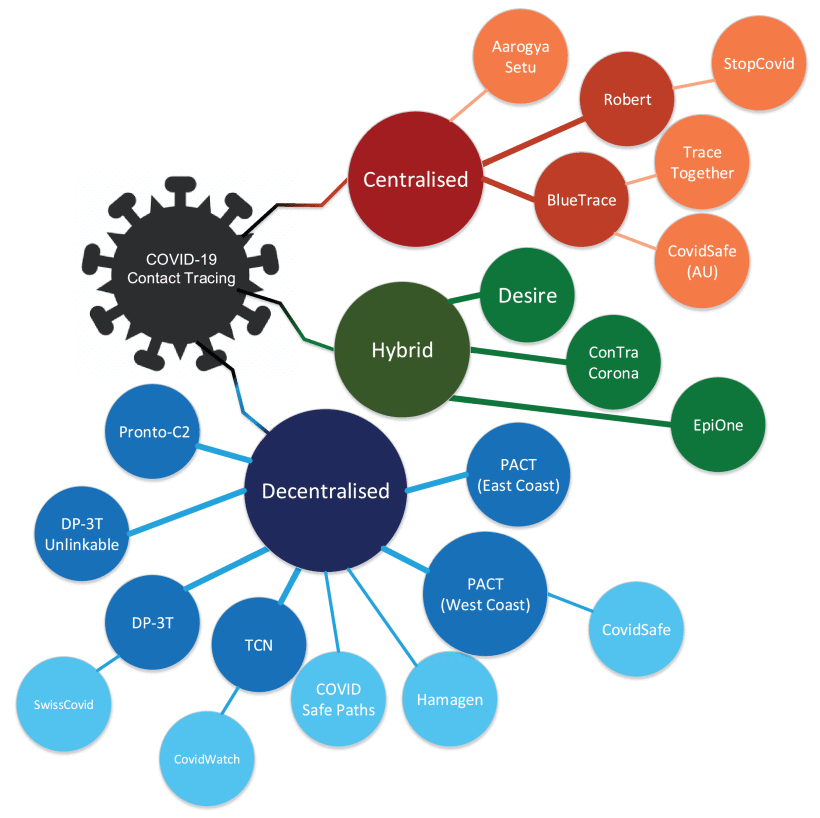
A Survey of COVID-19 Contact Tracing Apps
The recent outbreak of COVID-19 has taken the world by surprise, forcing lockdowns and straining public health care systems. COVID-19 is known to be a highly infectious virus, and infected individuals do not initially exhibit symptoms, while some remain asymptomatic. Thus, a non-negligible fraction of the population can, at any given time, be a hidden source of transmissions. In response, many governments have shown great interest in smartphone contact tracing apps that help automate the difficult task of tracing all recent contacts of newly identified infected individuals. However, tracing
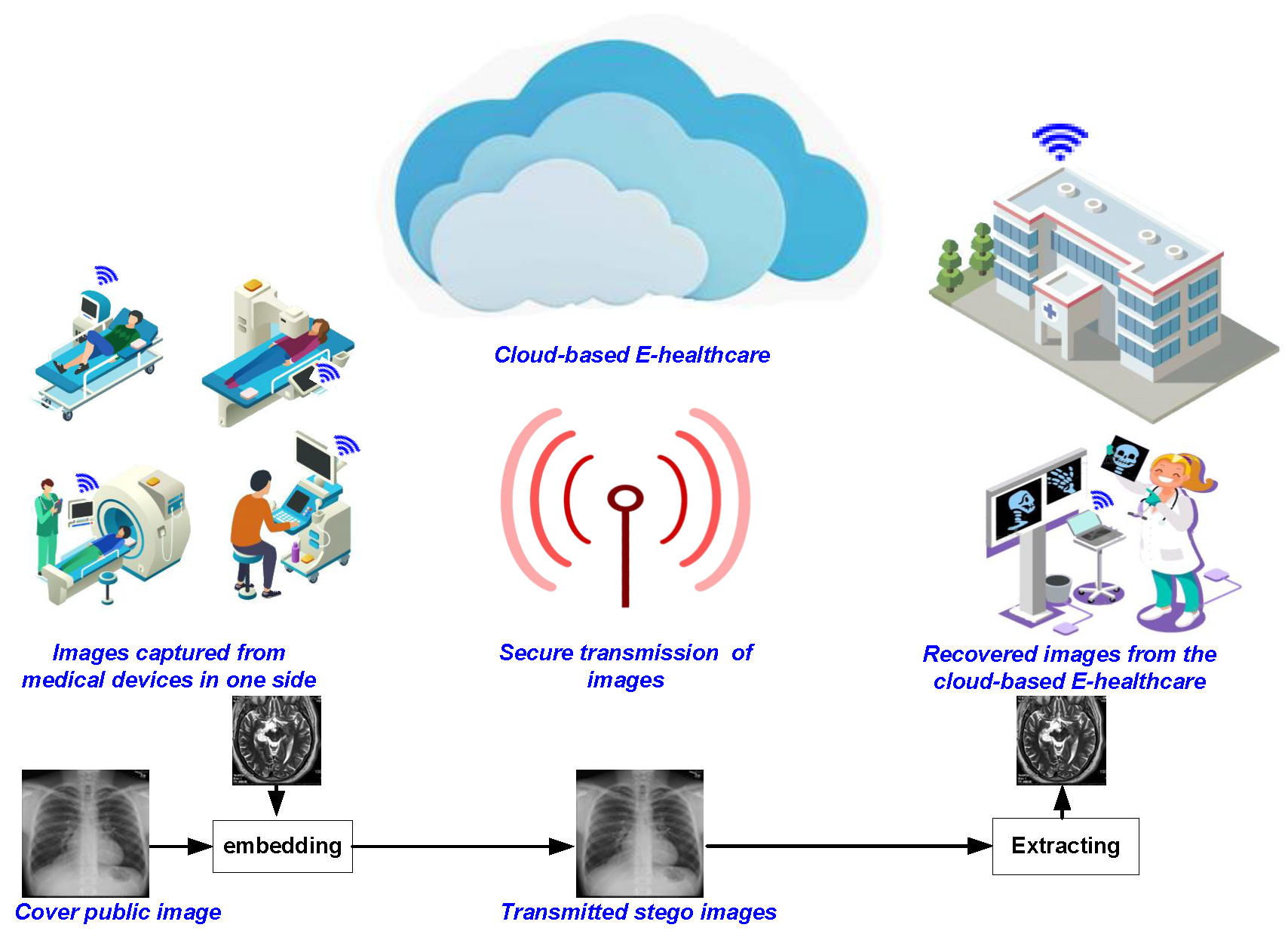
A robust quasi-quantum walks-based steganography protocol for secure transmission of images on cloud-based E-healthcare platforms
Traditionally, tamper-proof steganography involves using efficient protocols to encrypt the stego cover image and/or hidden message prior to embedding it into the carrier object. However, as the inevitable transition to the quantum computing paradigm beckons, its immense computing power will be exploited to violate even the best non-quantum, i.e., classical, stego protocol. On its part, quantum walks can be tailored to utilise their astounding ‘quantumness’ to propagate nonlinear chaotic behaviours as well as its sufficient sensitivity to alterations in primary key parameters both important
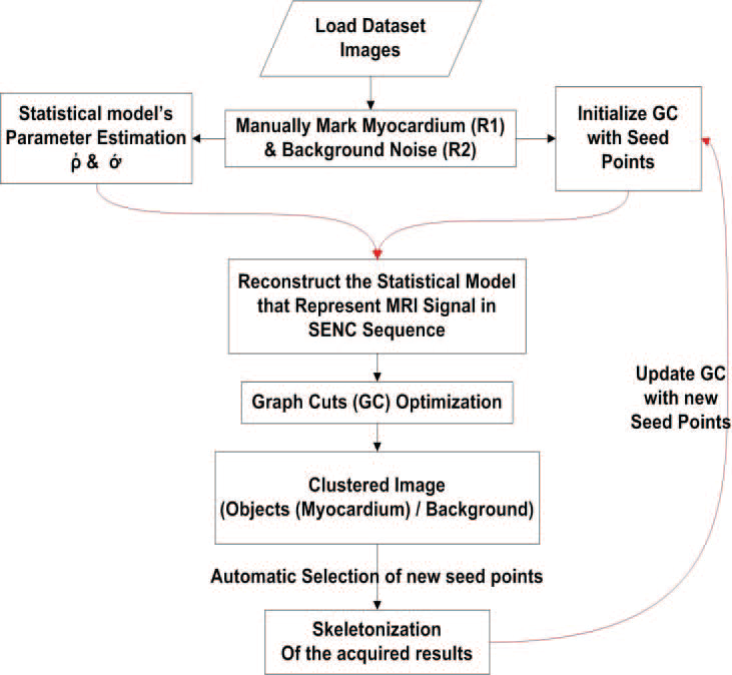
Segmentation of strain-encoded magnetic resonance images using graph-cuts
Imaging of the heart anatomy and function using Strain Encoded (SENC) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a powerful tool for diagnosing a number of heart diseases. Despite excellent sensitivity to tissue deformation, the technique inherently suffers from elevated noise