Arabic fake news detection using deep learning
Nowadays, an unprecedented number of users interact through social media platforms and generate a massive amount of content due to the explosion of online communication. However, because user-generated content is unregulated, it may contain offensive content such as fake news, insults, and harassment phrases. The identification of fake news and rumors and their dissemination on social media has become a critical requirement. They have adverse effects on users, businesses, enterprises, and even political regimes and governments. State of the art has tackled the English language for news and
AutoDLCon: An Approach for Controlling the Automated Tuning for Deep Learning Networks
Neural networks have become the main building block on revolutionizing the field of artificial intelligence aided applications. With the wide availability of data and the increasing capacity of computing resources, they triggered a new era of state-of-the-art results in diverse directions. However, building neural network models is domain-specific, and figuring out the best architecture and hyper-parameters in each problem is still an art. In practice, it is a highly iterative process that is very time-consuming, requires substantial computing resources, and needs deep knowledge and solid
Tracking ground targets from a UAV using new P-N constraints
This paper presents improved automatic moving target detection and tracking framework that is suitable for UAV imagery. The framework is comprised of motion compensation phase to detect moving targets from a moving camera, target state estimation with Kalman filter, and overlap-rate-based data association. Finally, P-N learning is used to maintain target appearance by utilizing novel structural constraints to select positive and negative samples, where data association decisions are used as positive (P) constraints. After learning target appearance, a cascaded classifier is employed to detect
Remote Diagnosis, Maintenance and Prognosis for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems Using Machine Learning Algorithms
New challenges and complexities are continuously increasing in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) development (e.g. active safety, driver assistant and autonomous vehicle systems). Therefore, the health management of ADAS’ components needs special improvements. Since software contribution in ADAS’ development is increasing significantly, remote diagnosis and maintenance for ADAS become more important. Furthermore, it is highly recommended to predict the remaining useful life (RUL) for the prognosis of ADAS’ safety critical components; e.g. (Ultrasonic, Cameras, Radar, LIDAR). This paper
Motion and depth augmented semantic segmentation for autonomous navigation
Motion and depth provide critical information in autonomous driving and they are commonly used for generic object detection. In this paper, we leverage them for improving semantic segmentation. Depth cues can be useful for detecting road as it lies below the horizon line. There is also a strong structural similarity for different instances of different objects including buildings and trees. Motion cues are useful as the scene is highly dynamic with moving objects including vehicles and pedestrians. This work utilizes geometric information modelled by depth maps and motion cues represented by
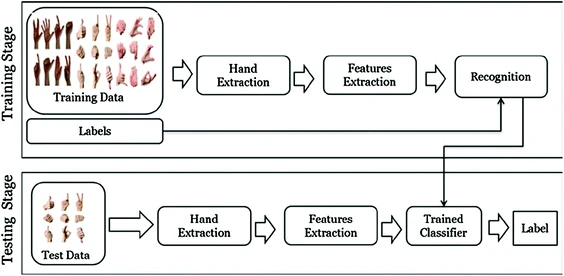
Gesture recognition for improved user experience in augmented biology lab
