
Accurate analysis of cardiac tagged MRI using combined HARP and optical flow tracking
In this work, we present a new method for analyzing cardiac tagged Magnetic Resonance Imaging (tMRI). The method combines two major tracking techniques: Harmonic Phase (HARP) and Optical Flow (OF). The results of the two techniques are fused together to accurately estimate the displacement of each myocardium point. The developed methods were tested using numerical MRI phantom at different SNR levels and deformation rates. The results show that the proposed method is more accurate and reliable than the HARP and the OF methods. © 2012 IEEE.
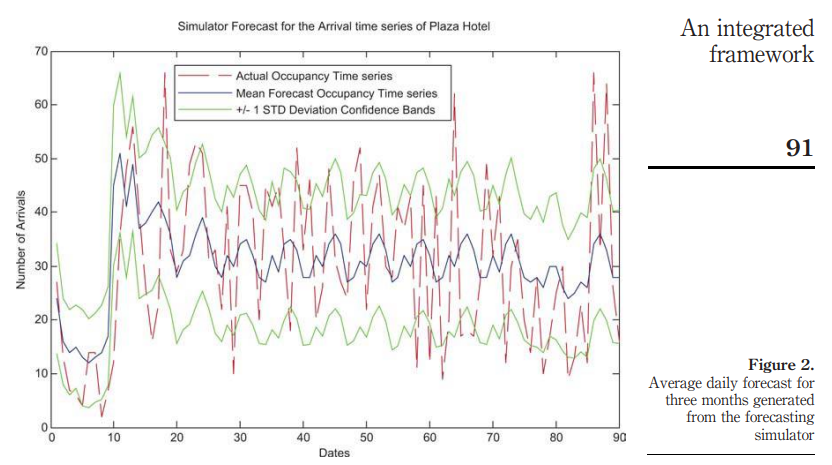
An integrated framework for advanced hotel revenue management
Purpose: This paper aims to present an integrated framework for hotel revenue room maximization. The revenue management (RM) model presented in this work treats the shortcomings in existing systems. In particular, it extends existing optimization techniques for hotel revenue management to address group reservations and uses "forecasted demand" arrivals generated from the real data. Design/methodology/approach: The proposed forecasting module attempts to model the hotel reservation process from first principles. In particular, it models hotel arrivals as an interrelated process of stochastic
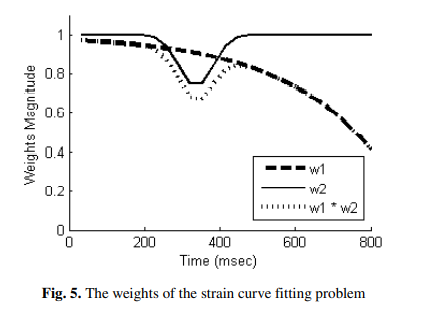
Correction of left ventricle strain signals estimated from tagged MR images
Strain measurement is a quantity used for assessing the regional function of the left ventricular (LV) of the heart. They are computed by tracking the motion of the non-invasive, virtual tags in the cardiac muscle with time. Tracking these tags gives information for each region of the cardiac muscle by quantifying its deformation during contraction (systolic period) and relaxation (diastolic period). However, these strain measurements suffer from inaccuracies caused by the degradation of the tags and the image quality. In this work, numerical simulations are used to investigate the factors
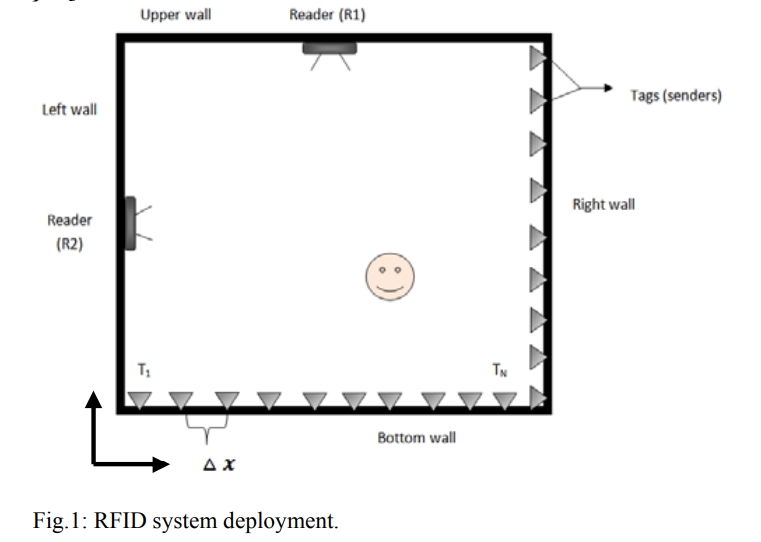
RFID-based indoors localization of tag-less objects
Object localization has become a necessary module in many radiofrequency identification (RFID) systems that require tracking features besides the conventional identification feature. A number of techniques exists in literature that uses the RFID signal information to locate the tagged objects, i.e. objects wearing RFID tags. Nevertheless, in many applications, it is required to track objects that do not carry a tag (whether intentionally or unintentionally). In this work, we propose a technique for tag-less object localization. The technique is based on reconstructing the attenuation map of