level which hinders proper automatic segmentation using conventional techniques. In this work, we propose a method to accurately segment the left ventricle myocardium from strain encoded-MR short axis images. The method is based on a modified formulation of the graph cuts algorithm. A novel cost function based on a
Error analysis of fundus image registration using quadratic model transfformation
Based registration of retinal images proved to be very successful especially for minimally overlapping images. The most commonly used transformation method uses a quadratic model to represent the geometry of the retinal surface. Although this model has been used for more than one decade, there is no literature that studies the model errors for abnormal eye geometries. In this work, we present a study of the registration errors of the quadratic model in case of diseased eyes. The study includes two basic models of the retinal surface for eyes suffering from: myopia; and retinal diseases (e.g
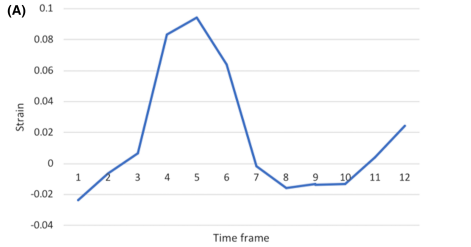
Detecting liver fibrosis using a machine learning-based approach to the quantification of the heart-induced deformation in tagged MR images
Liver disease causes millions of deaths per year worldwide, and approximately half of these cases are due to cirrhosis, which is an advanced stage of liver fibrosis that can be accompanied by liver failure and portal hypertension. Early detection of liver fibrosis helps in improving its treatment and prevents its progression to cirrhosis. In this work, we present a novel noninvasive method to detect liver fibrosis from tagged MRI images using a machine learning-based approach. Specifically, coronal and sagittal tagged MRI imaging are analyzed separately to capture cardiac-induced deformation
Segmentation of Diabetic Macular Edema in fluorescein angiograms
