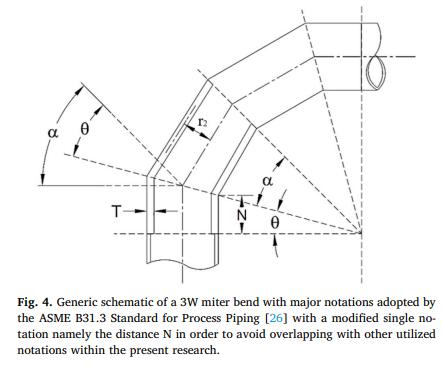
Load carrying capacities of pressurized 90 degree miter and smooth bends subjected to monotonic in-plane and out-of-plane bending loadings
The present research focuses on generating interaction diagrams (i.e. limit moment boundaries vs steady internal pressure spectra) of pressurized 90 o miter and smooth bends. One-, two-, three-, and four-weld miter bends are modelled and analyzed. Additionally, 90 o smooth bends (SBs) bearing the miter bends’ same material and major geometric parameters are analyzed thus providing broader range of comparisons concerning structural responses to external applied loadings. All bends analyzed are subjected to steady internal pressure spectra and monotonic in-plane closing, in-plane opening, and
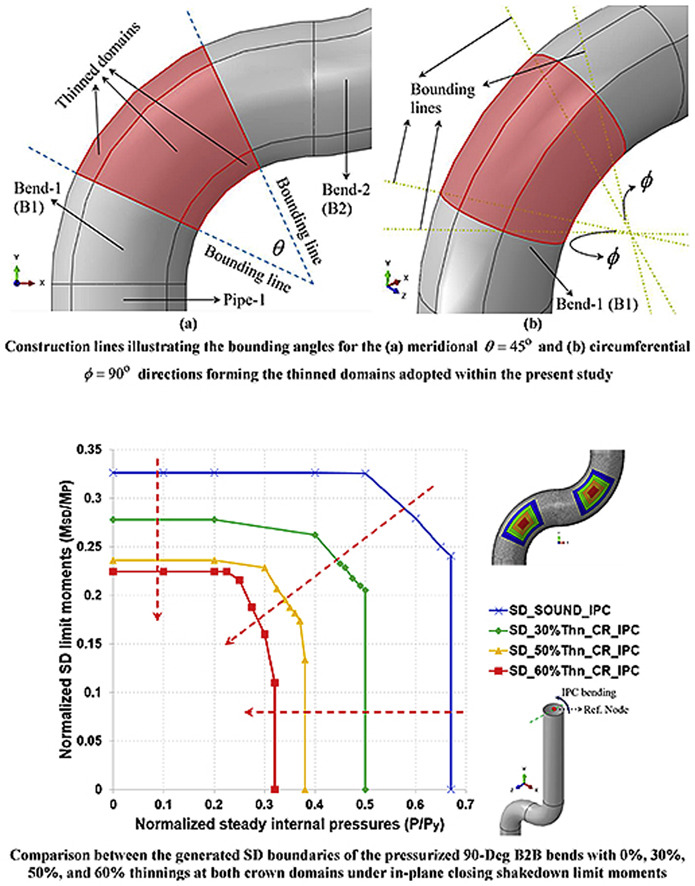
Effect of wall thinning on the Shakedown Interaction Diagrams of 90-degree back-to-Back Bends Subjected to Simultaneous Steady Internal Pressures and Cyclic In Plane Bending Moments
This research studies the effect of wall thinning on generated shakedown (SD) interaction diagrams of pressurized low-carbon steel 90-degree (90-Deg) back-to-back (B2B) bends. More precisely, the SD limit moments are determined for various steady internal pressure spectra thus generating the targeted SD boundaries. The SD limit moments are computed utilizing a direct non-cyclic technique termed: SD-DNT short for Shakedown-Direct Noncyclic Technique. The bends analyzed are subjected to simultaneous steady internal pressure spectra and cyclic in-plane closing (IPC) and in-plane opening (IPO)
Effect of cracks in wind turbine blades on natural frequencies during operation
Most publications that are concerned with the crack detection via analyzing Eigenfrequencies or deformation modes of wind turbine blades (WTBs) are done in stationary condition. This paper however proposes a novel approach that could study the effect of WTB cracks during rotation at any speed without the need to stop the turbine by using multibody analysis. This approach will reduce the cost of its maintenance substantially, since it will avoid the cost of downtime for wind turbine during crack detection. This approach considers both the increase in stiffness due to rotation (known as
