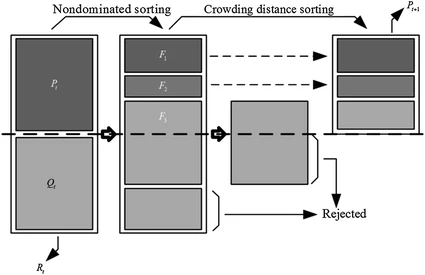
Chaotic system modelling using a neural network with optimized structure
In this work, the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to model a chaotic system. A method based on the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is used to determine the best parameters of a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network. Using NSGA-II, the optimal connection weights between the input layer and the hidden layer are obtained. Using NSGA-II, the connection weights between the hidden layer and the output layer are also obtained. This ensures the necessary learning to the neural network. The optimized functions by NSGA-II are the number of neurons in the

Chaotic system modelling using a neural network with optimized structure
In this work, the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to model a chaotic system. A method based on the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is used to determine the best parameters of a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network. Using NSGA-II, the optimal connection weights between the input layer and the hidden layer are obtained. Using NSGA-II, the connection weights between the hidden layer and the output layer are also obtained. This ensures the necessary learning to the neural network. The optimized functions by NSGA-II are the number of neurons in the
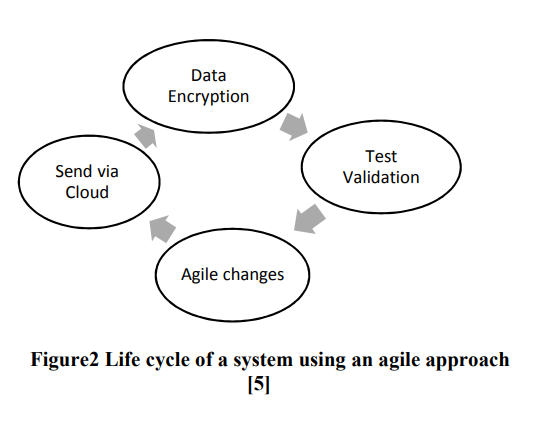
IoT Agile Framework Enhancement
Internet of Things (IoT) is considered as a trend nowadays. Devices connected to the internet interact with surrounding; this poses strong challenges in handling big data with a certain level of security. In this paper IoT devices will be divided in to two categories high vulnerability devices and low vulnerability devices. The classification depends on the ease of attacks. In order to ensure the security of IoT devices, an agile approach is used to secure high vulnerability devices as first step and then low vulnerability devices by applying encryption algorithms. © 2018 IEEE.
Control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators: A review
In this article, different control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators are presented with two distinguished classes of control strategies in the literature. These are the model-free control and the dynamic control strategy, which is mainly a model-based scheme, and is mostly the alternative when the control requirements are more stringent. The authors strongly believe that this paper will be helpful for researchers and engineers in the field of robotic systems. Copyright 2017 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
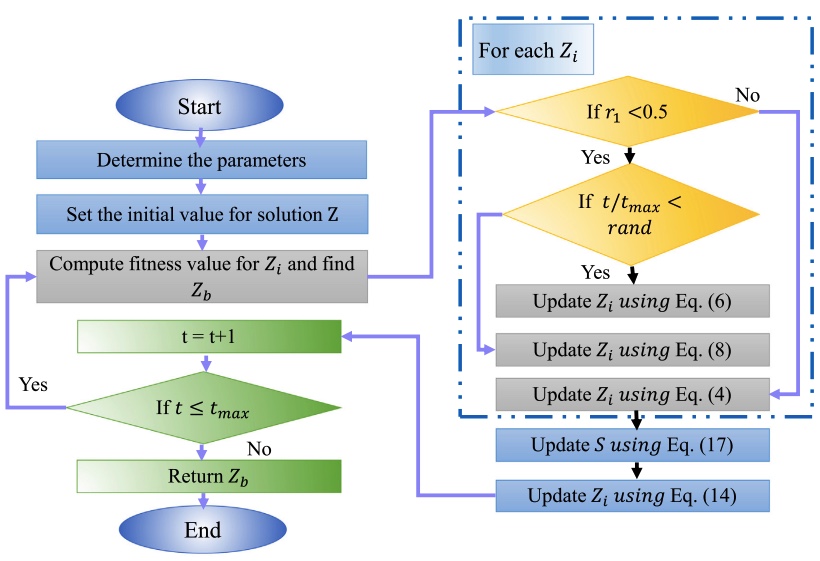
A Grunwald–Letnikov based Manta ray foraging optimizer for global optimization and image segmentation
This paper presents a modified version of Manta ray foraging optimizer (MRFO) algorithm to deal with global optimization and multilevel image segmentation problems. MRFO is a meta-heuristic technique that simulates the behaviors of manta rays to find the food. MRFO established its ability to find a suitable solution for a variant of optimization problems. However, by analyzing its behaviors during the optimization process, it is observed that its exploitation ability is less than exploration ability, which makes MRFO more sensitive to attractive to a local point. Therefore, we enhanced MRFO by
Gray Wolf Optimization of Fractional Order Control of 3-Omni Wheels Mobile Robot: Experimental Study
