Indoor localization and movement prediction algorithms with light-fidelity
Indoor localization has recently attended an increase in interest due to the potential for a wide range of services. In this paper, indoor high-precision positioning and motion prediction algorithms are proposed by using light fidelity (LI-FI) system with angular diversity receiver (ADR). The positioning algorithm uses to estimate the location of an object in the room. Furthermore, the prediction algorithm applies to predict the motion of that object. The simulation results show that the average root mean squares error of the positioning algorithm is about 0.6 cm, and the standard deviation
Asymmetrical clipping optical filter bank multi-carrier modulation scheme
Filter bank multi-carrier (FBMC) is considered a promising alternative to the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) scheme. It improves spectral efficiency by eliminating the need for cyclic prefix while attenuating interference due to the robustness of the out-of-band emission. In this work, we present a framework, and the performance evaluation of FBMC is a multi-carrier modulation scheme for the direct detection of optical communications. As the proposed model has higher spectral efficiency than the classical ACO-OFDM, as removing the guard interval enhances the spectral
Improved spectrum mobility using virtual reservation in collaborative cognitive radio networks
Cognitive radio technology would enable a set of secondary users (SU) to opportunistically use the spectrum licensed to a primary user (PU). On the appearance of this PU on a specific frequency band, any SU occupying this band should free it for PUs. Typically, SUs may collaborate to reduce the impact of cognitive users on the primary network and to improve the performance of the SUs. In this paper, we propose and analyze the performance of virtual reservation in collaborative cognitive networks. Virtual reservation is a novel link maintenance strategy that aims to maximize the throughput of
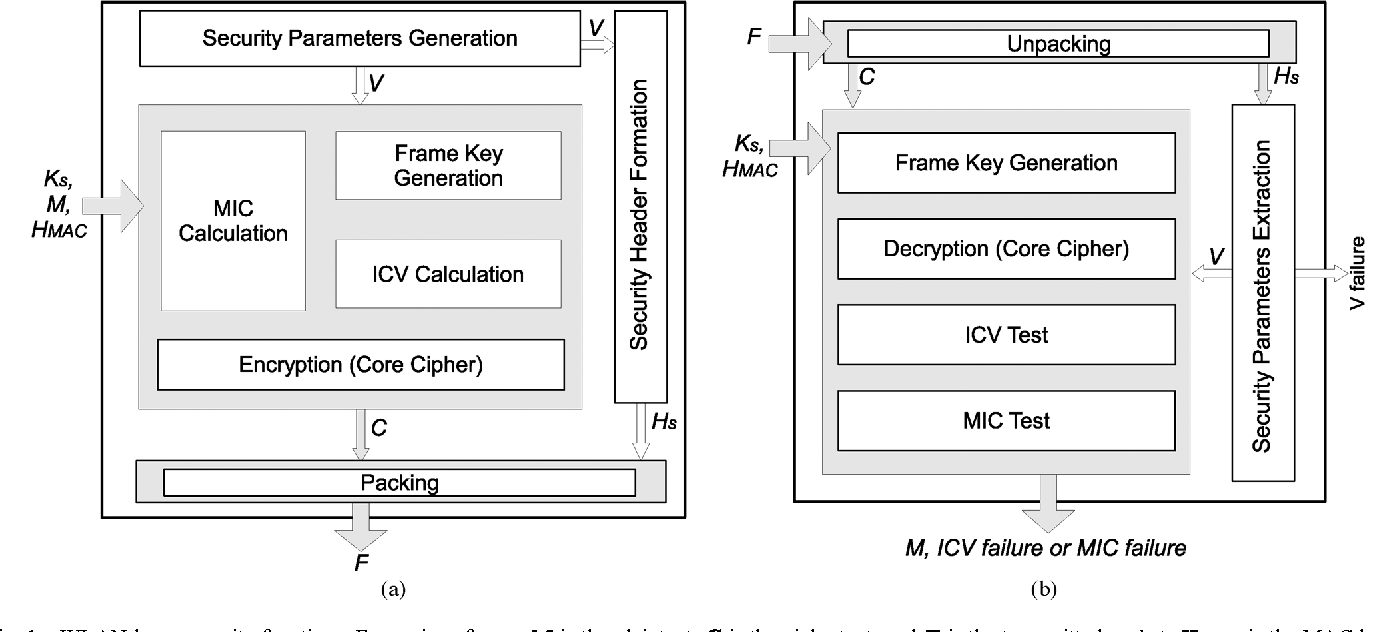
Keys through ARQ: Theory and practice
