Hybrid Information Filtering Engine for Personalized Job Recommender System
The recommendation system, also known as recommender system or recommendation engine/platform, is considered as an interdisciplinary field. It uses the techniques of more than one field. Recommender system inherits approaches from all of machine learning, data mining, information retrieval, information filtering and human-computer interaction. In this paper, we propose our value-added architecture of the hybrid information filtering engine for job recommender system (HIFE-JRS). We discuss our developed system’s components to filter the most relevant information and produce the most
Towards efficient and secure cloud
Cloud computing is becoming more and more popular. It is increasing in popularity with companies as it enables them to share various resources in a cost effective way. Cloud computing has lots of advantages, however some issues need to be handled before organizations and individuals have the confidence to rely on it. Security and privacy are at the forefront of these important issues. In this paper, the evolution of cloud computing along with its deployment and delivery models are highlighted. Also, the difference between cloud computing and other deployment models are discussed. We present
Software-Defined Networks Towards Big Data: A Survey
Both Big Data and Software-Defined Network have a significant impact in both academic and practical aspects. These two areas have been addressed separately, but both did not contribute to the same subset area of contribution. However, Big Data can greatly facilitate, improve, and have a great impact on Software Defined Network, and vice versa. In this paper, we show how SDN helps Big Data solve several issues regarding Big Data applications, including data processing in the data centers, data delivery and traffic monitoring. For Big Data, we also show how it can help SDN as well, including
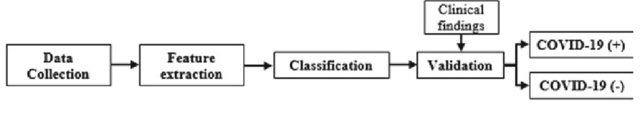
Using CNN-XGBoost Deep Networks for COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Images
