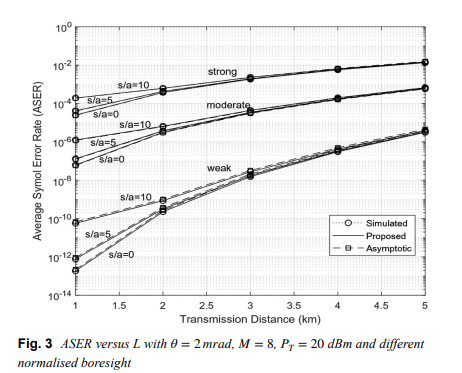
Generic evaluation of FSO system over Málaga turbulence channel with MPPM and non-zero-boresight pointing errors
Free space optical (FSO) communication channels are affected by fluctuations in irradiance due to atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors. Recently, a generalized statistical model knows as Málaga (M) was developed to describe irradiance fluctuations of the beam propagating through a turbulent medium. In this paper, an approximate finite-series probability density function (PDF) for composite M turbulence with pointing errors is verified. Considering multiple pulseposition- modulation (MPPM) with intensity modulation and direct detection, specific closed-form expressions for average symbol

6G: A comprehensive survey on technologies, applications, challenges, and research problems
The inherent limitations of the network keep on going to be revealed with the continuous deployment of cellular networks. The next generation 6G is motivated by these drawbacks to properly integrate important rate-hungry applications such as extended reality, wireless brain-computer interactions, autonomous vehicles, and so on. Also, to support significant applications, 6G will handle large amounts of data transmission in smart cities with much lower latency. It combines many state-of-the-art trends and technology to provide higher data rates for ultra-reliable and low latency communications
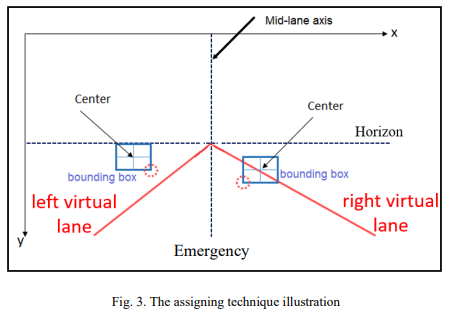
Demonstration of Forward Collision Warning System Based on Real-Time Computer Vision
This paper demonstrates the software and hardware of a forward-collision warning system using techniques of realtime computer vision which helps self-driving cars and autonomous vehicles systems to merge with the road environment safely and ensure the reliability of these systems. The software approach of the paper consists of five parts: car detection, depth estimation, lane assignation, the relative speed of other cars and their corresponding speed limit and finally ultrasonic sensors which completes the front of the vehicle as the camera can't cover it alone. Besides these five objectives
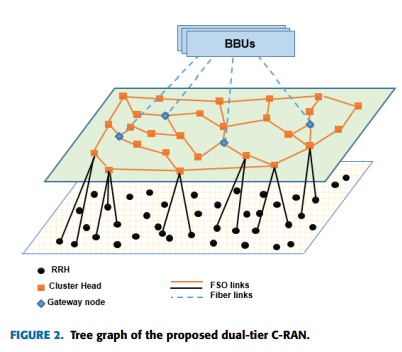
Dynamic Traffic Model with Optimal Gateways Placement in IP Cloud Heterogeneous CRAN
In this paper, topology design, optimal routing, and gateways placement selection algorithms are proposed in Heterogeneous Cloud Radio Access Network (C-RAN) with exploiting Free Space Optical (FSO) communication. The proposed network consists of two tiers; the lower tier concerns with clustering Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) based on traffic demands. The upper tier consists of transceivers along with the Cluster Heads (CHs) and gateways. Algorithms are proposed to achieve the lowest number of edges and the highest possible throughput based on the presented optimization problem. Moreover, route

Review organic solar cells parameters extraction and characterization techniques
Organic photovoltaic research is continuing in order to improve the efficiency and stability of the products. Organic devices have recently demonstrated excellent efficiency, bringing them closer to the market. Understanding the relationship between the microscopic parameters of the device and the conditions under which it is prepared and operated is essential for improving performance at the device level. This review paper emphasizes the importance of the parameter extraction stage for organic solar cell investigations by offering various device models and extraction methodologies. In order