Committing robotics with artificial intelligence becomes mandatory collaboration with distinct environments. Omnidirectional Wheeled (Omni-WD) mobile robots are one of the robots that interact with humans in various circumstances, where it is important to function effectively and accurately. In this paper, the distinction of a 3WD-Omni model and control using machine vision is demonstrated. The use of fractional order (FO) calculus has been stated to increase the degrees of freedom of the controller over the integer ones. Hybridization of FO control and metaheuristics optimization is reported
Experimental Kinematic Modeling of 6-DOF Serial Manipulator Using Hybrid Deep Learning
According to its significance, robotics is always an area of interest for research and further development. While robots have varying types, design and sizes, the six degrees of freedom (DOF) serial manipulator is a famous robotic arm that has a vast areas of applications, not only in industrial application, but also in other fields such as medical and exploration applications. Accordingly, control and optimization of such robotic arm is crucial and needed. In this paper, different analyses are done on the chosen design of robotic arm. Forward kinematics are calculated and validated, then
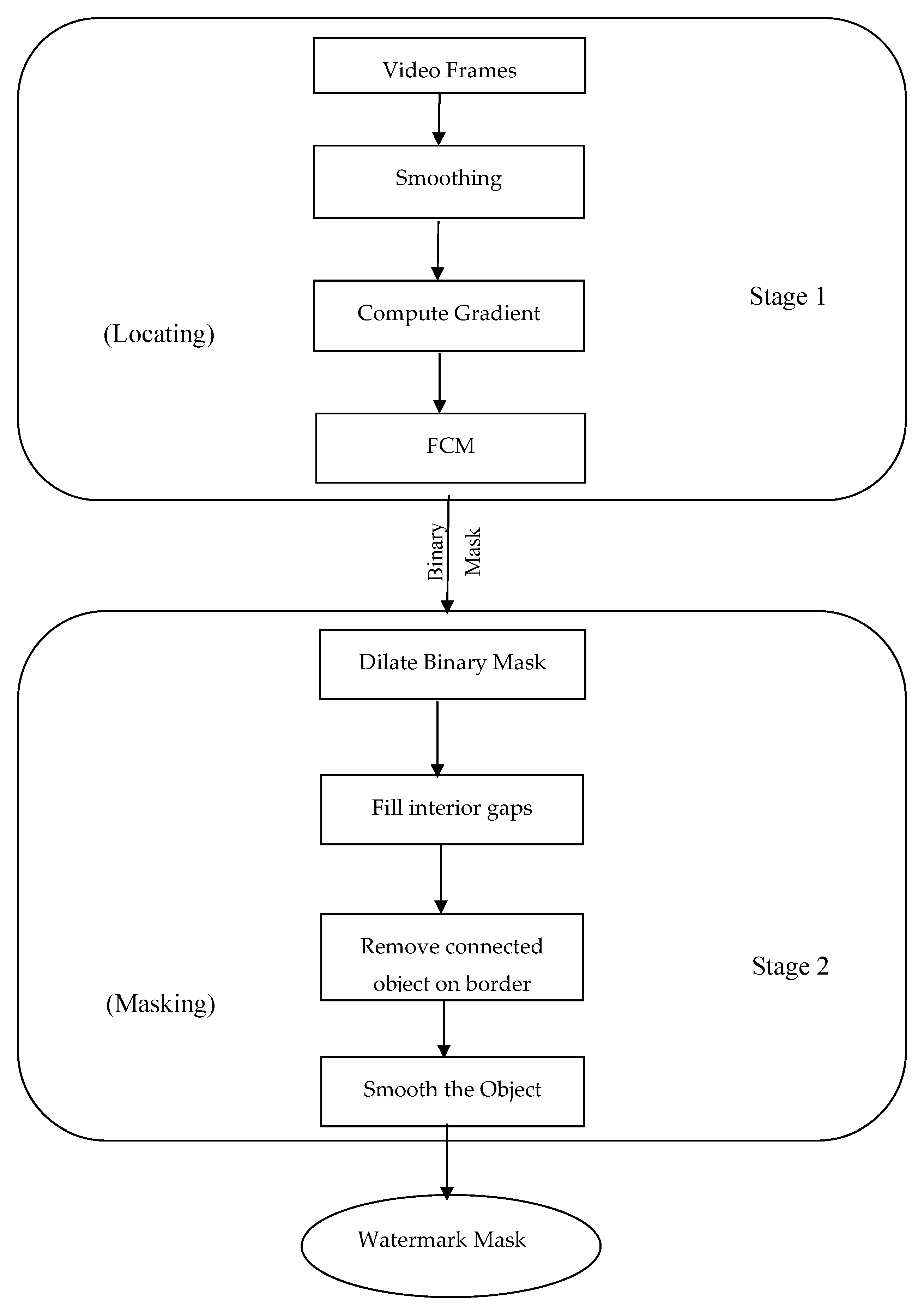
FCM-based approach for locating visible videowatermarks
The increased usage demand for digital multimedia has induced significant challenges regarding copyright protection, which is the copy control and proof of ownership. Digital watermarking serves as a solution to these kinds of problems. Among different types of digital watermarking, visible watermarking protects the copyrights effectively, since the approach not only prevents pirates but also visually proves the copyright of the broadcasted video. A visible watermark could be in any location on the frame (corner, center, diagonal, etc.). In addition, it could either completely or partially
Supervised fuzzy C-means techniques to solve the capacitated vehicle routing problem
Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) clustering technique is among the most effective partitional clustering algorithms available in the literature. The Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP) is an important industrial logistics and managerial NP-hard problem. Cluster-First Route-Second Method (CFRS) is one of the efficient techniques used to solve CVRP. In CFRS technique, customers are first divided into clusters in the first phase, then each cluster is solved independently as a Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) in the second phase. This research is concerned with the clustering phase of CFRS, and TSP is
Modified fuzzy c-means clustering approach to solve the capacitated vehicle routing problem
Fuzzy C-Means clustering is among the most successful clustering techniques available in the literature. The capacitated vehicle routing problem (CVRP) is one of the most studied NP-hard problems. CVRP has attracted the attention of many researchers due to its importance within the supply chain management field. This study aims to develop a fuzzy c-means clustering heuristic to efficiently solve the CVRP with large numbers of customers by using cluster-first route-second method (CFRS). CFRS is a two-phase technique, where in the first phase customers are grouped into, and in the second phase
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