The Learning process in education systems is one of the most important issues that affect all societies. Advances in technology have influenced how people communicate and learn. Gaming Techniques (GT) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies provide new opportunities for a learning process. They transform the student’s role from passive to active in the learning process. It can provide a realistic, authentic, engaging and interesting learning environment. Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) is a major driver in the field of Augmented Reality (AR). In this paper, we propose an initiative Augmented
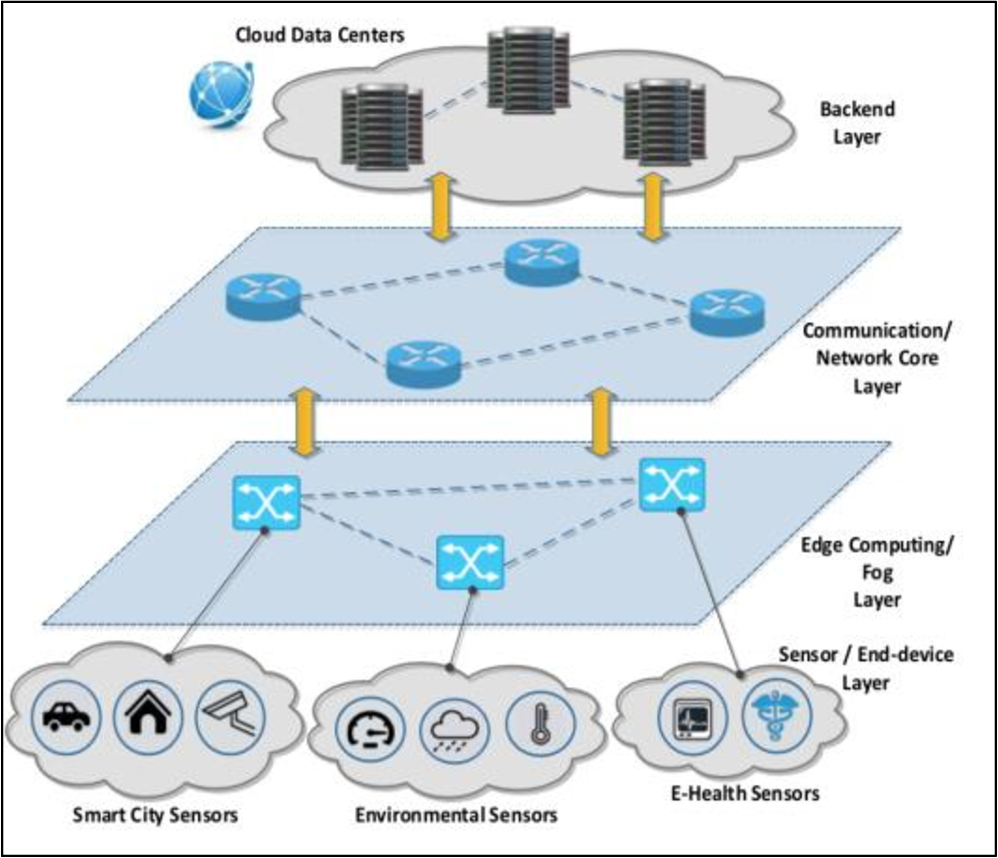
IoT Modes of Operations with Different Security Key Management Techniques: A Survey
The internet of things (IoT) has provided a promising opportunity to build powerful systems and applications. Security is the main concern in IoT applications due to the privacy of exchanged data using limited resources of IoT devices (sensors/actuators). In this paper, we present a classification of IoT modes of operation based on the distribution of IoT devices, connectivity to the internet, and the typical field of application. It has been found that the majority of IoT services can be classified into one of four IoT modes: Gateway, device to device, collaborative, and centralized. The

Native Mobile Applications UI Code Conversion
With the widespread use of mobile applications in daily life, it has become crucial for software companies to develop the applications for the most popular platforms like Android and iOS. Using a native development is time consuming and costly. Cross-platform mobile development like Xamarin and React native emerged as a solution to the mentioned problem of native development for the time and cost. Meanwhile it requires the developers to learn a new language. Other tools are converting the mobile apps of specific platform to the corresponding platform, but most of them still lack the mobile
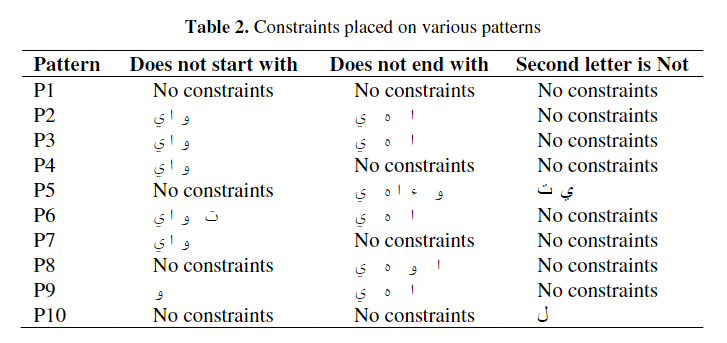
A corpus based approach for the automatic creation of Arabic broken plural dictionaries
Research has shown that Arabic broken plurals constitute approximately 10% of the content of Arabic texts. Detecting Arabic broken plurals and mapping them to their singular forms is a task that can greatly affect the performance of information retrieval, annotation or tagging tasks, and many other text mining applications. It has been reported that the most effective way of detecting broken plurals is through the use of dictionaries. However, if the target domain is a specialized one, or one for which there are no such dictionaries, building those manually becomes a tiresome, not to mention

Open issues in the sentiment analysis of Arabic social media: A case study
With the rapid increase in the volume of Arabic opinionated posts on different microblogging mediums comes an increasing demand for Arabic sentiment analysis tools. Yet, research in the area of Arabic sentiment analysis is progressing at a very slow pace compared to that being carried out in English and other languages. This paper highlights the major problems and open research issues that face sentiment analysis of Arabic social media. The paper also presents a case study the goal of which is to investigate the possibility of determining the semantic orientation of Arabic Egyptian tweets and
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 16
- Next page ››
