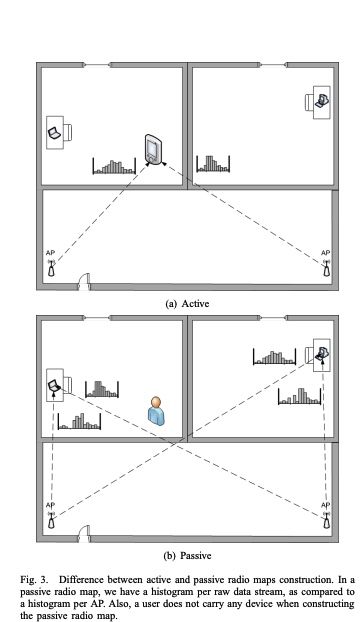
A deterministic large-scale device-free passive localization system for wireless environments
The widespread usage of wireless local area networks and mobile devices has fostered the interest in localization systems for wireless environments. The majority of research in the context of wirelessbased localization systems has focused on device-based active localization, in which a device is attached to tracked entities. Recently, device-free passive localization (DfP) has been proposed where the tracked entity is neither required to carry devices nor participate actively in the localization process. DfP systems are based on the fact that RF signals are affected by the presence of people
Asymmetric degrees of freedom of the full-duplex MIMO 3-way channel
In this paper, we characterize the asymmetric total degrees of freedom (DoF) of a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) 3-way channel. Each node has a separate-antenna full-duplex MIMO transceiver with a different number of antennas, where each antenna can be configured for either signal transmission or reception. Each node has two unicast messages to be delivered to the two other nodes. We first derive upper bounds on the total DoF of the system. Cut-set bounds in conjunction with genie-aided bounds are derived to characterize the achievable total DoF. Afterwards, we analytically derive the
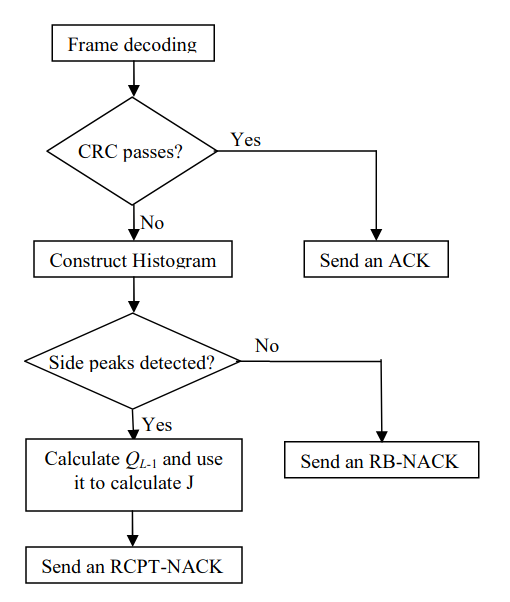
Novel reliability-based hybrid ARQ technique
In this paper we propose a novel technique for hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) systems where turbo codes are used as the forward error correction (FEC) techniques. This technique uses the histogram of the soft values generated by the turbo decoder to control the size and the contents of the retransmissions needed when the packet can not be decoded correctly. These soft values represent the reliabilities of the information bits; hence the proposed technique is a reliability-based (RB) HARQ technique. The proposed technique is compared to the conventional RB-HARQ and the conventional rate
Graph transformer for communities detection in social networks
