic optimization algorithm called Honey Badger Algorithm (HBA). The proposed algorithm is inspired from the intelligent foraging behavior of honey badger, to mathematically develop an efficient search strategy for solving optimization problems. The dynamic search behavior of honey badger with digging and honey finding approaches are formulated into exploration and exploitation phases in HBA. Moreover, with
Innovative human-robot interaction for a robot tutor in biology game
Robots nowadays, are introduced to many domains and fields. One of these fields is education. We introduce integrating robots and games in education. We have designed a humanoid robot tutoring biology. Our robot is interacting with a student to play a game to enhance and examine the student's knowledge. In our game, we developed cognitive capabilities for the robot. We analyzed the features that both the robot and the game have to possess, and we developed a system for organ detection and recognition with the highest possible accuracy and lowest processing time. Our game introduces a multi
Towards IT-Legal Framework for Cloud Computing
As the common understanding of Cloud Computing is continuously evolving, the terminology and concepts used to define it often need clarifying. Therefore, Cloud customers and Cloud Providers are used to dispute about Service Level Agreements, Service Level Objectives and Quality of Service. Simultaneously, SLAs/SLOs/QoS represent other related technical problems such as Security, Privacy, Compliancy and others. Technical problems are usually defined within technical context, where both parties ignore analyzing problem's legally related causes. In fact, these problems are stemming from the
Traffisense: A smart integrated visual sensing system for traffic monitoring
Intelligent camera systems provide an effective solution for road traffic monitoring with traffic stream characteristics, such as volumes and densities, continuously computed and relayed to control stations. However, developing a functional vision-based traffic monitoring system is a complex task that entails the creation of appropriate visual sensing platforms with on-board visual analytics algorithms, integration of versatile technologies for data provision and stream management, and development of data visualization techniques suitable for end-users. This paper describes TraffiSense, a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 55
- Next page ››
