Remote prognosis, diagnosis and maintenance for automotive architecture based on least squares support vector machine and multiple classifiers
Software issues related to automotive controls account for an increasingly large percentage of the overall vehicles recalled. To alleviate this problem, vehicle diagnosis and maintenance systems are increasingly being performed remotely, that is while the vehicle is being driven without need for factory recall and there is strong consumer interest in Remote Diagnosis and Maintenance (RD&M) systems. Such systems are developed with different building blocks/elements and various capabilities. This paper presents a novel automotive RD&M system and prognosis architecture. The elements of the
ITS navigation and live timetables for the blind based on RFID robotic localization algorithms and ZigBee broadcasting
This paper tries to alleviate some challenges facing blind and visually impaired people in public transportation systems by providing them with in-station navigation information and real-time schedule information. Novel system architecture for the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) navigation for blind and visually impaired people based on recent Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) localization technologies, commonly used in robotics, is proposed. Furthermore, a live timetable using a new ZigBee network broadcasting protocol with detailed frame structure is used for provision of real
Convergence study of IPv6 tunneling techniques
IPv4 address exhaustion pushed IETF to create IPv6, the improved substitute of IPv4. The Internet complexity and its enormous size prolong the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 process. This means that both versions will necessarily co-exist. Meanwhile, tunneling appears as a solution trend. The tunneling is a transition technique that is considered temporary till all ISPs would support IPv6. At this paper, we compare the routing convergence of two tunnel types, 6to4 and Manually Configured versus the conventional IPv4 and IPv6 protocols. We analyze the network resources consumed during cold start
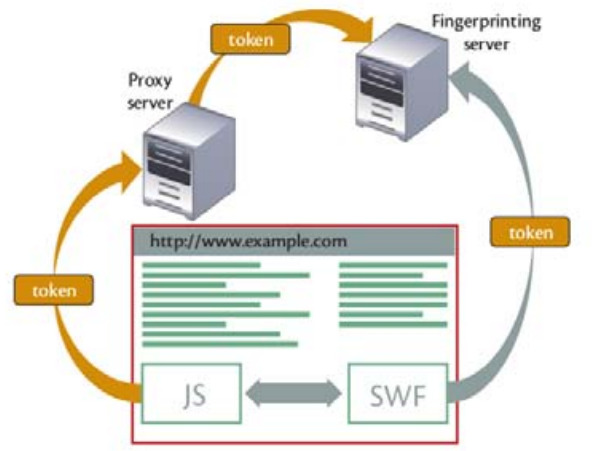
Browsers fingerprinting motives, methods, and countermeasures
With the continuous and aggressive competition in advertising businesses, uncontrollably desires have emerged to identify and classify consumers. It is proven that companies must have a clear definition of its target market. Based on this we have seen different ways to identify, analyze, and track consumers, either voluntarily or without their consent. Browser fingerprinting techniques have evolved from being privacy-friendly to privacy intrusive to serve these demands. This also has pushed privacy concerned people to save no effort to advance countermeasures. In this paper we introduce

NONYM!ZER: Mitigation Framework for Browser Fingerprinting
Not only recent compelled cookies regulations have radically restrained their threats but also increased people awareness has played a fundamental part. This has placed huge pressure on enterprises to find alternatives to bridge this gap and satisfy business demands. Since then fingerprinting has gained enormous popularity. In this paper, we introduce 'nonym!zer' as a mitigation framework for browser fingerprinting. It helps to hinder or impede browser fingerprinting on desktop browsers that web servers use such as WebGL or Canvas technologies. © 2019 IEEE.