Impact of Temporally Correlated Nakagami-m Interferers in D2D Cache-Aided Networks
In this paper, we exploit tools from stochastic geometry to characterize the average probability of successful content delivery in a cache-enabled device-to-device (D2D) network under Nakagami- m fading. Specifically, we focus on the impact of temporal interference correlation due to erroneous packets retransmissions. The aggregate network interference is characterized under a slotted Aloha scheme in a homogeneous Poisson field of static interferers. In addition, the effect of different system parameters, such as the content popularity, intensity of devices, and D2D communication range, on the
Improved spectrum mobility using virtual reservation in collaborative cognitive radio networks
Cognitive radio technology would enable a set of secondary users (SU) to opportunistically use the spectrum licensed to a primary user (PU). On the appearance of this PU on a specific frequency band, any SU occupying this band should free it for PUs. Typically, SUs may collaborate to reduce the impact of cognitive users on the primary network and to improve the performance of the SUs. In this paper, we propose and analyze the performance of virtual reservation in collaborative cognitive networks. Virtual reservation is a novel link maintenance strategy that aims to maximize the throughput of
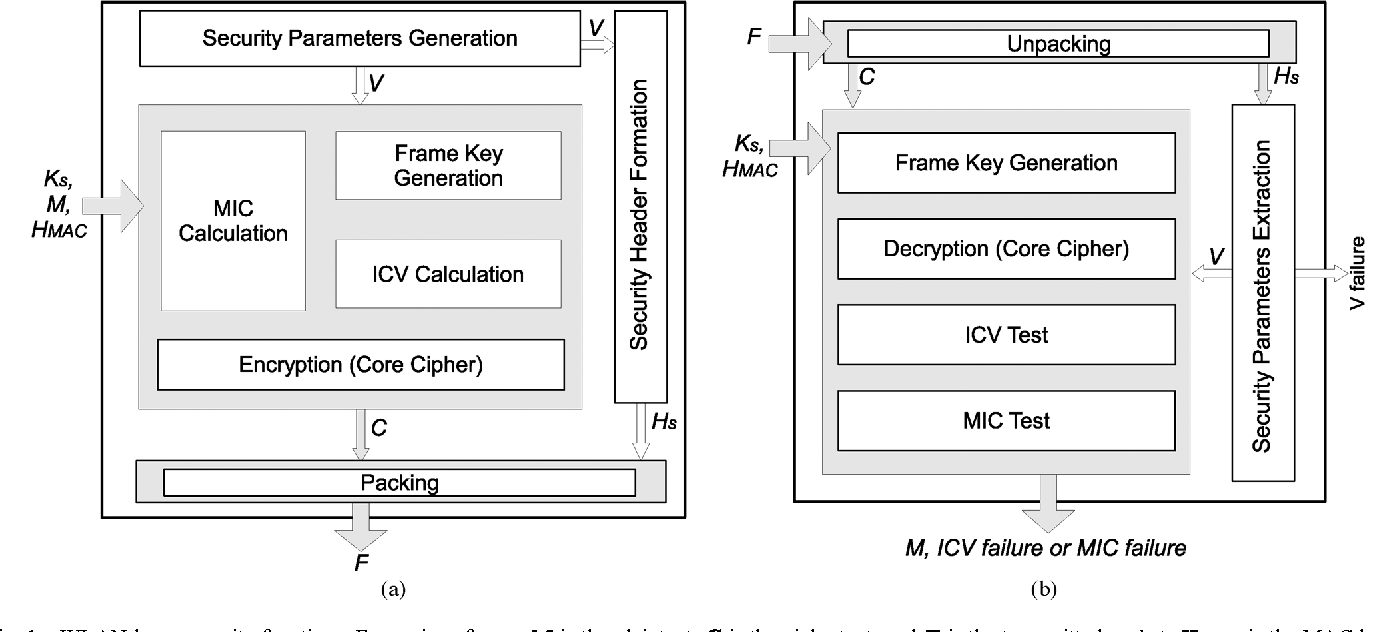
Keys through ARQ: Theory and practice
This paper develops a novel framework for sharing secret keys using the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) protocol. We first characterize the underlying information theoretic limits, under different assumptions on the channel spatial and temporal correlation function. Our analysis reveals a novel role of dumb antennas in overcoming the negative impact of spatial correlation on the achievable secrecy rates. We further develop an adaptive rate allocation policy, which achieves higher secrecy rates in temporally correlated channels, and explicit constructions for ARQ secrecy coding that enjoy low

Multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT)
In this paper we study the problem of tag identification in multi-reader RFID systems. In particular, we propose a novel solution to the reader-to-reader collisions and tag collisions in multi-reader systems, using the concept of bit tracking [1]. Towards this objective, we propose the multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT) algorithm which allows concurrent tag identification, by neighboring RFID readers, as opposed to time-consuming scheduling. First, MRTI-BT identifies tags exclusive to different RFIDs, concurrently. Second, the concept of bit tracking and the
Analytical Markov model for slotted ALOHA with opportunistic RF energy harvesting
In this paper, we investigate the performance of an ALOHA random access wireless network consisting of nodes with and without RF energy harvesting capability. We develop and analyze a Markov model for the system when nodes with RF energy harvesting capability are infinitely backlogged. Our results indicate that the network throughput is improved when the conventional nodes are underloaded. On the contrary, when all types of nodes have finite backlogs, we numerically demonstrate that the network throughput and delay are improved when the overall system is overloaded. We show that there exists a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
