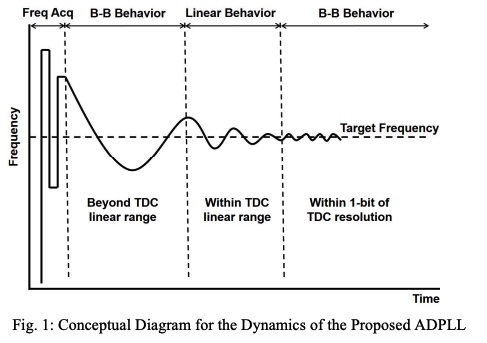
A fast locking hybrid TDC-BB ADPLL utilizing proportional derivative digital loop filter and power gated DCO
A hybrid Time to Digital Converter (TDC) - Bang Bang (BB) All Digital Phase Locked Loop (ADPLL) architecture is proposed to optimize power, area, lock time, and design complexity. The Hybrid ADPLL architecture utilizes a low resolution two synthesizable Time to Digital Converters to achieve fast lock time, and then switches to a Bang-Bang like architecture once it is in the locked state. Such hybrid architecture enables the ADPLL to achieve lock time in less than 1 μ sec using an adaptive proportional derivative digital loop filter while consuming a power of 5.1 mW when locked at 4GHz with 1
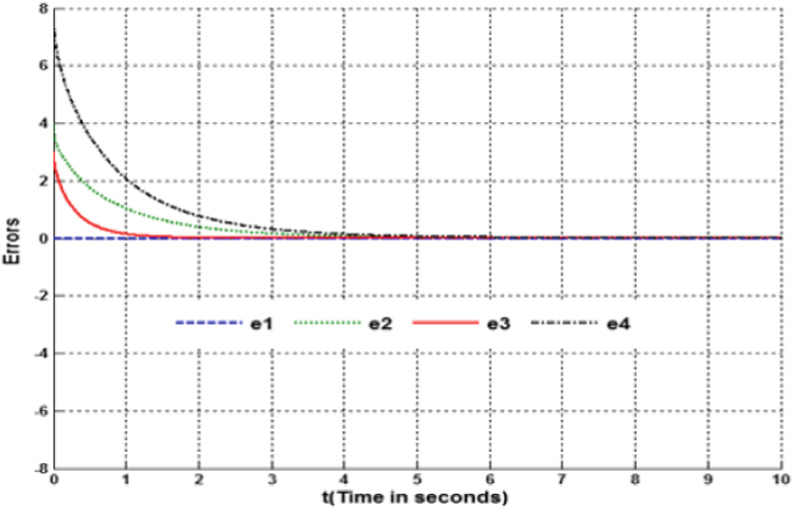
A New Generalized Synchronization Scheme to Control Fractional Chaotic Systems with Non-identical Dimensions and Different Orders
This paper addresses the problem of generalized synchronization (GS) between fractional order chaotic systems. In this paper, we propose a new control strategy for a complex generalized synchronization (GS) scheme dedicated to non-identical fractional-order chaotic systems characterized by different dimensions. The proposed control parameters are nonlinear in nature. In order to ensure that the proposed scheme converge towards zero, we establish the asymptotic stability of the zero solution to the error system by means of the stability of linear fractional-order systems. In order to assess the