This paper develops a novel framework for sharing secret keys using the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) protocol. We first characterize the underlying information theoretic limits, under different assumptions on the channel spatial and temporal correlation function. Our analysis reveals a novel role of dumb antennas in overcoming the negative impact of spatial correlation on the achievable secrecy rates. We further develop an adaptive rate allocation policy, which achieves higher secrecy rates in temporally correlated channels, and explicit constructions for ARQ secrecy coding that enjoy low

Multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT)
In this paper we study the problem of tag identification in multi-reader RFID systems. In particular, we propose a novel solution to the reader-to-reader collisions and tag collisions in multi-reader systems, using the concept of bit tracking [1]. Towards this objective, we propose the multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT) algorithm which allows concurrent tag identification, by neighboring RFID readers, as opposed to time-consuming scheduling. First, MRTI-BT identifies tags exclusive to different RFIDs, concurrently. Second, the concept of bit tracking and the
Towards evolving sensor actor networks
Sensor Actor NETworks (SANET) represent a major component of ubiquitous service environments promising interesting solutions to a wide range of problems. Despite the obvious increase in the research activities proposing architectures and protocols for SANETs, we are still no where near the production of industrial-grade SANET software that can be relied upon for mission critical applications. The cost of programming, deploying and maintaining SANET environments is still highly prohibitive due to the lack of industrial tools capable of realizing adaptive SANET software in a cost effective way
Hierarchical proactive caching for vehicular ad hoc networks
Recently, emerging vehicular applications are increasing the demand of vehicles which form significant burdens on network backhaul and represents a cause to the quality of experience (QoE) decay of the vehicular users. Proactive caching is a promising technique to mitigate the load on core networks by caching some of the expected data items. This work proposes a hierarchical proactive caching scheme which jointly considers caching in vehicles and roadside units (RSUs). Minimization of the vehicle communication latency is the main objective of our study. The optimization problem is formulated
