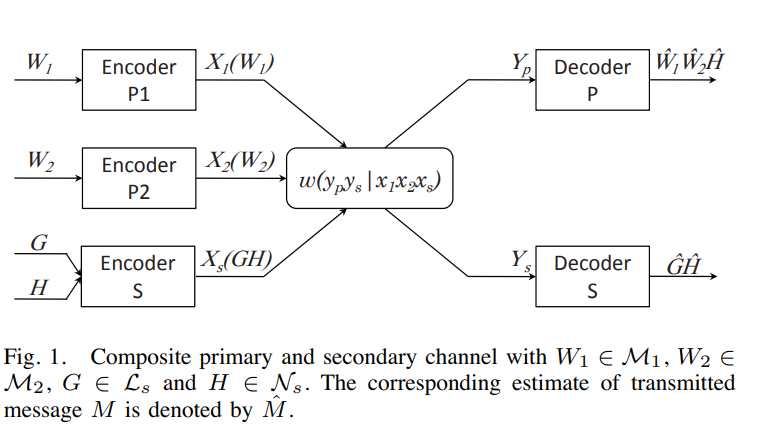
An achievable rate region for a primary network shared by a secondary link
We consider a multiple access primary network with N transmitters. A secondary link of one transmitter and a corresponding receiver causes interference to the primary network. An achievable rate region for the primary network and the secondary link is obtained given the following mode of operation. The secondary transmitter employs rate-splitting so that the primary receiver can decode part of the secondary's signal and cancel it. The secondary receiver, on the other hand, treats primary interference as noise. Given a Gaussian channel model, we investigate the effect of rate-splitting on the
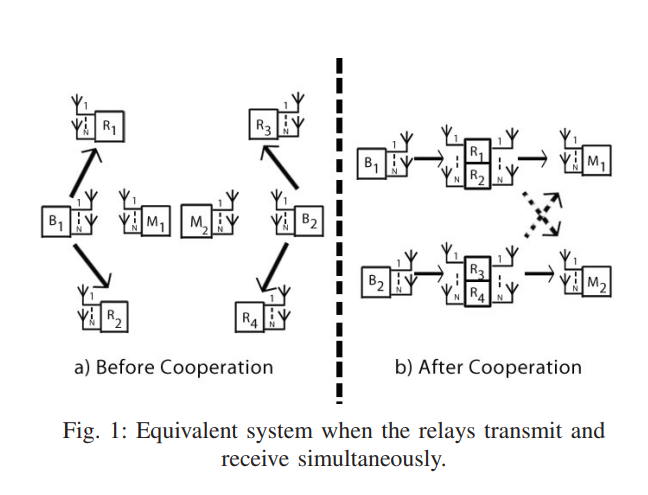
Alternate relaying and the degrees of freedom of one-way cellular relay networks
In this paper, a cellular relaying network consisting of two source-destination pairs, and four decode-and-forward relays operating in half-duplex mode is considered. Each source is assisted by two relays and all nodes are equipped with N antennas. In order to compensate for the loss of capacity by a factor of half due to the half-duplex mode, an alternate transmission protocol among the two relays is proposed. An outer bound on the degrees of freedom (DoF) of this system is developed. A constructive proof of achievability based on two different schemes is provided. Aligning the inter-relay
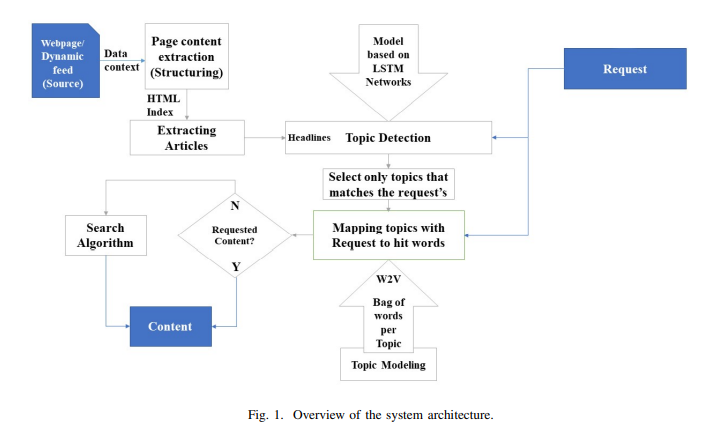
Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learning