Graphs are used in various disciplines such as telecommunication, biological networks, as well as social networks. In large-scale networks, it is challenging to detect the communities by learning the distinct properties of the graph. As deep learning has made contributions in a variety of domains, we try to use deep learning techniques to mine the knowledge from large-scale graph networks. In this paper, we aim to provide a strategy for detecting communities using deep autoencoders and obtain generic neural attention to graphs. The advantages of neural attention are widely seen in the field of
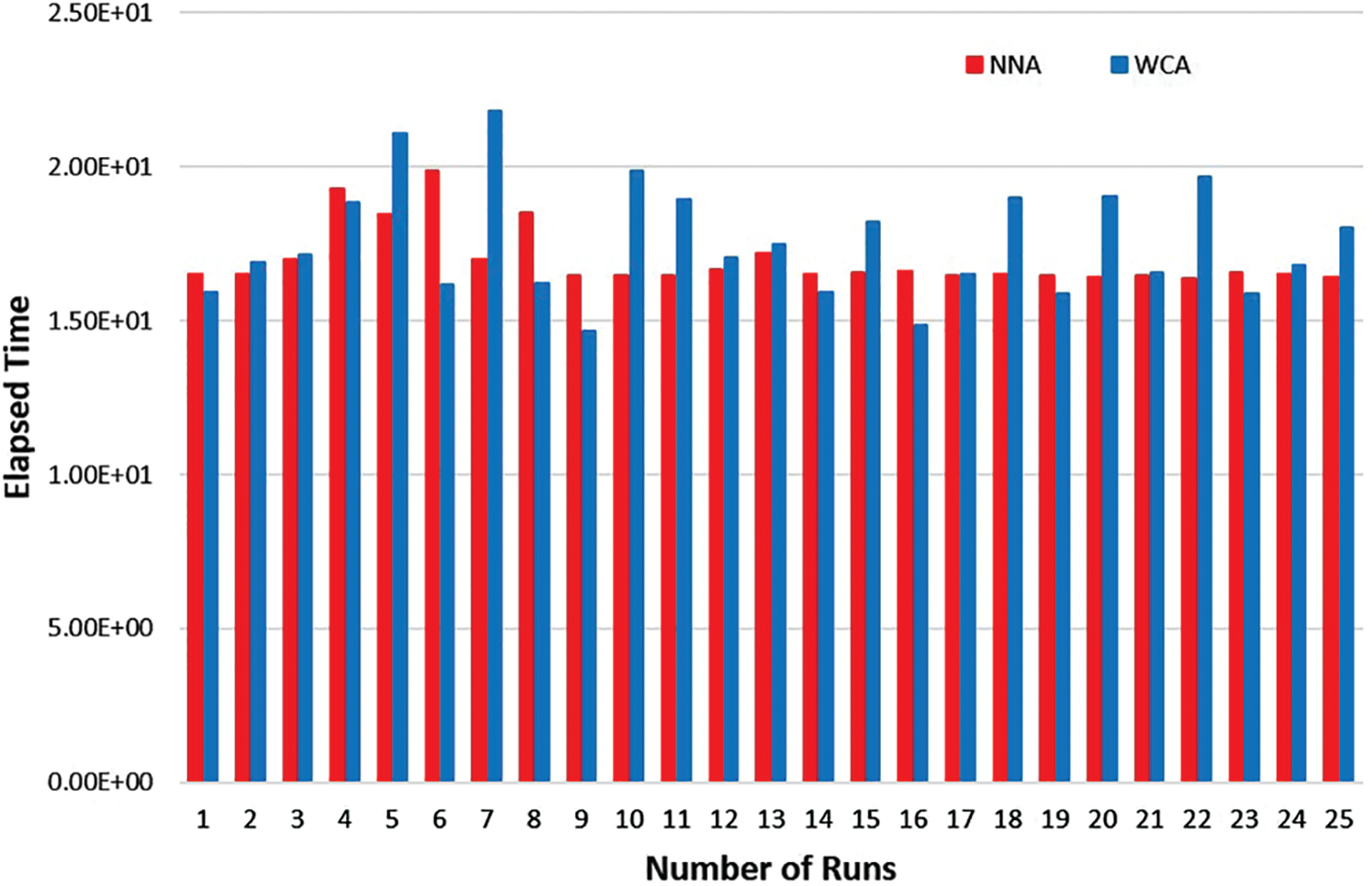
An artificial intelligence approach for solving stochastic transportation problems
Recent years witness a great deal of interest in artificial intelligence (AI) tools in the area of optimization. AI has developed a large number of tools to solve the most difficult search-and-optimization problems in computer science and operations research. Indeed, metaheuristic-based algorithms are a sub-field of AI. This study presents the use of the metaheuristic algorithm, that is, water cycle algorithm (WCA), in the transportation problem. A stochastic transportation problem is considered in which the parameters supply and demand are considered as random variables that follow the

Interference alignment for secrecy
This paper studies the frequency/time selective K-user Gaussian interference channel with secrecy constraints. Two distinct models, namely the interference channel with confidential messages and the interference channel with an external eavesdropper, are analyzed. The key difference between the two models is the lack of channel state information (CSI) of the external eavesdropper. Using interference alignment along with secrecy precoding, it is shown that each user can achieve non-zero secure degrees of freedom (DoF) for both cases. More precisely, the proposed coding scheme achieves K-2/2K-2
Feedback-based access schemes in CR networks: A reinforcement learning approach
In this paper, we propose a Reinforcement Learning-based MAC layer protocol for cognitive radio networks, based on exploiting the feedback of the Primary User (PU). Our proposed model relies on two pillars, namely an infinite-state Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) to model the system dynamics besides a queuing-theoretic model for the PU queue, where the states represent whether a packet is delivered or not from the PU's queue and the PU channel state. Based on the stability constraint for the primary user queue, the quality of service (QoS) for the PU is guaranteed. Towards
