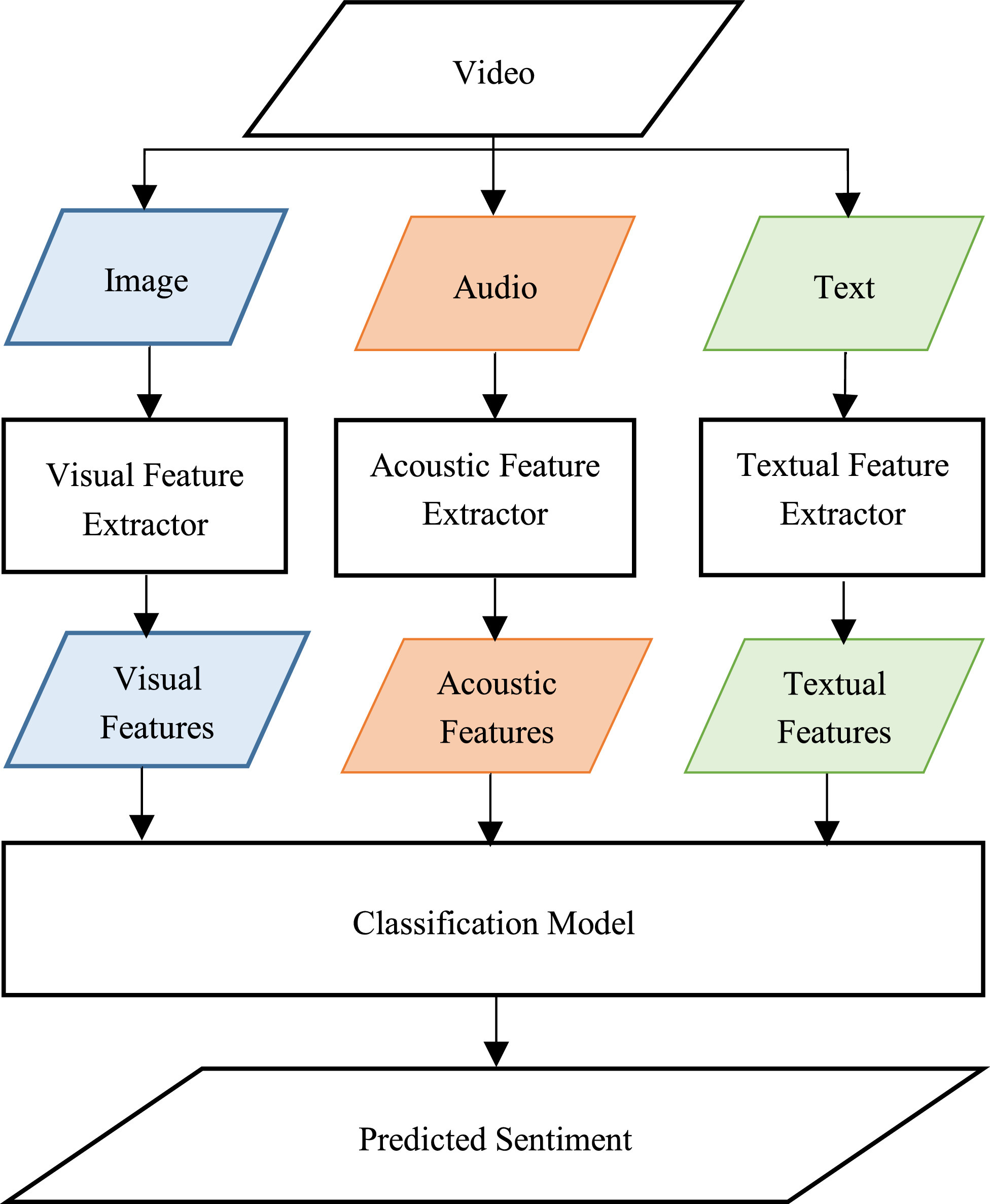
Multimodal Video Sentiment Analysis Using Deep Learning Approaches, a Survey
Deep learning has emerged as a powerful machine learning technique to employ in multimodal sentiment analysis tasks. In the recent years, many deep learning models and various algorithms have been proposed in the field of multimodal sentiment analysis which urges the need to have survey papers that summarize the recent research trends and directions. This survey paper tackles a comprehensive overview of the latest updates in this field. We present a sophisticated categorization of thirty-five state-of-the-art models, which have recently been proposed in video sentiment analysis field, into
Automated cardiac-tissue identification in composite strain-encoded (C-SECN) images using fuzzy K-means and bayesian classifier
Composite Strain Encoding (C-SENC) is an MRI acquisition technique for simultaneous acquisition of cardiac tissue viability and contractility images. It combines the use of black-blood delayed-enhancement imaging to identify the infracted (dead) tissue inside the heart wall muscle and the ability to image myocardial deformation (MI) from the strain-encoding (SENC) imaging technique. In this work, we propose an automatic image processing technique to identify the different heart tissues. This provides physicians with a better clinical decision-making tool in patients with myocardial infarction
Content based image retrieval of diabetic macular edema images
Colour fundus images play an important role in diagnosing and screening diabetic macular edema (DME). In rural areas, content-based image retrieval (CBIR) might compensate the lack of expert ophthalmologists. In this work, we present a fully automated CBIR system that retrieves fundus images according