Information extraction and reasoning from massive high-dimensional data at dynamic contexts, is very demanding and yet is very hard to obtain in real-time basis. However, such process capability and efficiency might be affected and limited by the available computational resources and the consequent power consumption. Conventional search mechanisms are often incapable of real-time fetching a predefined content from data source, without concerning the increased number of connected devices that contribute to the same source. In this work, we propose and present a concept for an efficient approach
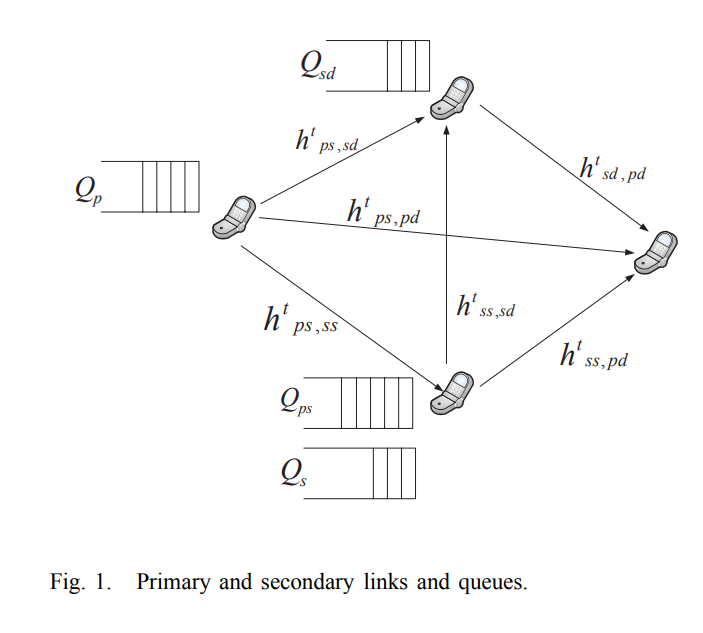
Transmit and receive cooperative cognition: Protocol design and stability analysis
In this paper, we investigate the stability of a cooperative cognitive system. We propose a cooperative secondary transmitter-receiver system (CSTR), where, the secondary transmitter (ST) and the secondary receiver (SR) increase the spectrum availability for the ST packets by relaying the unsuccessfully transmitted packets of the primary transmitter (PT). We assume receiving nodes with multipacket reception capability (MPR). We provide two inner bounds and two outer bounds on the stability region of the considered system. © 2013 ICST - The Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics
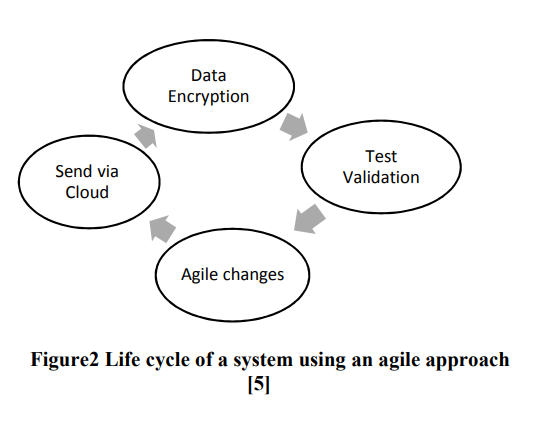
IoT Agile Framework Enhancement
Internet of Things (IoT) is considered as a trend nowadays. Devices connected to the internet interact with surrounding; this poses strong challenges in handling big data with a certain level of security. In this paper IoT devices will be divided in to two categories high vulnerability devices and low vulnerability devices. The classification depends on the ease of attacks. In order to ensure the security of IoT devices, an agile approach is used to secure high vulnerability devices as first step and then low vulnerability devices by applying encryption algorithms. © 2018 IEEE.