Machine learning methodologies in P300 speller brain-computer interface systems
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a one kind of communication system that enables control of devices or communication with others only through brain signal activities without using motor activities. P300 Speller is a BCI paradigm that helps disabled subjects to spell words by means of their brain signal activities. This paper tries to demonstrate the performance of different machine learning algorithms based on classification accuracy. Performance has been evaluated on the data sets acquired using BC12000's P300 Speller Paradigm provided by BCI competitions II (2003) & III (2004) organizers
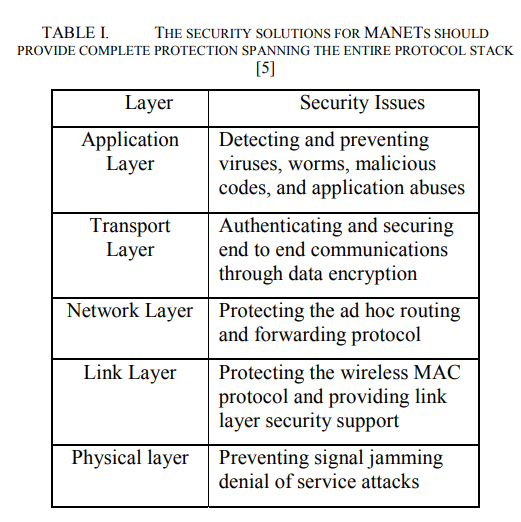
Security in Ad hoc networks: From vulnerability to risk management
Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) have lots of applications. Due to the features of open medium, absence of infrastructure, dynamic changing network topology, cooperative algorithms, lack of centralized monitoring and management point, resource constraints and lack of a clear line of defense, these networks are vulnerable to attacks. A vital problem that must be solved in order to realize these applications is that concerning the security aspects of such networks. Solving these problems combined with the widespread availability of devices such as PDAs, laptops, small fixtures on buildings and

Fuzzy gaussian process classification model
Soft labels allow a pattern to belong to multiple classes with different degrees. In many real world applications the association of a pattern to multiple classes is more realistic; to describe overlap and uncertainties in class belongingness. The objective of this work is to develop a fuzzy Gaussian process model for classification of soft labeled data. Gaussian process models have gained popularity in the recent years in classification and regression problems and are example of a flexible, probabilistic, non-parametric model with uncertainty predictions. Here we derive a fuzzy Gaussian model
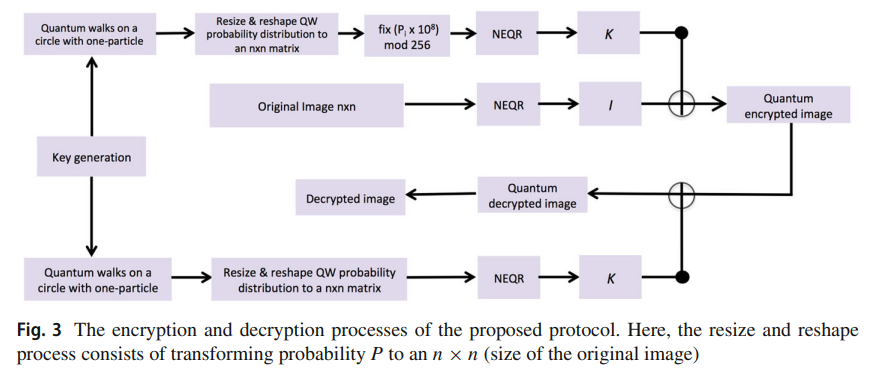
An encryption protocol for NEQR images based on one-particle quantum walks on a circle
Quantum walks are generalizations of random walks that have extensive applications in various fields including cryptography, quantum algorithms, and quantum networking. Discrete quantum walks can be seen as nonlinear mappings between quantum states and position probability distributions, and this mathematical property may be thought of as an imprint of chaotic behavior and consequently used to generate encryption keys. In this paper, we introduce encryption and decryption algorithms for NEQR images based on discrete quantum walks on a circle. We present full quantum circuits of proposed

Modeling intrastromal photorefractive keratectomy procedures
The main idea to correct sight disorders using lasers is to modify corneal curvature by applying laser to specific layers of the cornea. Intrastromal Photorefractive keratectomy is a laser technique used to correct sight disorders by evaporating corneal tissue, which results in small cavities that may coincide to form a larger cavity that will collapse to deform the curvature of the cornea. In this work, a 3D finite element model of the cornea was designed with typical parameters to simulate the procedure. The model outcome was compared with an earlier 2D model used for the same purpose, so as

Machine learning methodologies in Brain-Computer Interface systems
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a one kind of communication system that enables control of devices or communication with others only through brain signal activities without using motor activities. The main application for BCI is to provide an alternative channel for helping disabled persons, hereafter mentioned as subjects, to communicate with the external world. This paper tries to demonstrate the performance of different machine learning algorithms based on classification accuracy. Performance has been evaluated on dataset II from BCI Competition III for the year 2004 for two subjects 'A'
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 34
- Next page ››
