Complementary feature splits for co-training
In many data mining and machine learning applications, data may be easy to collect. However, labeling the data is often expensive, time consuming or difficult. Such applications give rise to semi-supervised learning techniques that combine the use of labelled and unlabelled data. Co-training is a popular semi-supervised learning algorithm that depends on splitting the features of a data set into two redundant and independent views. In many cases however such sets of features are not naturally present in the data or are unknown. In this paper we test feature splitting methods based on
Building large arabic multi-domain resources for sentiment analysis
While there has been a recent progress in the area of Arabic SentimentAnalysis, most of the resources in this area are either of limited size, domainspecific or not publicly available. In this paper, we address this problemby generating large multi-domain datasets for Sentiment Analysis in Arabic.The datasets were scrapped from different reviewing websites and consist of atotal of 33K annotated reviews for movies, hotels, restaurants and products.Moreover we build multi-domain lexicons from the generated datasets. Differentexperiments have been carried out to validate the usefulness of the
Combining lexical features and a supervised learning approach for arabic sentiment analysis
The importance of building sentiment analysis tools for Arabic social media has been recognized during the past couple of years, especially with the rapid increase in the number of Arabic social media users. One of the main difficulties in tackling this problem is that text within social media is mostly colloquial, with many dialects being used within social media platforms. In this paper, we present a set of features that were integrated with a machine learning based sentiment analysis model and applied on Egyptian, Saudi, Levantine, and MSA Arabic social media datasets. Many of the proposed
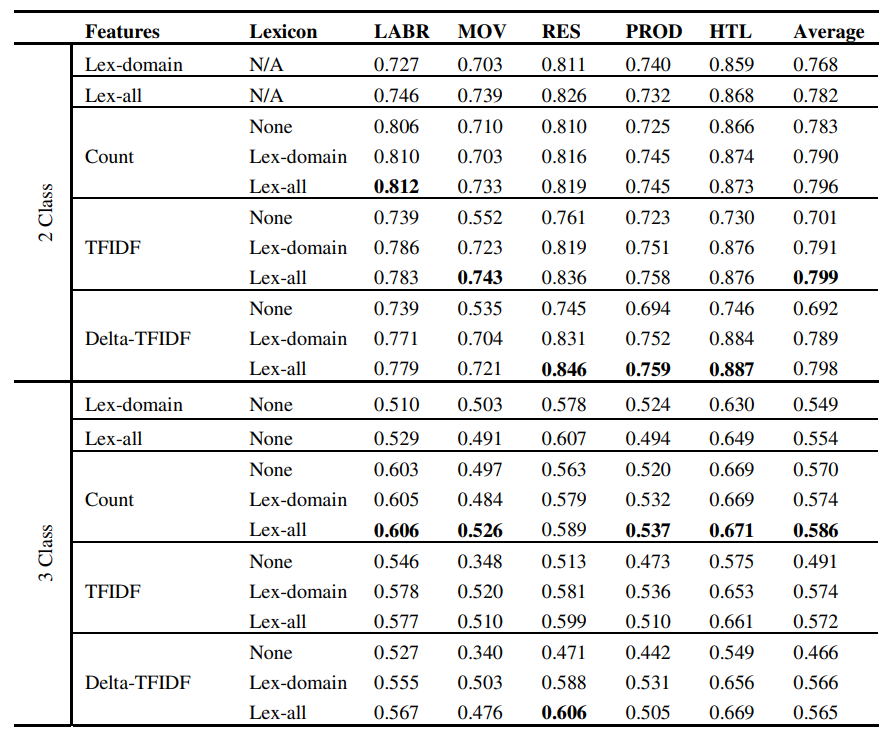
An Analytical Computational Algorithm for Solving a System of Multipantograph DDEs Using Laplace Variational Iteration Algorithm
In this research, an approximation symbolic algorithm is suggested to obtain an approximate solution of multipantograph system of type delay differential equations (DDEs) using a combination of Laplace transform and variational iteration algorithm (VIA). The corresponding convergence results are acquired, and an efficient algorithm for choosing a feasible Lagrange multiplier is designed in the solving process. The application of the Laplace variational iteration algorithm (LVIA) for the problems is clarified. With graphics and tables, LVIA approximates to a high degree of accuracy with a few
IoT Based AI and its Implementations in Industries
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an Internet revolution that is increasingly used in business, industry, medicine, the economy and other modern information society. IoT, particularly transport, industrial robots and automation systems are supported by artificial intelligence in a wide range of daily implementations with dominant industrial applications. IoT is an interconnected network of physical objects, which enables them to gather and share information, using software, sensor units and network connectivity. In industries; IoT brought about a new revolution in industries. In the field of IoT
Controlled alternate quantum walk-based pseudo-random number generator and its application to quantum color image encryption
Pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) are a key component in the design of modern cryptographic mechanisms and are regarded as a backbone element of many modern cryptographic applications. However and in spite of their robustness, quantum computers could crack down PNGR-based systems. Quantum walks, a universal model of quantum computation, have nonlinear properties that make them a robust candidate to produce PRNG. In this paper, we utilize controlled alternate quantum walk (CAQW) to create PRNG. Moreover, we use the presented PRNG mechanism as a component of a new quantum color image
Combating sybil attacks in vehicular ad hoc networks
Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs) are considered as a promising approach for facilitating road safety, traffic management, and infotainment dissemination for drivers and passengers. However, they are subject to an attack that has a severe impact on their security. This attack is called the Sybil attack, and it is considered as one of the most serious attacks to VANETs, and a threat to lives of drivers and passengers. In this paper, we propose a detection scheme for the Sybil attack. The idea is based on public key cryptography and aims to ensure privacy preservation, confidentiality, and non
Complexwavelet Transform Cwt Based Video Magnification for 3d Facial Video Identification
Magnifying micro changes in motion and brightness of videos that are unnoticeable by the human visual system have recently been an interesting area to explore. In this paper, we explore this technique in 3D facial video identification, we utilize this technique to identify 3D objects from 2D images. We present a Complex Wavelet Transform CWT, 2D-Dual CWT based technique, to calculate any changes between subsequent video frames of CWT sub-bands at different spatial locations. In this technique, a gradient based method is proposed to determine the orientation of each CWT sub band in addition to
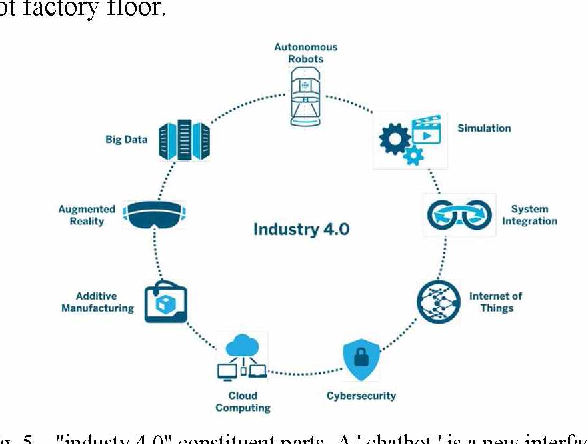
A distributed data collection algorithm for wireless sensor networks with persistent storage nodes
A distributed data collection algorithm to accurately store and forward information obtained by wireless sensor networks is proposed. The proposed algorithm does not depend on the sensor network topology, routing tables, or geographic locations of sensor nodes, but rather makes use of uniformly distributed storage nodes. Analytical and simulation results for this algorithm show that, with high probability, the data disseminated by the sensor nodes can be precisely collected by querying any small set of storage nodes.
Complete genome sequence and bioinformatics analysis of nine Egyptian females with clinical information from different geographic regions in Egypt
Egyptians are at a crossroad between Africa and Eurasia, providing useful genomic resources for analyzing both genetic and environmental factors for future personalized medicine. Two personal Egyptian whole genomes have been published previously by us and here nine female whole genome sequences with clinical information have been added to expand the genomic resource of Egyptian personal genomes. Here we report the analysis of whole genomes of nine Egyptian females from different regions using Illumina short-read sequencers. At 30x sequencing coverage, we identified 12 SNPs that were shared in
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 21
- Next page ››