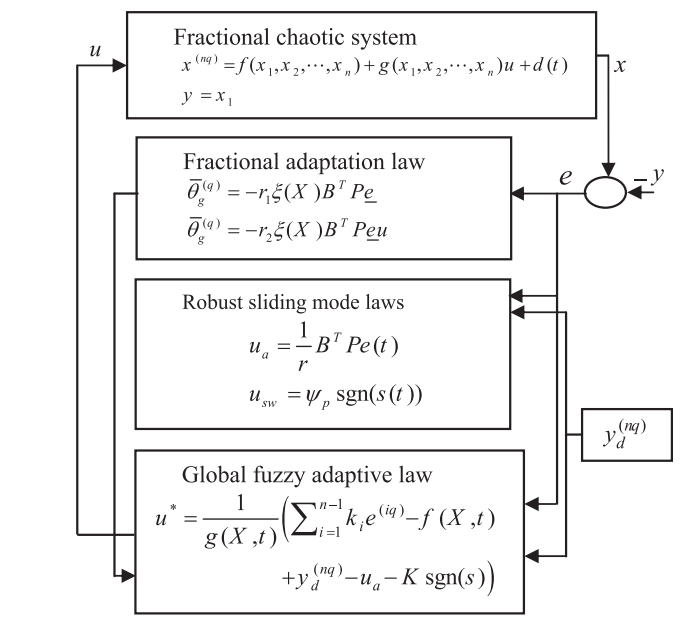
Enhanced Fractional Order Indirect Fuzzy Adaptive Synchronization of Uncertain Fractional Chaotic Systems Based on the Variable Structure Control : Robust H ∞ Design Approach
This work presents a novel fractional H8 robust indirect adaptive fuzzy logic control strategy based on the variable structure control theory design (FRAFC-VSC) to synchronize two fractional-order chaotic systems. The contribution of this work is the use of an adaptive fractional order PI-regulator and a saturation function to eliminate the chattering phenomena in the control and surface signals. Stability analysis is performed for the proposed method with an acceptable synchronization error level based on Lyapunov stability criterion. The synchronization of two different fractional order
Private communications method based on chua's chaotic system
In this paper a simple private communications system is proposed based on Chua's chaotic system. The system mainly consists of two synchronized chaotic circuits, the system encodes values to a message function according to the state of synchronization between the two circuits. Numerical simulations were carried out to prove the validity of the system, and spice simulations were carried out on the proposed physical system. © 2019 IEEE.
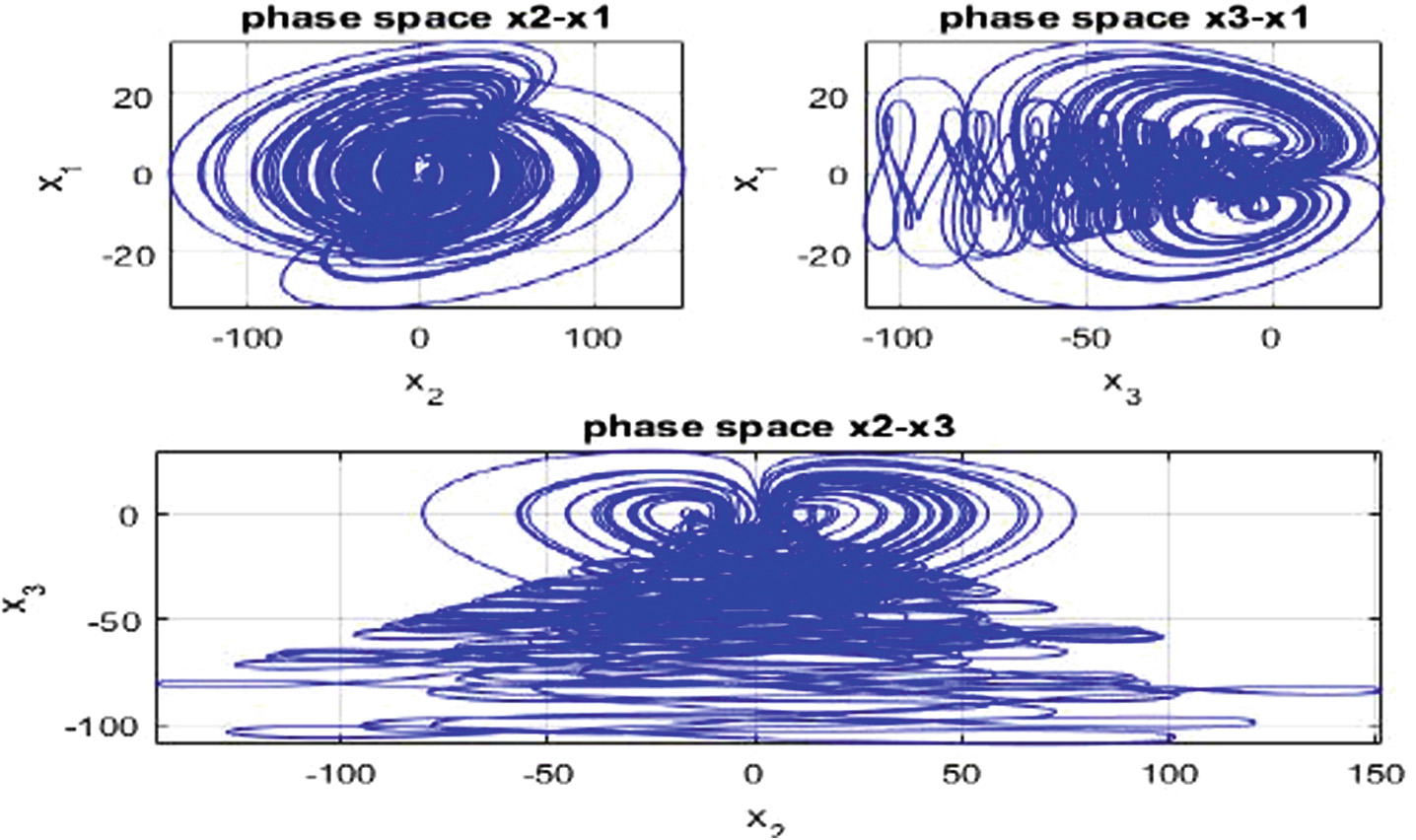