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FA) is a powerful tool for imaging and evaluating Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), where the fluorescein dye leaks and accumulates in the diseased areas. Currently, the assessment of FA images is qualitative and suffers from large inter-observer variability. A necessary step towards quantitative assessment of DME is automatic segmentation of fluorescein leakage. In this work, we present an automatic method for segmenting DME areas in FA images. The method is based on modeling the macular image in the early time frame using 2D Gaussian surfaces, which is then
Comparison of Machine Learning Approaches for Prediction of Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients
Background/Aim: Using machine learning approaches as non-invasive methods have been used recently as an alternative method in staging chronic liver diseases for avoiding the drawbacks of biopsy. This study aims to evaluate different machine learning techniques in prediction of advanced fibrosis by combining the serum bio-markers and clinical information to develop the classification models. Methods: A prospective cohort of 39,567 patients with chronic hepatitis C was divided into two sets - one categorized as mild to moderate fibrosis (F0-F2), and the other categorized as advanced fibrosis (F3
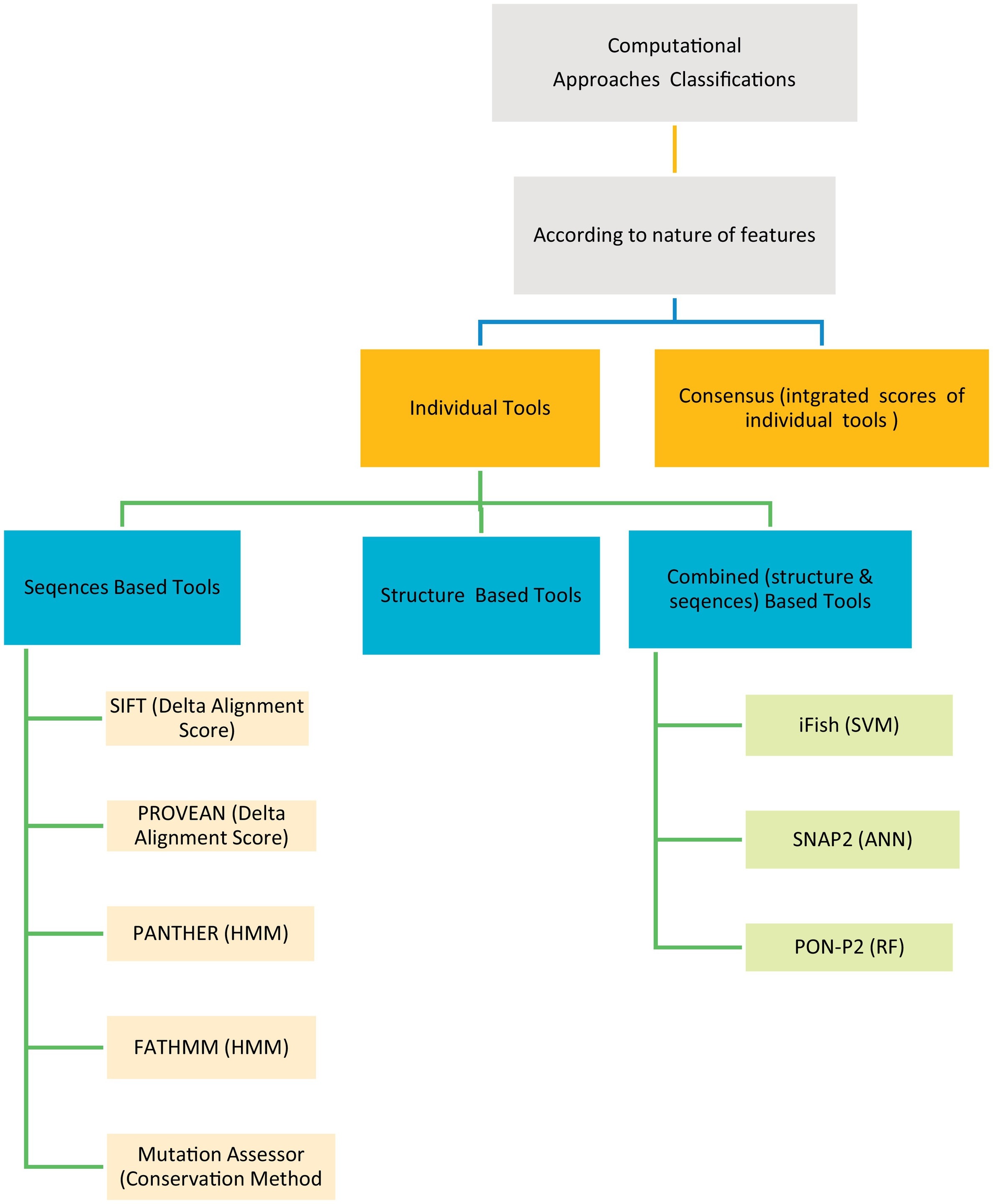
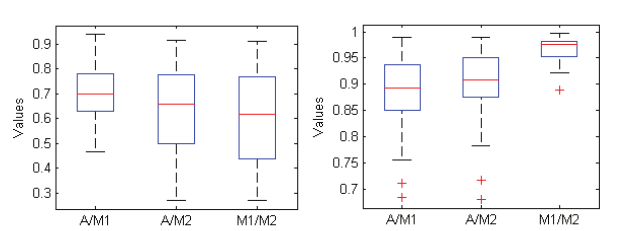
Evaluation of computational techniques for predicting non-synonymous single nucleotide variants pathogenicity
The human genetic diseases associated with many factors, one of these factors is the non-synonymous Single Nucleotide Variants (nsSNVs) cause single amino acid change with another resulting in protein function change leading to disease. Many computational techniques have been released to expect the