Transmission power adaptation for cognitive radios
In cognitive radio (CR) networks, determining the optimal transmission power for the secondary users (SU) is crucial to achieving the goal of maximizing the secondary throughput while protecting the primary users (PU) from service disruption and interference. In this paper, we propose an adaptive transmission power scheme for cognitive terminals opportunistically accessing a primary channel. The PU operates over the channel in an unslotted manner switching activity at random times. The secondary transmitter (STx) adapts its transmission power according to its belief regarding the PU's state of
AROMA: Automatic generation of radio maps for localization systems
Current methods for building radio maps for wireless localization systems require a tedious, manual and error-prone calibration of the area of interest. Each time the layout of the environment is changed or different hardware is used, the whole process of location fingerprinting and constructing the radio map has to be repeated. The process gets more complicated in the case of localizing multiple entities in a device-free scenario, since the radio map needs to take all possible combinations of the location of the entities into account. In this demo, we present a novel system (AROMA) that is
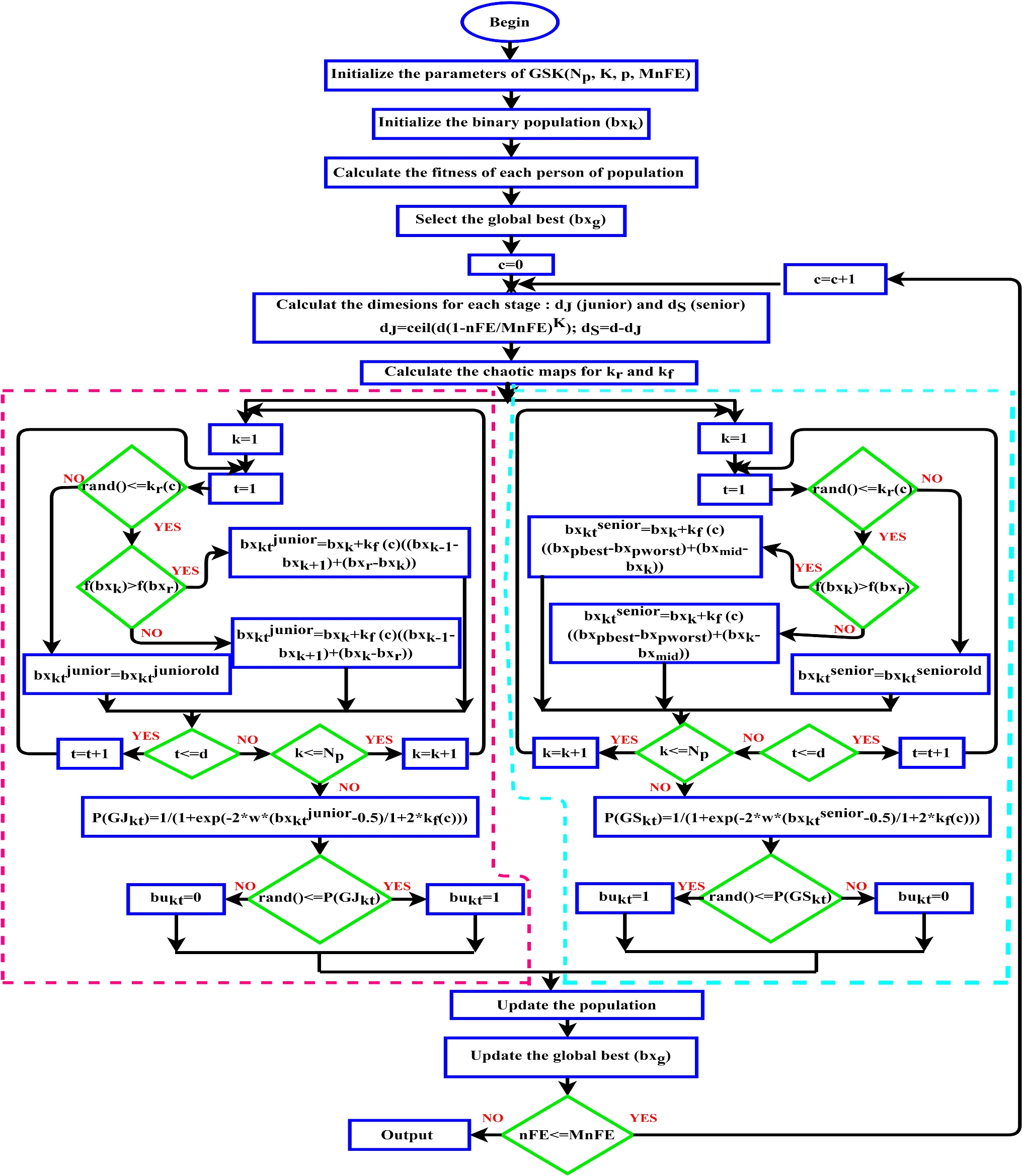
Chaotic gaining sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm: an improved metaheuristic algorithm for feature selection
The gaining sharing knowledge based optimization algorithm (GSK) is recently developed metaheuristic algorithm, which is based on how humans acquire and share knowledge during their life-time. This paper investigates a modified version of the GSK algorithm to find the best feature subsets. Firstly, it represents a binary variant of GSK algorithm by employing a probability estimation operator (Bi-GSK) on the two main pillars of GSK algorithm. And then, the chaotic maps are used to enhance the performance of the proposed algorithm. Ten different types of chaotic maps are considered to adapt the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 43
- Next page ››