A New Control Scheme for Hybrid Chaos Synchronization
This paper presents a new hybrid chaos synchronization scheme, which assures the co-existence of the full-state hybrid function projective synchronization (FSHFPS) and the inverse full-state hybrid function projective synchronization (IFSHFPS) between wide classes of three-dimensional master systems and four-dimensional slave systems. In order to show the capability of co-existence approach, numerical example is reported, which illustrates the co-existence of FSHFPS and IFSHFPS between 3D chaotic system and 4D hyperchaotic system in different dimensions. © Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2019.
A new hyperchaotic temperature fluctuations model, its circuit simulation, FPGA implementation and an application to image encryption
In this paper, we propose a new hyperchaotic temperature fluctuations model and describe its modelling in detail. We study the characteristics of the new hyperchaotic temperature fluctuations model such as its phase portraits, rest points, symmetry, invariance, Lyapunov characteristic exponents, bifurcation analysis, etc. In fact, it is shown that the new temperature fluctuations model has a self-excited, two-scroll, hyperchaotic attractor with complex properties. The circuit simulation of the new temperature fluctuations model is carried out in MultiSim to verify the feasibility of the
Frequency survey simulation for developing novel radio frequency energy harvesting model
Renewable Energy sources are the center of attraction for research and development all over the world nowadays, the demand of a lasting cheap source of energy that is environmental friendly, is the main challenge recently. Energy Harvesting is a new technology that is going to make a revolution in the coming decade. Energy Harvesting is a technique to provide alternative sources of energy that are environmental friendly and low in cost. Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting is one of the methods to provide electrical energy from the ambient Radio Frequency waves that already exists in the
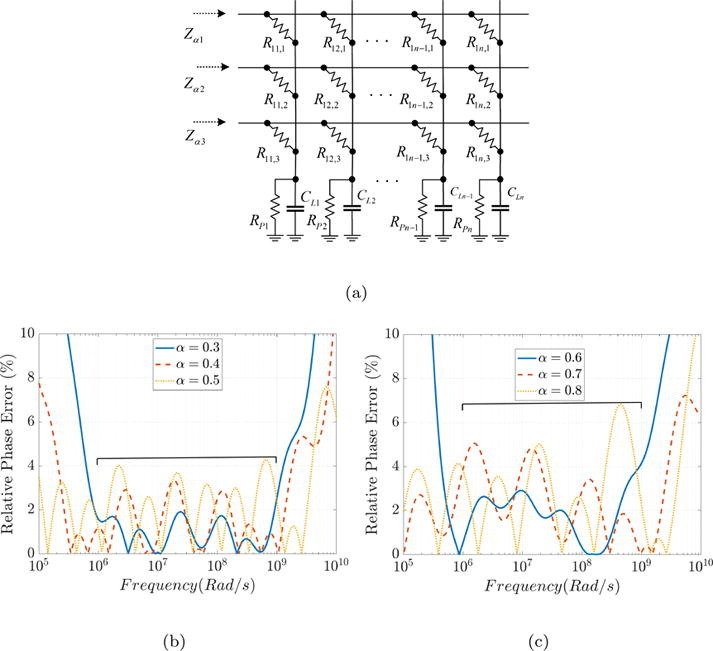
Programmable constant phase element realization with crossbar arrays
Introduction: Constant Phase Elements (CPEs) have been widely used in many applications due to the extra degree of freedom, which offers new responses and behaviors. Objectives: This paper proposes a new programmable CPE realization using resistive crossbar arrays. By programming the resistive devices, different CPEs can be obtained. Methods: The proposed realization can be approximated as a weighted sum of low and high pass filters having the same cut-off frequency (i.e., Lapicque model). The closed-form approximation expression is derived, and then the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA) is
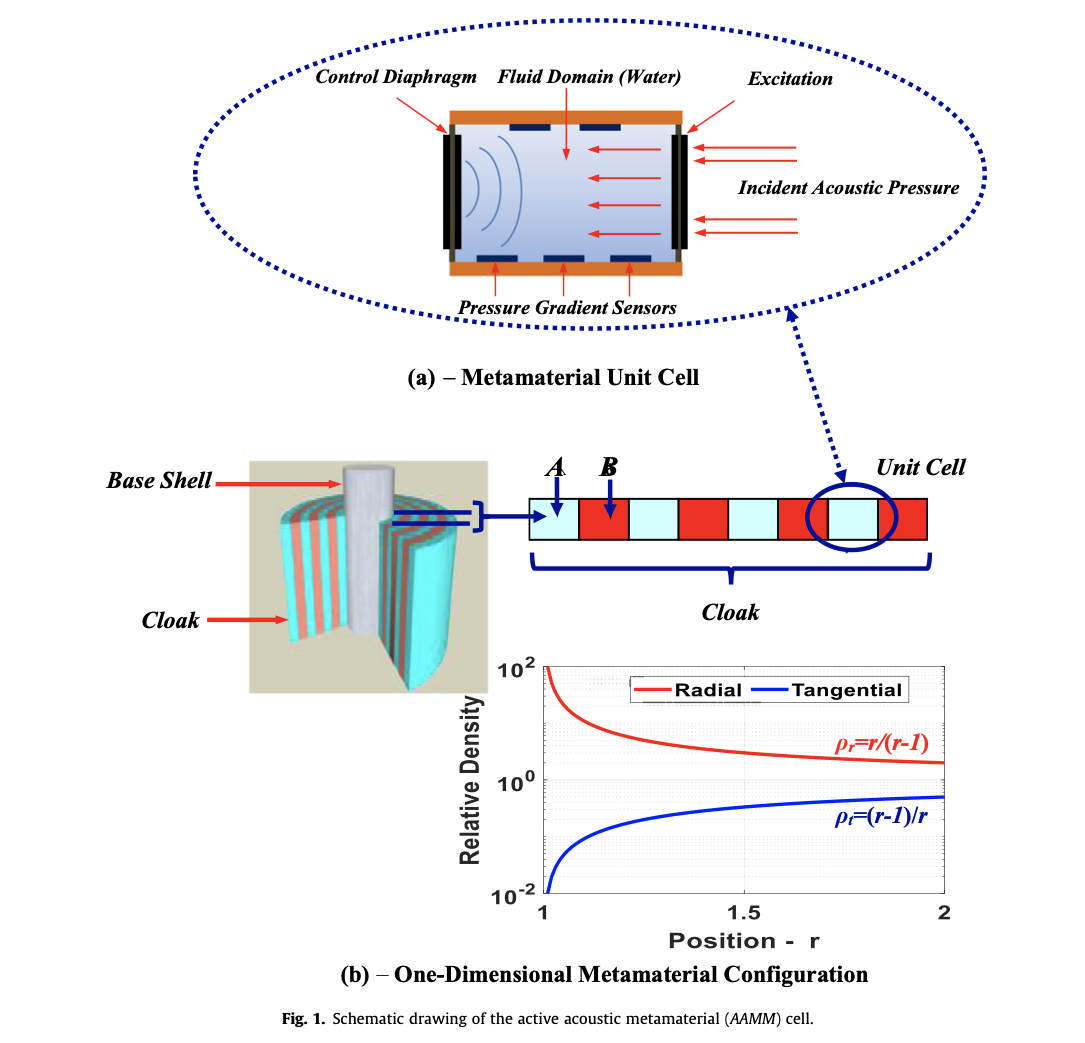