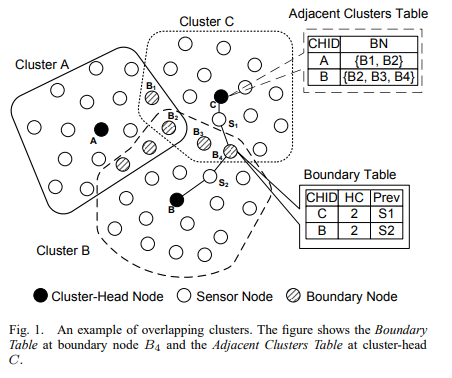
Overlapping multihop clustering for wireless sensor networks
Clustering is a standard approach for achieving efficient and scalable performance in wireless sensor networks. Traditionally, clustering algorithms aim at generating a number of disjoint clusters that satisfy some criteria. In this paper, we formulate a novel clustering problem that aims at generating overlapping multihop clusters. Overlapping clusters are useful in many sensor network applications, including intercluster routing, node localization, and time synchronization protocols. We also propose a randomized, distributed multihop clustering algorithm (KOCA) for solving the overlapping
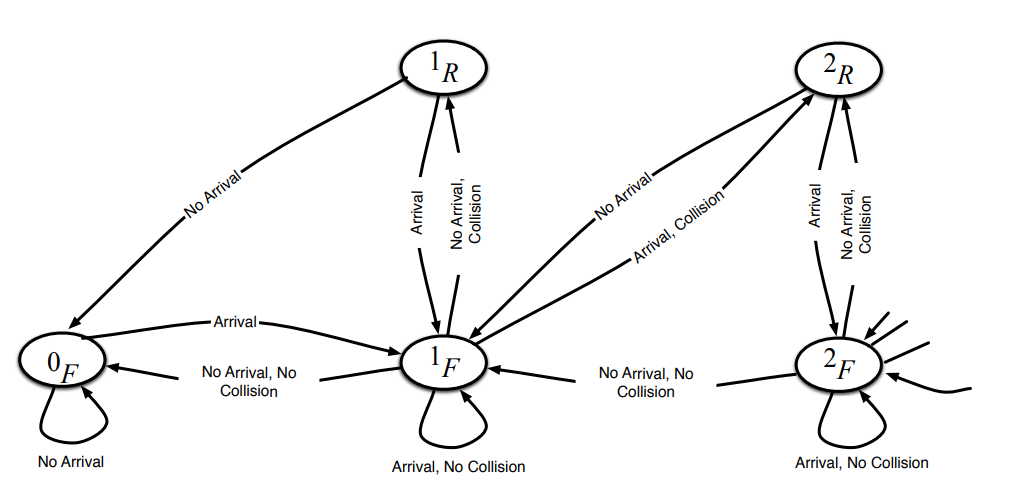
A reinforcement learning approach to ARQ feedback-based multiple access for cognitive radio networks
In this paper, we propose a reinforcement learning (RL) approach to design an access scheme for secondary users (SUs) in a cognitive radio (CR) network. In the proposed scheme, we introduce a deep Q-network to enable SUs to access the primary user (PU) channel based on their past experience and the history of the PU network's automatic repeat request (ARQ) feedback. In essence, SUs cooperate to avoid collisions with other SUs and, more importantly, with the PU network. Since SUs cannot observe the state of the PUs queues, they partially observe the system's state by listening to the PUs' ARQ
Symbol based log-MAP in concatenated LDPC-convolutional codes
In this paper we study the use of a high rate Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes in concatenated coding structures. Specifically, we use the LDPC code as an outer code, with a convolutional code as an inner code. We decode the convolutional code using a symbol based Log-MAP (Maximum a posteriori probability) decoder, and feed the soft outputs of this decoder into a non-binary Galois Field LDPC decoder. We compare this concatenation scheme using 16 QAM modulation with one using a bit based Log-MAP decoder over Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) and Stanford University Interim (SUI-3)
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 43
- Next page ››
