New Control Schemes for Fractional Chaos Synchronization
Chaos theory deals with the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. Chaotic systems are characterized by the property that small changes in the initial conditions result in widely diverging responses. In this paper, new control schemes of synchronization for different arbitrary incommensurate and commensurate fractional order chaotic systems are presented. Synchronization stability, based on stability of linear fractional-order systems and fractional Lyapunov stability, is proved theoretically. Numerical examples are given to show the effectiveness of the
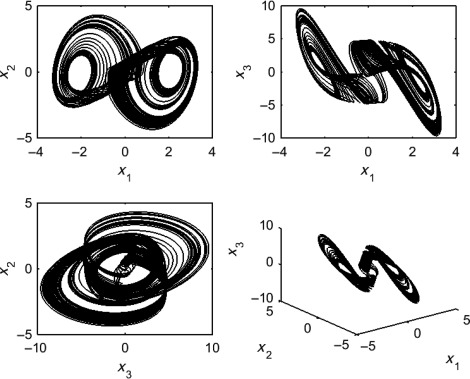
Multiswitching synchronization of commensurate fractional order hyperchaotic systems via active control
In this chapter, the multiswitching synchronization scheme has been investigated for a class of nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems. The multiswitching complete synchronization scheme has been examined such that the state variables of the slave system synchronize with different state variables of the master system. For the synchronization of two nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems suitable controllers have been designed using active control technique. The stability of fractional order chaotic systems has been used to stabilize the error dynamical system. Two
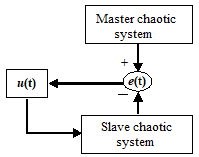
Multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems
This paper investigates the multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems in which state variables of a master system are synchronized with different state variables of a slave system using the sliding mode control technique. To design the appropriate controllers via sliding mode control for different switches, Lyapunov stability theory is taken into account. Theoretical results are applied by considering two non-identical chaotic systems where one is considered as master system and another is considered as slave system. Numerical simulations are performed to
Cole-Cole Bio-Impedance Parameters Extraction from a Single Time-Domain Measurement