Differential Evolution Mutations: Taxonomy, Comparison and Convergence Analysis
During last two decades, Differential Evolution (DE) proved to be one of the most popular and successful evolutionary algorithms for solving global optimization problems over continuous space. Proposing new mutation strategies to improve the optimization performance of (DE) is considered a significant research study. In DE, mutation operation plays a vital role in the performance of the algorithm. Therefore, in this paper, comprehensive analysis of the contributions on basic and novel mutation strategies that were proposed between 1995 and 2020 is presented. A new taxonomy based on the
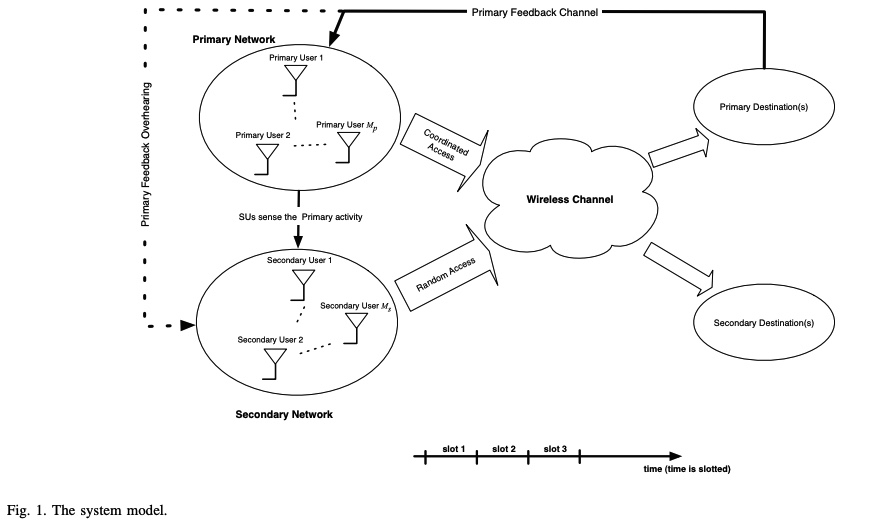
A feedback-soft sensing-based access scheme for cognitive radio networks
In this paper, we examine a cognitive spectrum access scheme in which secondary users exploit the primary feedback information. We consider an overlay secondary network employing a random access scheme in which secondary users access the channel by certain access probabilities that are functions of the spectrum sensing metric. In setting our problem, we assume that secondary users can eavesdrop on the primary link's feedback. We study the cognitive radio network from a queuing theory point of view. Access probabilities are determined by solving a secondary throughput maximization problem
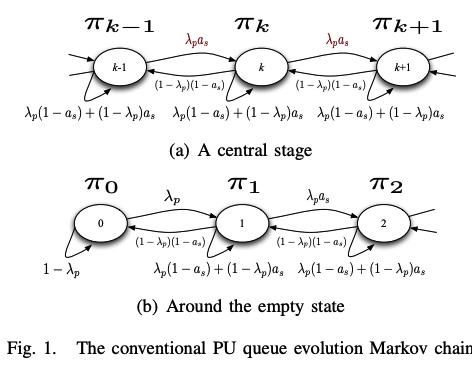
A feedback-based access scheme for cognitive radio systems
In this paper, we consider the design of access schemes for secondary users in cognitive radio systems based on the primary user feedback information. We consider a secondary user employing a random access scheme with an access probability that depends on the primary user feedback state. We show that the proposed scheme can enhance the system performance in terms of the secondary throughput and/or primary user delay while guaranteeing a certain quality of service (QoS) for the primary user; this is due to the fact that the proposed scheme avoids sure collisions between the primary and
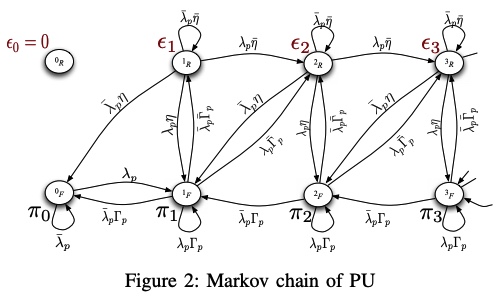
A feedback-based access scheme for cognitive-relaying networks
In this paper, we consider a cognitive relaying network in which the secondary user accesses the channel with a certain access probability that depends on the feedback information sent by the primary destination. In addition, the secondary user is granted relaying capabilities by which it can relay primary traffic that was unsuccessfully transmitted by the primary user. We show that this proposed scheme enhances the performance of the secondary user as well as the primary user, while the QoS requirements of the primary user is unviolated. The secondary user can avoid sure collisions with the
Full-duplex cooperative cognitive radio networks
In this paper, we study the impact of a full-duplex secondary node on a cognitive cooperative network with Multipacket Reception (MPR) capabilities at the receivers. Motivated by recent schemes that make full-duplex communication feasible, we study a model with one primary and one secondary transmitter-receiver pair, where the secondary transmitter is able to relay primary unsuccessful packets. Cooperation between primary and secondary users has been previously shown to be beneficial for the primary and the secondary users in terms of stable throughput. Our model assumes an imperfect full
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 16
- Next page ››