to their content (quantity and location) of exudates. First, the macula is divided into three concentric regions whose texture discontinuities are used to represent lesion content of the retina. The image-to-image distance measure gives higher weights to lesions closer to the fovea to reflect the
Content based image retrieval of diabetic macular edema images
Colour fundus images play an important role in diagnosing and screening diabetic macular edema (DME). In rural areas, content-based image retrieval (CBIR) might compensate the lack of expert ophthalmologists. In this work, we present a fully automated CBIR system that retrieves fundus images according to their content (quantity and location) of exudates. First, the macula is divided into three concentric regions whose texture discontinuities are used to represent lesion content of the retina. The image-to-image distance measure gives higher weights to lesions closer to the fovea to reflect the
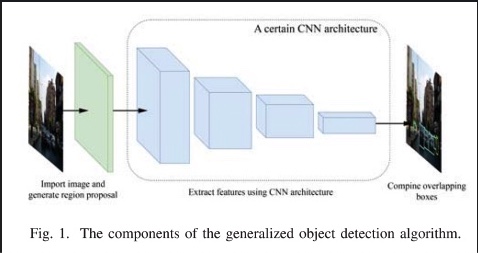
A Deep Learning Approach for Vehicle Detection
The autonomous driving needs some several features to achieve driving without human interference. One of these features is vehicle classification and detection since the target of this process is to help the CPU ''Central Processing Unit" of the vehicle to see what is around the vehicle, in order to evaluate the situation to take the best decision for each situation in real time. This paper is focusing on the classification process of the video-based vehicle detection, to achieve that, different deep learning techniques have been implemented which are known as convolutional neural networks
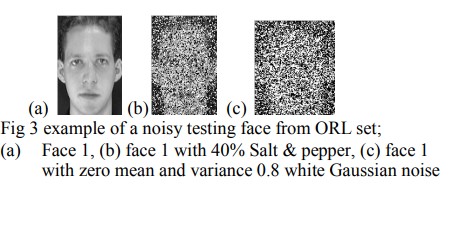
Performance evaluation of transform domain diagonal principal component analysis for facial recognition employing different pre-processing spatial domain approaches
