Control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators: A review
In this article, different control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators are presented with two distinguished classes of control strategies in the literature. These are the model-free control and the dynamic control strategy, which is mainly a model-based scheme, and is mostly the alternative when the control requirements are more stringent. The authors strongly believe that this paper will be helpful for researchers and engineers in the field of robotic systems. Copyright 2017 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
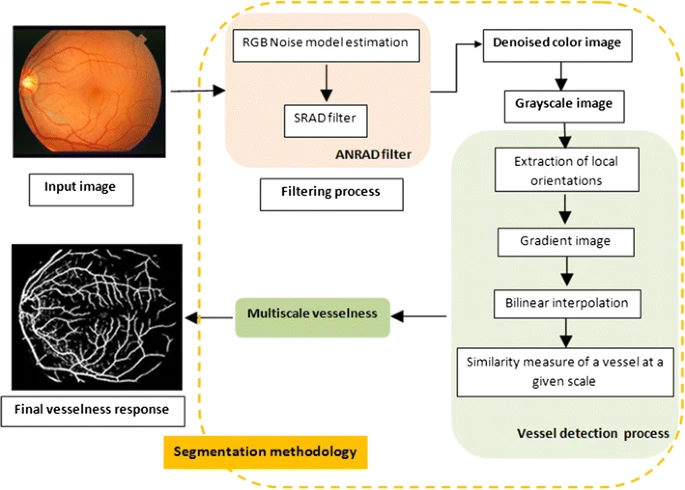
Noise-estimation-based anisotropic diffusion approach for retinal blood vessel segmentation
Recently, numerous research works in retinal-structure analysis have been performed to analyze retinal images for diagnosing and preventing ocular diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, which is the first most common causes of vision loss in the world. In this paper, an algorithm for vessel detection in fundus images is employed. First, a denoising process using the noise-estimation-based anisotropic diffusion technique is applied to restore connected vessel lines in a retinal image and eliminate noisy lines. Next, a multi-scale line-tracking algorithm is implemented to detect all the blood
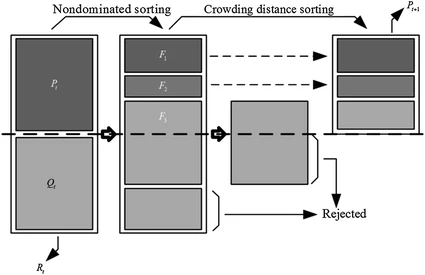
Chaotic system modelling using a neural network with optimized structure
In this work, the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to model a chaotic system. A method based on the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is used to determine the best parameters of a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network. Using NSGA-II, the optimal connection weights between the input layer and the hidden layer are obtained. Using NSGA-II, the connection weights between the hidden layer and the output layer are also obtained. This ensures the necessary learning to the neural network. The optimized functions by NSGA-II are the number of neurons in the

Chaotic system modelling using a neural network with optimized structure
In this work, the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to model a chaotic system. A method based on the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is used to determine the best parameters of a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network. Using NSGA-II, the optimal connection weights between the input layer and the hidden layer are obtained. Using NSGA-II, the connection weights between the hidden layer and the output layer are also obtained. This ensures the necessary learning to the neural network. The optimized functions by NSGA-II are the number of neurons in the
FPGA-Based Memristor Emulator Circuit for Binary Convolutional Neural Networks
Binary convolutional neural networks (BCNN) have been proposed in the literature for resource-constrained IoTs nodes and mobile computing devices. Such computing platforms have strict constraints on the power budget, system performance, processing and memory capabilities. Nonetheless, the platforms are still required to efficiently perform classification and matching tasks needed in various applications. The memristor device has shown promising results when utilized for in-memory computing architectures, due to its ability to perform storage and computation using the same physical element
IoT ethics challenges and legal issues
IoT systems have different technologies such as: RIFD, NFC, 3G, 4G, and Sensors. Their function is to transfer very large sensitive and private data. There are many ethical challenges that need to be taken into consideration by individuals and companies that use this technology. Amongst the challenges is the user awareness of attack risks. This paper discusses different ethical and legal challenges that need to be taken in account for IoT health care applications during the near future. © 2017 IEEE.
Fractional canny edge detection for biomedical applications
This paper presents a comparative study of edge detection algorithms based on integer and fractional order differentiation. A performance comparison of the two algorithms has been proposed. Then, a soft computing technique has been applied to both algorithms for better edge detection. From the simulations, it shows that better performance is obtained compared to the classical approach. The noise performances of those algorithms are analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The performance has been compared to peak signal to noise
Study of Energy Harvesters for Wearable Devices
Energy harvesting was and still an important point of research. Batteries have been utilized for a long time, but they are now not compatible with the downsizing of technology. Also, their need to be recharged and changed periodically is not very desirable, therefore over the years energy harvesting from the environment and the human body have been investigated. Three energy harvesting methods which are the Piezoelectric energy harvesters, the Enzymatic Biofuel cells, and Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are being discussed in the paper. Although Biofuel cells have been investigated for a
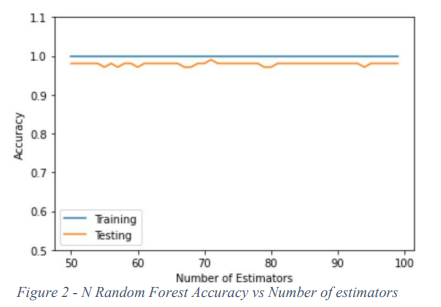
Diabetes Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Comparative Study
Diabetes is a common, metabolic disease, that results in a high level of blood sugar. Patients diagnosed with diabetes suffer from a body that cannot effectively use the insulin or cannot produce a sufficient amount of insulin. Providing a method of detection via symptoms that can be noticed by the patient can prompt the patient to seek medical assistance more promptly and in turn to be correctly diagnosed and treated. This paper proposed a solution for the problem using machine learning techniques. We applied eight algorithms on a data set of 521 subjects. The results are compared to each
AROMA: Automatic generation of radio maps for localization systems
Current methods for building radio maps for wireless localization systems require a tedious, manual and error-prone calibration of the area of interest. Each time the layout of the environment is changed or different hardware is used, the whole process of location fingerprinting and constructing the radio map has to be repeated. The process gets more complicated in the case of localizing multiple entities in a device-free scenario, since the radio map needs to take all possible combinations of the location of the entities into account. In this demo, we present a novel system (AROMA) that is
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