At the time of writing, the COVID-19 pandemic is one of the lead causes of death worldwide and has caused significant changes to everyone's lives. While a vaccine is still unavailable, early screenings and detection of the disease can significantly help in managing the healthcare system's capacity as well as allow radiologists and clinicians better assign their priorities. With deep learning's rapid advancements over the last few years, its application in solving this issue is only natural. This paper aims to outline the works of a few major developments in the field of using deep learning to
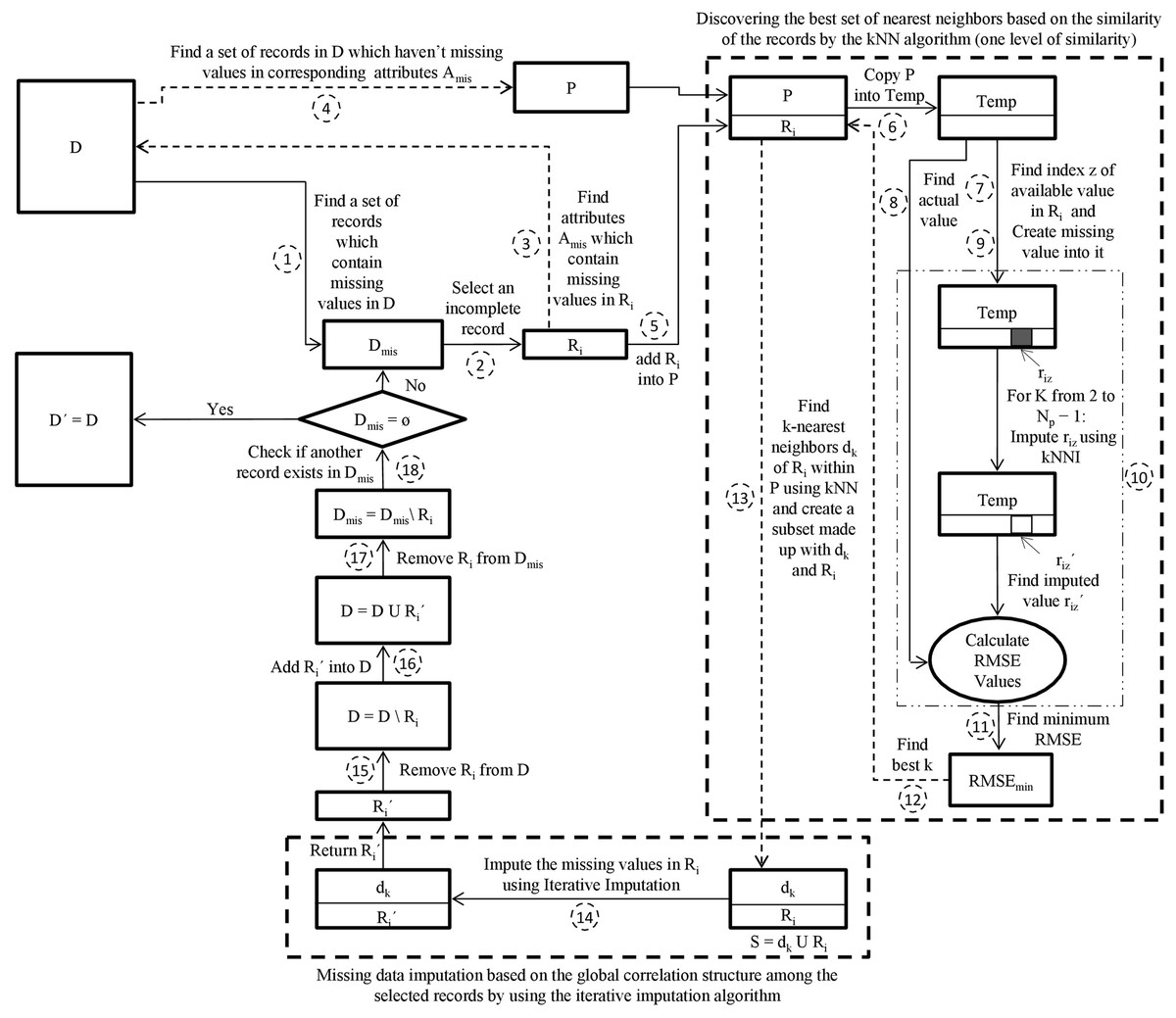
Advanced methods for missing values imputation based on similarity learning
The real-world data analysis and processing using data mining techniques often are facing observations that contain missing values. The main challenge of mining datasets is the existence of missing values. The missing values in a dataset should be imputed using the imputation method to improve the data mining methods’accuracy and performance. There are existing techniques that use k-nearest neighbors algorithm for imputing the missing values but determining the appropriate k value can be a challenging task. There are other existing imputation techniques that are based on hard clustering
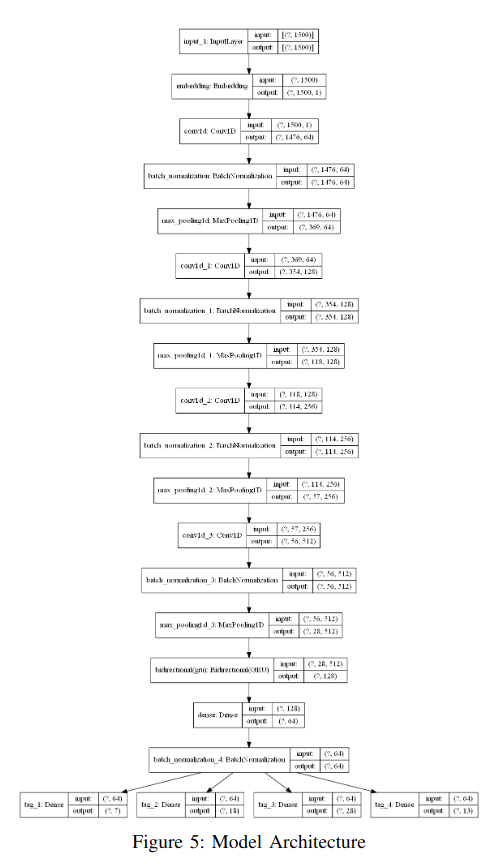
NnDPI: A Novel Deep Packet Inspection Technique Using Word Embedding, Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks
Traffic Characterization, Application Identification, Per Application Classification, and VPN/Non-VPN Traffic Characterization have been some of the most notable research topics over the past few years. Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) promises an increase in Quality of Service (QoS) for Internet Service Providers (ISPs), simplifies network management and plays a vital role in content censoring. DPI has been used to help ease the flow of network traffic. For instance, if there is a high priority message, DPI could be used to enable high-priority information to pass through immediately, ahead of
Remote prognosis, diagnosis and maintenance for automotive architecture based on least squares support vector machine and multiple classifiers
Software issues related to automotive controls account for an increasingly large percentage of the overall vehicles recalled. To alleviate this problem, vehicle diagnosis and maintenance systems are increasingly being performed remotely, that is while the vehicle is being driven without need for factory recall and there is strong consumer interest in Remote Diagnosis and Maintenance (RD&M) systems. Such systems are developed with different building blocks/elements and various capabilities. This paper presents a novel automotive RD&M system and prognosis architecture. The elements of the