Active control of the dynamic density of acoustic metamaterials
All attempts to develop acoustic metamaterials with prescribed characteristics are based on utilizing the concepts of resonance frequencies of the metamaterial cell structure or on the spatial arrangement of two-or multi-phase domains to realize density or bulk modulus values on the micro scale that influence the wave propagation on the macro scale. In here, a radically different concept is presented whereby active acoustic metamaterial cell has been developed to manipulate the incompressible material dynamic density and reach relative stable values of 0.35–13 times the original fluid domain
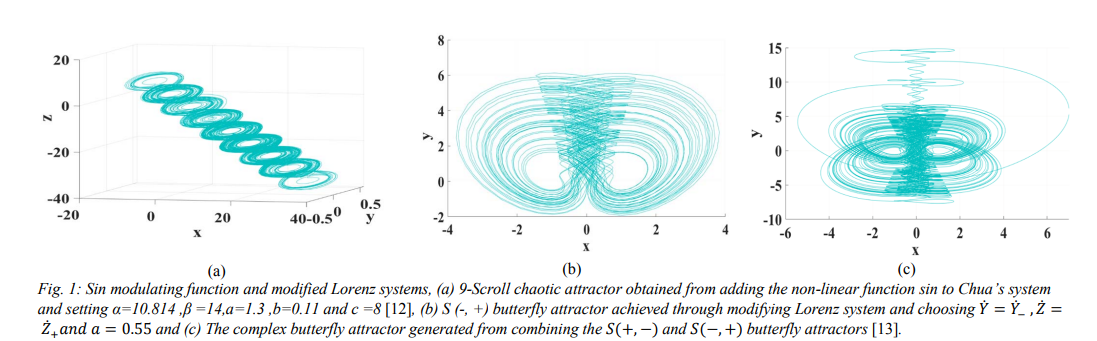
Generalized Formula for Generating N-Scroll Chaotic Attractors
The generation of Multi-scroll chaotic attractors and chaos theory has gained much attention due to its many usages in a wide range of applications such as image-encryption and random number generators. There have been many previous attempts to establish a system that is able to generate large numbers of n - scroll chaotic attractors by modifying existing systems such as Lorenz and Chua's systems. In this paper, a proposed system based on generalizing Chua's system that has shown its ability to produce an unprecedentedly large number of even and odd chaotic scrolls is introduced. MATLAB
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 54
- Next page ››