We show that the four parameters of a single-dispersion Cole-Cole bio-impedance model can be extracted from an one time-domain measurement with a fixed frequency. In particular, a periodic triangle waveform current excitation signal is injected into the biological sample under study while measuring the voltage developed across this sample in a galvanostatic measurement setup. The voltage response due to this triangle-wave excitation is firstly analytically derived in closed form. After that the Flower Pollination optimization Algorithm (FPA) is applied to extract the unknown model parameters
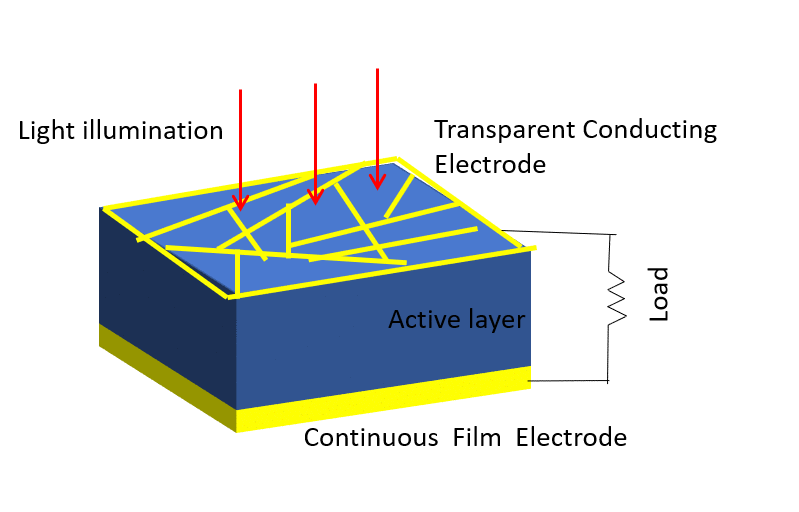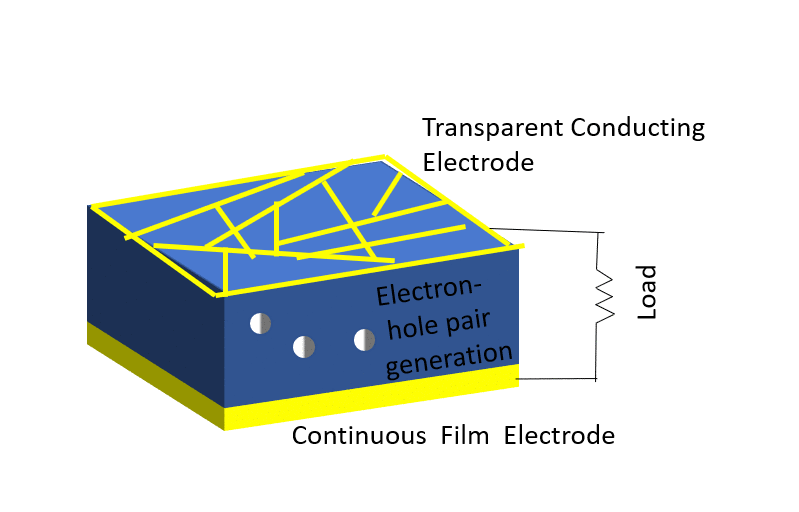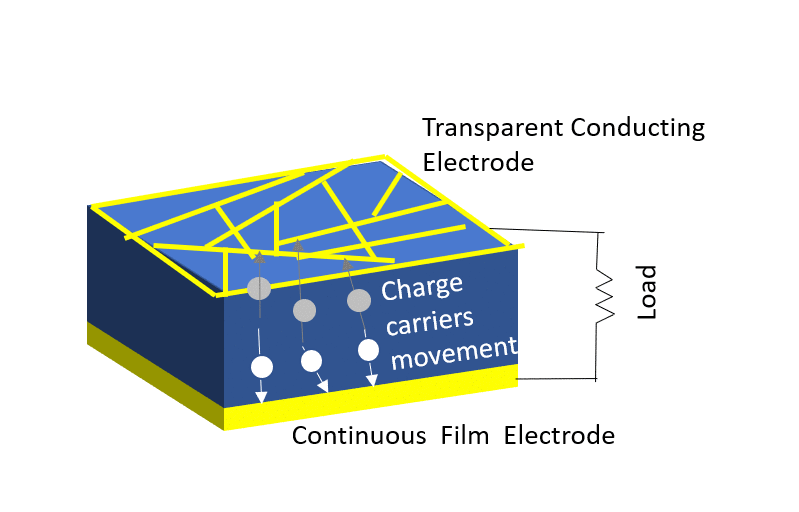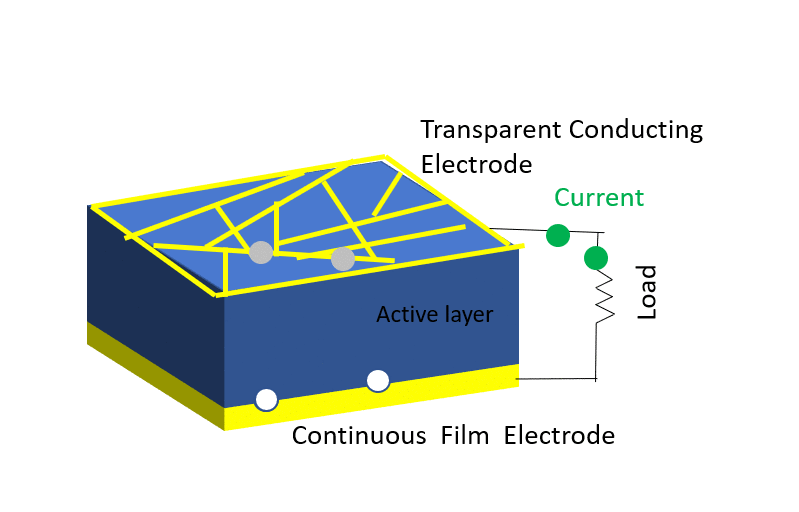
Investigation of properties limiting efficiency in Cu2ZnSnSe4-based solar cells
We have investigated different nonidealities in Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cells with 9.7% conversion efficiency, in order to determine what is limiting the efficiency of these devices. Several nonidealities could be observed. A barrier of about 300 meV is present for electron flow at the absorber-buffer heterojunction leading to a strong crossover behavior between dark and illuminated current-voltage curves. In addition, a barrier of about 130 meV is present at the Mo-absorber contact, which could be reduced to 15 meV by inclusion of a TiN interlayer. Admittance spectroscopy results on the
Replay attack on lightweight CAN authentication protocol
Day after day, users' expectations of tomorrow vehicles' features are increasing. Although the industry's prime goal is users' satisfaction, many unsolved problems are still present. Amongst the major challenges are the huge interconnections and dependability within the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) used inside vehicles. Five years ago, the number of ECUs within a vehicle was about 70 ECUs. This number has doubled nowadays, and it is expected to double again in the near future. This adds challenges to both of network management and network security. The purpose of this paper is to enhance the
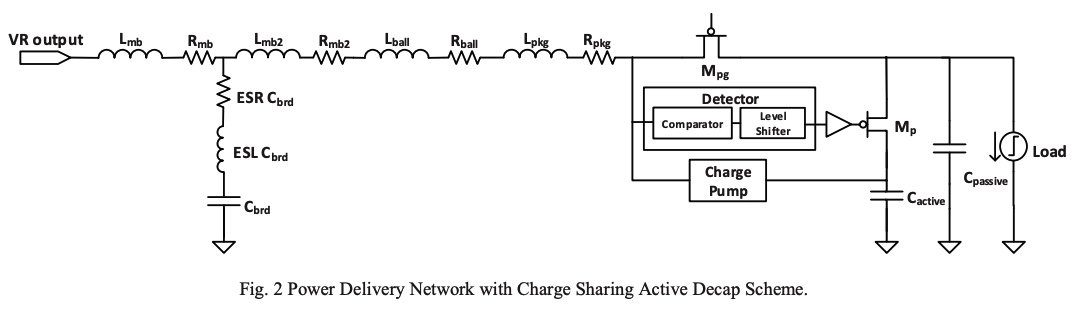
A fully integrated charge sharing active decap scheme for power supply noise suppression