Cloud computing security: Challenges & future trends
Cloud computing is one of the most trendy terminologies. Cloud providers aim to satisfy clients' requirements for computing resources such as services, applications, networks, storage and servers. They offer the possibility of leasing these resources rather than buying them. Many popular companies, such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft, began to enhance their services and apply the technology of cloud computing to provide cloud environment for their customers. Although there are lots of advantages in using a cloud-based system, some issues must be handled before organisations and individuals
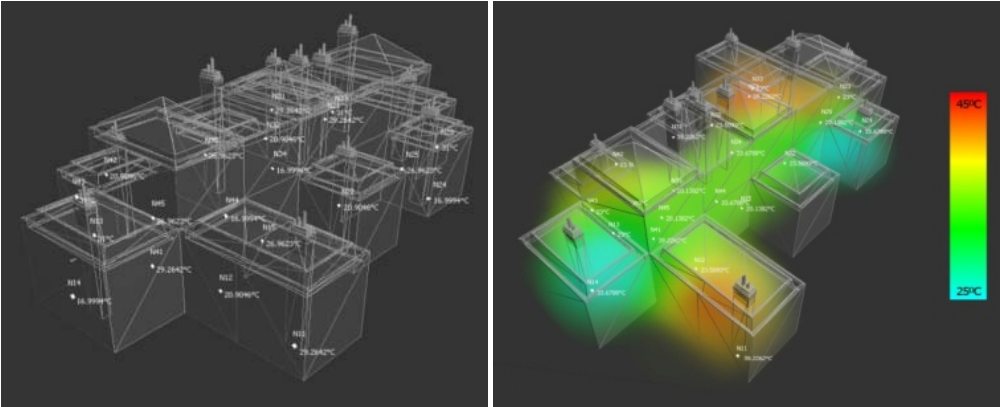
Monitoring and visualization of large WSN deployments
Recent developments in wireless sensor networks have ushered in novel ubiquitous computing applications based on distributed large-scale data acquisition and interactive interpretation. However, current WSNs suffer from lack of effective tools to support large network deployment and administration as well as unavailability of interactive visualization techniques required to explore and analyze captured sensing data, which is hindering the development of real-life WSN-based ubiquitous systems. Sensor Explorer addresses the above problems by providing modular efficient stream management engine

Ambient and wearable sensing for gait classification in pervasive healthcare environments
Pervasive healthcare environments provide an effective solution for monitoring the wellbeing of the elderly where the general trend of an increasingly ageing population has placed significant burdens on current healthcare systems. An important pervasive healthcare system functionality is patient motion analysis where gait information can be used to detect walking behavior abnormalities that may indicate the onset of adverse health problems, for quantifying post-operative recovery, and to observe the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The development of accurate motion analysis models
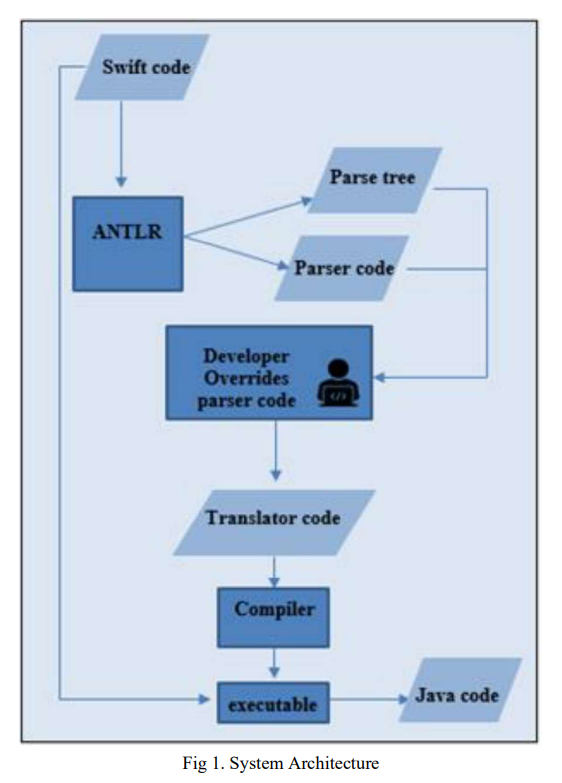
Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications code converter: Swift to java
Numerous commercial tools like Xamarin, React Native and PhoneGap utilize the concept of cross-platform mobile applications development that builds applications once and runs it everywhere opposed to native mobile app development that writes in a specific programming language for every platform. These commercial tools are not very efficient for native developers as mobile applications must be written in specific language and they need the usage of specific frameworks. In this paper, a suggested approach in TCAIOSC tool to convert mobile applications from Android to iOS is used to develop the
In-silico development and assessment of a Kalman filter motor decoder for prosthetic hand control
Up to 50% of amputees abandon their prostheses, partly due to rapid degradation of the control systems, which require frequent recalibration. The goal of this study was to develop a Kalman filter-based approach to decoding motoneuron activity to identify movement kinematics and thereby provide stable, long-term, accurate, real-time decoding. The Kalman filter-based decoder was examined via biologically varied datasets generated from a high-fidelity computational model of the spinal motoneuron pool. The estimated movement kinematics controlled a simulated MuJoCo prosthetic hand. This clear-box
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 44
- Next page ››