Facial recognition using spatial domain Diagonal Principal Component Analysis (DiaPCA) algorithm produces better accuracy compared to the Two Dimensional PCA (2DPCA). Transform Domain - 2DPCA (TD2DPCA) retains the high recognition accuracy of the 2DPCA while considerably reducing storage requirements and computational complexity. In this work, the Transform Domain PCA implementation of the DiaPCA (TDDiaPCA) is presented. All the test results, for noise free and noisy images, consistently confirm the considerable storage and computational savings for different spatial domain pre-processing
Efficient quantum-based security protocols for information sharing and data protection in 5G networks
Fifth generation (5G)networks aim at utilizing many promising communication technologies, such as Cloud Computing, Network Slicing, and Software Defined Networking. Supporting a massive number of connected devices with 5G advanced technologies and innovating new techniques will surely bring tremendous challenges for trust, security and privacy. Therefore, secure mechanisms and protocols are required as the basis for 5G networks to address this security challenges and follow security-by-design but also security-by-operations rules. In this context, new efficient cryptographic protocols and
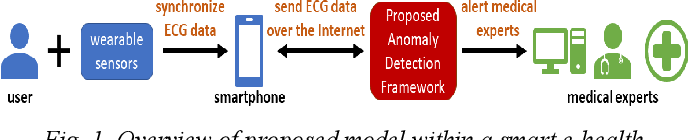
A Multitier Deep Learning Model for Arrhythmia Detection
An electrocardiograph (ECG) is employed as a primary tool for diagnosing cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). ECG signals provide a framework to probe the underlying properties and enhance the initial diagnosis obtained via traditional tools and patient-doctor dialogs. Notwithstanding its proven utility, deciphering large data sets to determine appropriate information remains a challenge in ECG-based CVD diagnosis and treatment. Our study presents a deep neural network (DNN) strategy to ameliorate the aforementioned difficulties. Our strategy consists of a learning stage where classification