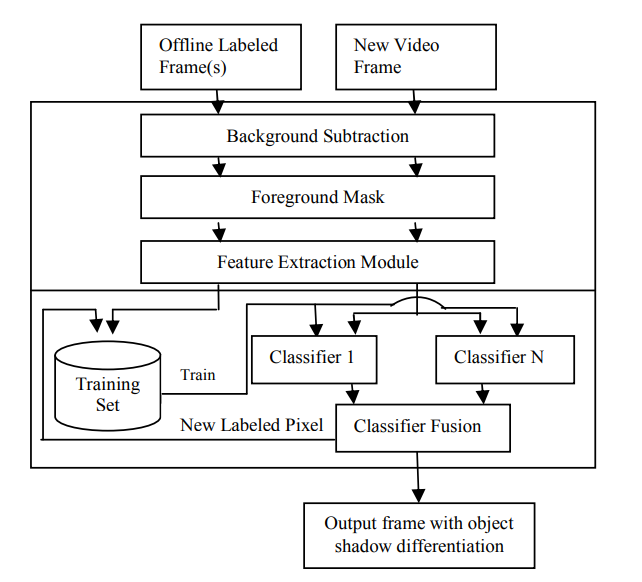
A semi supervised learning-based method for adaptive shadow detection
In vision-based systems, cast shadow detection is one of the key problems that must be alleviated in order to achieve robust segmentation of moving objects. Most methods for shadow detection require significant human input and they work in static settings. This paper proposes a novel approach for adaptive shadow detection by using semi-supervised learning which is a technique that has been widely utilized in various pattern recognition applications and exploits the use of labeled and unlabeled data to improve classification. The approach can be summarized as follows: First, we extract color
Motion history of skeletal volumes for human action recognition
Human action recognition is an important area of research in computer vision. Its applications include surveillance systems, patient monitoring, human-computer interaction, just to name a few. Numerous techniques have been developed to solve this problem in 2D and 3D spaces. However most of the existing techniques are view-dependent. In this paper we propose a novel view-independent action recognition algorithm based on the motion history of skeletons in 3D. First, we compute a skeleton for each volume and a motion history for each action. Then, alignment is performed using cylindrical
Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Urban Signatures with Application to Drone Localization
Most commercial Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (SUAVs) rely solely on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs) - such as GPS and GLONASS - to perform localization tasks during the execution of autonomous navigation activities. Despite being fast and accurate, satellite-based navigation systems have typical vulnerabilities and pitfalls in urban settings that may prevent successful drone localization. This paper presents the novel concept of 'Deep Urban Signatures' where a deep convolutional neural network is used to compute a unique characterization for each urban area or district based on
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 29
- Next page ››