impacts of amino acid alteration on protein function and classify mutations as pathogenic or neutral. Here in this article, we assessed the performance of eight techniques; FATHMM, SIFT, Provean, iFish, Mutation Assessor, PANTHER, SNAP2, and PON- P2 using a VaribenchSelectedPure dataset of 2144
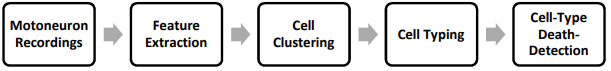
Automated Cell-Type Classification and Death-Detection of Spinal Motoneurons
Spinal motoneurons (MNs) play a crucial role in movement control. Decoding the firing activity of spinal MNs could help in real-life challenges, such as enhancing the control of myoelectric prostheses and diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases. In this paper, we propose a machine learning approach to automatically classify MNs based on their firing activity. Applying the proposed approach to data from a MN computational model, the classification accuracy of all examined datasets exceeded 95%. We extended the approach to detecting the death of a given MN type using clustering validity index
Segmentation of Choroidal Neovascularization lesions in fluorescein angiograms using parametric modeling of the intensity variation
Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) is a severe retinal disease characterized by abnormal growth of blood vessels in the choroidal layer. Current diagnosis of CNV depends mainly on qualitative assessment of a temporal sequence of fundus fluorescein angiography images. Automated segmentation and identification of the CNV lesion types (either occult or classic) is required to reduce the inter-and intra- observer variability and also to reduce the manual segmentation effort and time. In this work, we present automatic segmentation method for the CNV lesions. The method is based on developing a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 22
- Next page ››
