Cad tool for two-digit ternary functions design
Ternary number, which attracts the research attention for its high capacity, has emerged in many applications, recently. Unlike binary numbers, two bit ternary number involves 93 = 729 different functions while two bit binary number involves only 42 = 16 different possible functions. In this paper, a novel automatic software description two bits ternary functions design tool is presented. Different examples are provided and synthesized to ternary logic circuits. Finally, the presented logic circuits are verified by SPICE simulation using carbon nano-Tube (CNTFET) transistors. © 2019 IEEE.
Comparative study of fractional filters for Alzheimer disease detection on MRI images
This paper presents a comparative study of four fractional order filters used for edge detection. The noise performance of these filters is analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) of the detected images is numerically compared. The mean square error (MSE) of the detected images as well as the execution time are also adopted as evaluation methods for comparison. The visual comparison of the filters capability in medical image edge detection is presented, that can help in the diagnosis of

Guest editorial mission critical networking
[No abstract available]
Fractional canny edge detection for biomedical applications
This paper presents a comparative study of edge detection algorithms based on integer and fractional order differentiation. A performance comparison of the two algorithms has been proposed. Then, a soft computing technique has been applied to both algorithms for better edge detection. From the simulations, it shows that better performance is obtained compared to the classical approach. The noise performances of those algorithms are analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The performance has been compared to peak signal to noise
FPGA realization of ALU for mobile GPU
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the most important component of processors. All arithmetic and logical computations are performed inside the ALU. This paper presents the design and the implementation of the ALU. The design is based on Approximated Precision Shader and Look-Up Table (LUT) multiplier. The lookup table, Wallace tree, and Carry Look-ahead Adder (CLA) are used in combination to speed up the multiplier operation. The proposed ALU is designed using Verilog and verified using Xilinx Virtex-5 XC5VLX30 FPGA. © 2016 IEEE.
Reconfigurable chaotic pseudo random number generator based on FPGA
This paper presents an FPGA Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) that is based on the Lorenz and Lü chaotic systems. These two systems are used to generate four different 3D chaotic attractors. One attractor is generated from Lorenz while the other three attractors are generated from Lü. The output attractor of the proposed PRNG can be reconfigured during real time operation using an efficient hardwired shifting and multiplexing scheme. Furthermore, in order to exploit the proposed reconfiguration feature, the proposed PRNG has been embedded in an FPGA cascaded encryption processor that
Controllable OTA Slew-rate for CMOS Image Sensor
In this work, a proposed circuit is implemented using tsmc 0.18um technology of area 16642 um2 with supply voltage equals 5V. A proposed implementation of a controllable Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) slew rate for CMOS image sensor (CIS) is proposed. The slew rate is controlled by switching between various bias circuits for the OTA. The biasing circuit controls the value of OTA biased current, which allows controlling the amplifier's characteristics. As the flicker noise in the main contributor in reducing the quality of image sensors performance. The proposed circuit allows
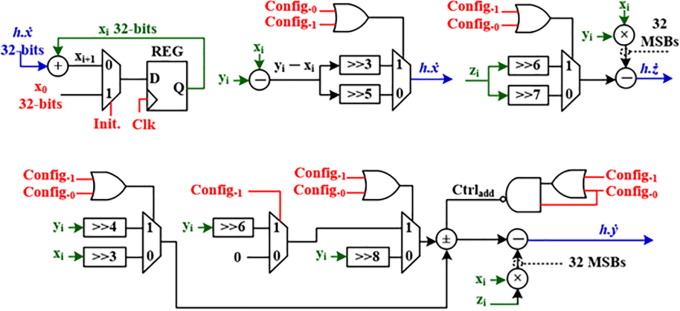
Advance Interconnect Circuit Modeling Design Using Fractional-Order Elements
Nowadays, the interconnect circuits' conduct plays a crucial role in determining the performance of the CMOS systems, especially those related to nano-scale technology. Modeling the effect of such an influential component has been widely studied from many perspectives. In this article, we propose a new general formula for RLC interconnect circuit model in CMOS technology using the fractional-order elements approach. The study is based on approximating an infinite transfer function of the CMOS circuit with a noninteger distributed RLC load to a finite number of poles. It is accurate due to the
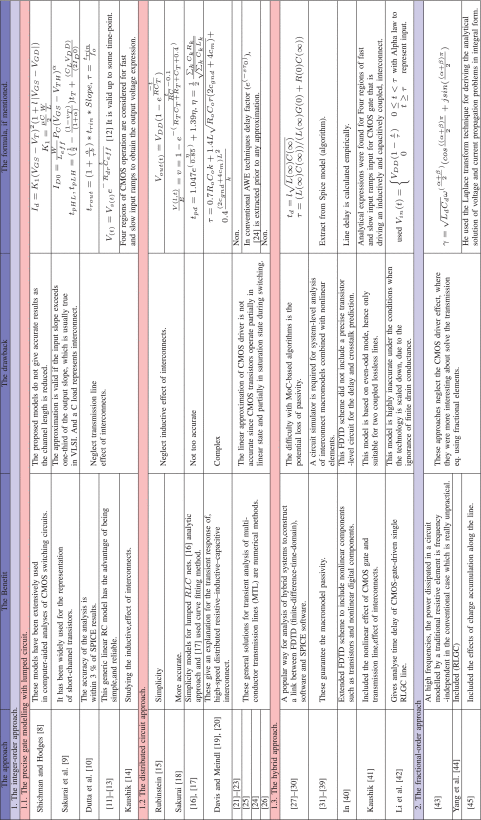
Fully balanced LED driving circuit for optogenetics stimulation
Implantable probes with built-in light emitters have a promising potential for a range of applications, in particular optogenetic neural stimulation. However, where soft encapsulation methods are used, lifetime will be a function of the quality of encapsulation and the driving mechanism. We have found that a balanced driving mechanism - whereby the integral voltage on encapsulated contacts, can significantly prolong lifetimes. As such, in this work, we have designed a driving circuit that drives current but ensures balanced electric fields with an error of less than 1%. The circuit has been
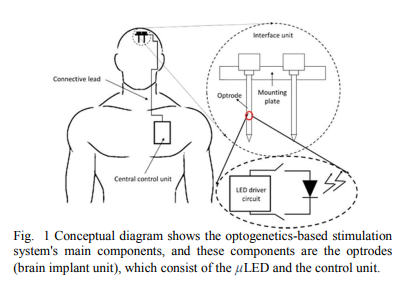
IoT ethics challenges and legal issues
IoT systems have different technologies such as: RIFD, NFC, 3G, 4G, and Sensors. Their function is to transfer very large sensitive and private data. There are many ethical challenges that need to be taken into consideration by individuals and companies that use this technology. Amongst the challenges is the user awareness of attack risks. This paper discusses different ethical and legal challenges that need to be taken in account for IoT health care applications during the near future. © 2017 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