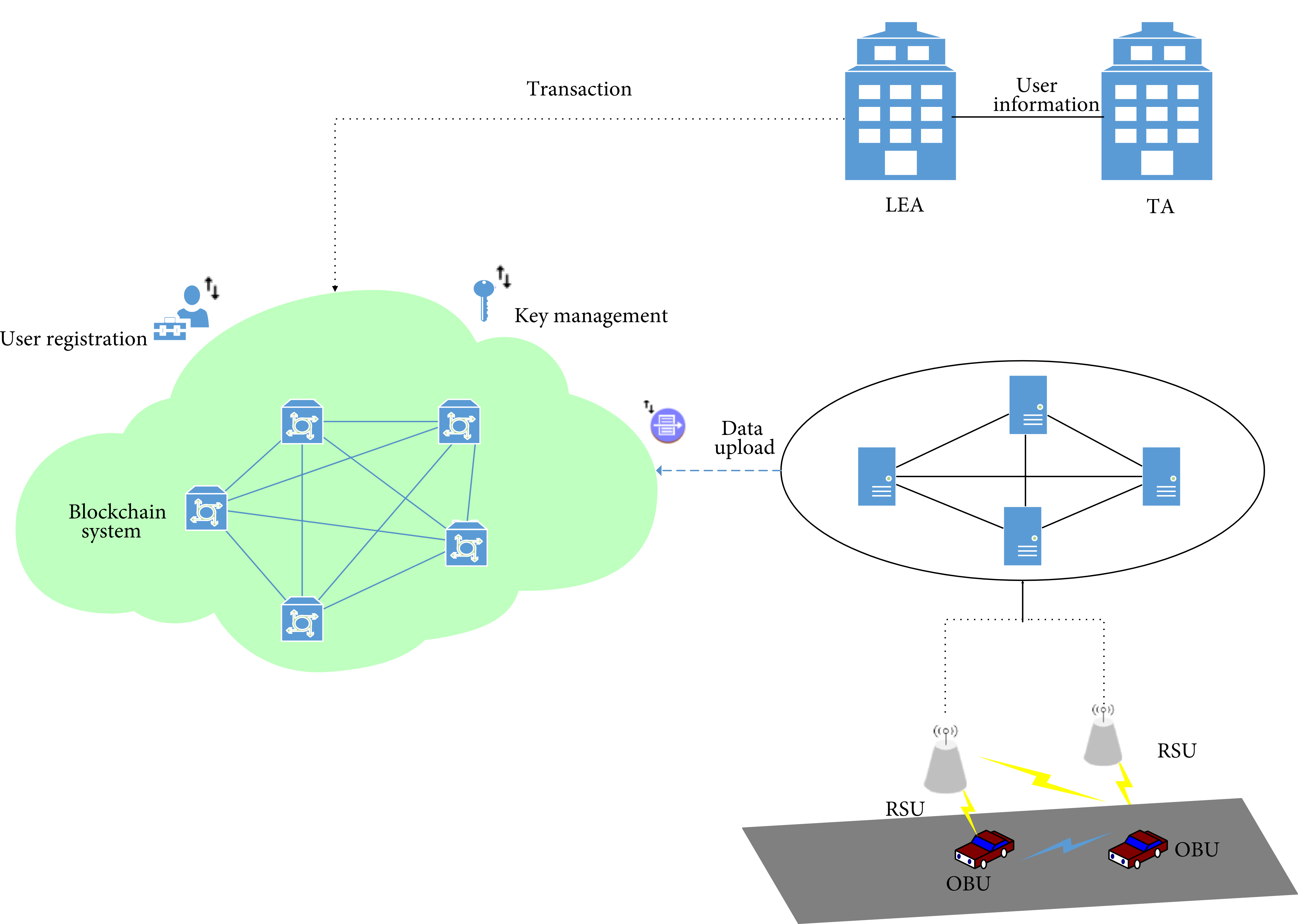
Using Blockchain Technology for the Internet of Vehicles
The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) aims to connect vehicles with their surroundings and share data. In IoV, various wireless technologies like 5G, WIFI, DSRC, WiMAX, and ZigBee are used. To share data within wireless surroundings in a secure way, some security aspects need to be fulfilled. Blockchain technology is a good fit to cover these countermeasures. IoV uses a lot of technologies and interacts with different types of wireless nodes, and this increases the vulnerability to some attacks that could endanger lives. Using blockchain technology within the IoV architecture could provide efficient
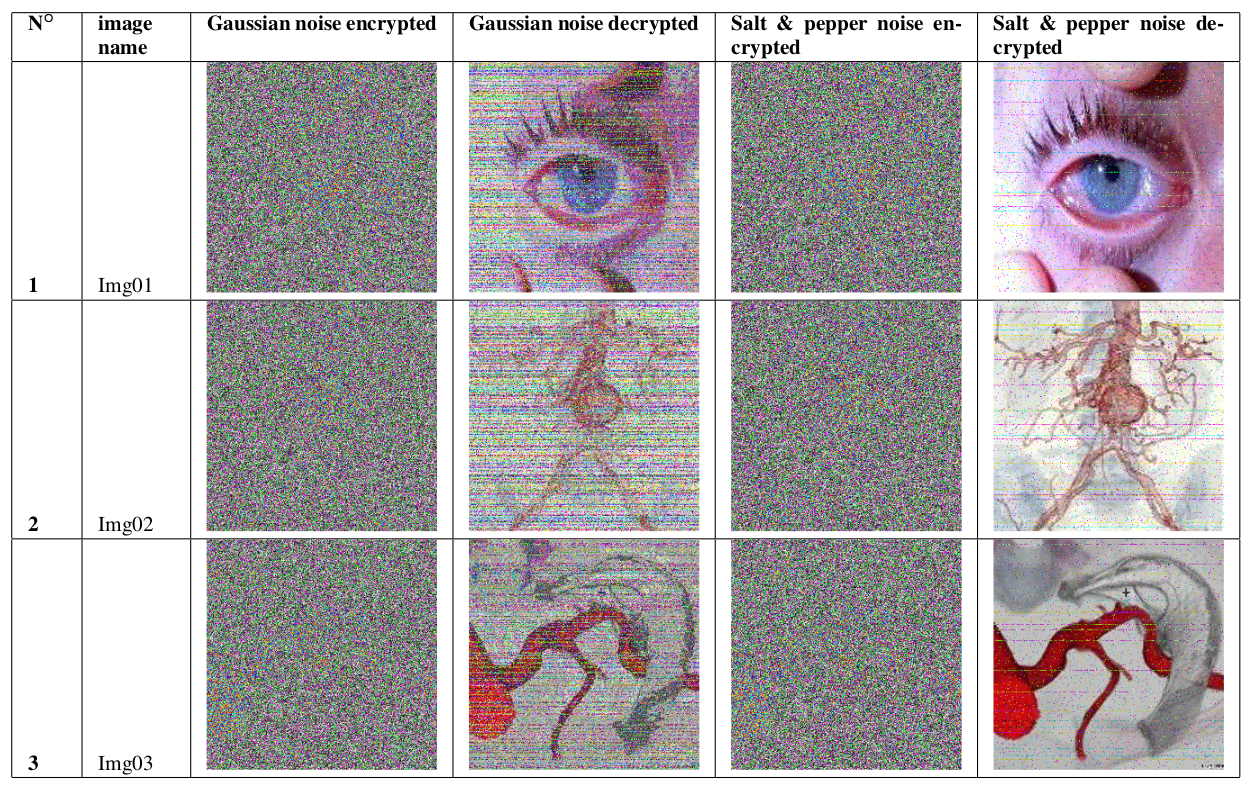

A New Chaotic Map with Dynamic Analysis and Encryption Application in Internet of Health Things
In this paper, we report an effective cryptosystem aimed at securing the transmission of medical images in an Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT) environment. This contribution investigates the dynamics of a 2-D trigonometric map designed using some well-known maps: Logistic-sine-cosine maps. Stability analysis reveals that the map has an infinite number of solutions. Lyapunov exponent, bifurcation diagram, and phase portrait are used to demonstrate the complex dynamic of the map. The sequences of the map are utilized to construct a robust cryptosystem. First, three sets of key streams are
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 23
- Next page ››