Power supply noise has become a major challenge for proper operation of circuits with continuous scaling of CMOS technology along with supply voltage scaling. Conventional passive decoupling capacitors exhibit significant die area penalty resulting in a limited regulation effect. This paper presents a fully integrated charge-sharing-based active decap scheme for power supply noise suppression. The proposed idea is based on allocating a portion of the available passive decap to be used as an active decap that is charged up to a higher voltage and shares its boosted charge with the noisy rail
Comparative Study of Two Level and Three Level PWM-Rectifier with Voltage Oriented Control
This article presents performance evaluation and comparison between Voltage Oriented Control (VOC) methods for PWM-rectifiers, two levels and three levels, in order to demonstrate the great advantages of using a three-level Neutral Point Clamped (NPC). The control of the DC bus voltage is carried out using the PI controller. The effectiveness of this approach is illustrated by simulation results using MATLAB/Simulink. © Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2019.
Architectures and Challenges Towards Software Defined Cloud of Things (SDCoT)
Last decade witnessed a growth on developing of IoT architecture models to cope with various challenges and domains requirements. This leads to rapid increasing the number of the connected devices, which means large amount of data are needed to be stored and processed. Form this context, Cloud Computing is emerged as a solution to enable centrally unlimited storage of data and programs with the ability to access anytime from anywhere. The integration between IoT and cloud brings the concept of Cloud of Things (CoT) to support different types of data and multiple services with data ubiquity
Fractional chaos maps with flower pollination algorithm for chaotic systems’ parameters identification
Meta-heuristic optimization algorithms are the new gate in solving most of the complicated nonlinear systems. So, improving their robustness, reliability, and convergence speed is the main target to meet the requirements of various optimization problems. In the current work, three different fractional-order chaos maps (FC-maps), which have been introduced recently, are incorporated with the fundamental flower pollination algorithm to tune its parameters adaptively. These maps are fractional logistic map, fractional sine map, fractional tent map, and their integer-order versions. As a result
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 28
- Next page ››