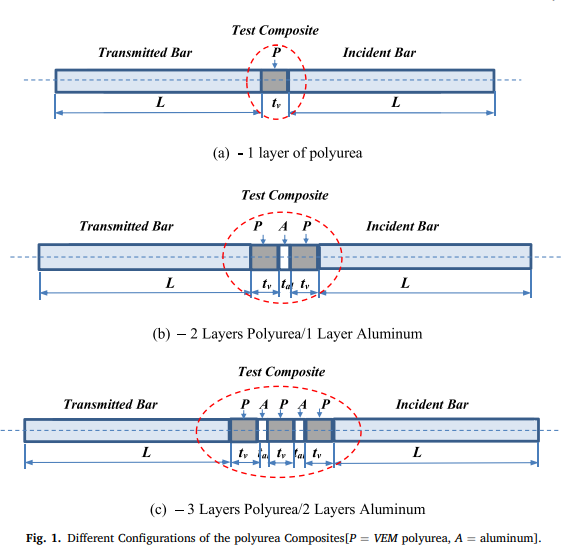
Dynamic behavior of polyurea composites subjected to high strain rate loading
A comprehensive theoretical and experimental investigation is presented of the behavior of polyurea composites subjected to high strain-rate impact loading. The composites under consideration consist of an assembly of steel sections and inserts manufactured from layers of polyurea or polyurea augmented with aluminum layers (AL). A finite element model (FEM) is developed to predict the dynamics of this class of polyurea composites by integrating the dynamics of the solid steel sections with those of polyurea using the Golla-Hughes-Mctavish (GHM) mini-oscillator approach. The predictions of the
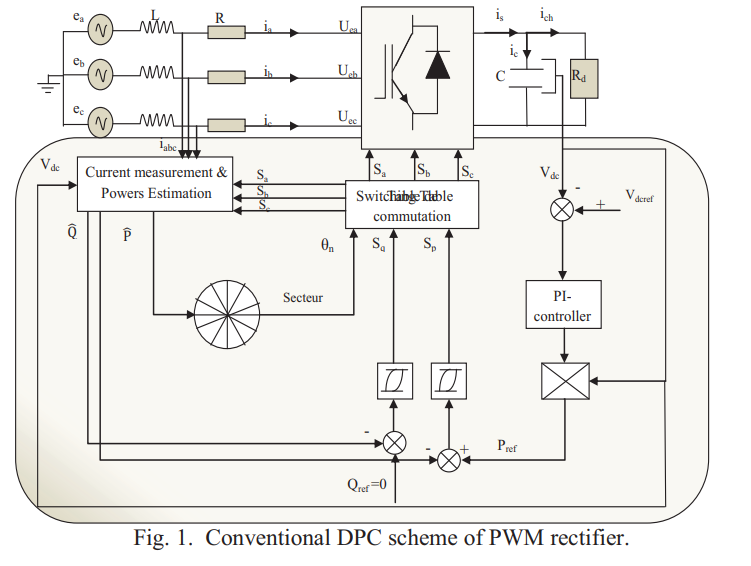
Direct Power Control of a three-phase PWM-Rectifier based on Petri nets for the selection of Switching States
This article proposes a new simple scheme for direct power control of a PWM rectifier without a switch table and voltage sensor. The selection of the switching state of the converter is based on the transition of a Petri net, using the instantaneous active and reactive power tracking errors and the angular position of the network line voltage estimated as variables of Controller input based on Petri nets. Simulation and experimental results demonstrated better performance and verified the validity of the new command with the Petri nets applied to the bridge rectifier connected to the
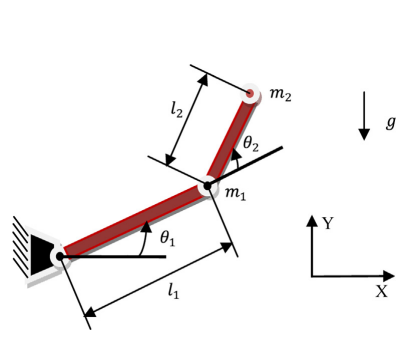
Design of fractional order fuzzy sliding mode controller for nonlinear complex systems
Controlling a nonlinear, time-varying, uncertain, coupled multiinput-multioutput (MIMO) complex system is always a challenging task for control engineers. A linear PID controller is not able to control effectively these complex systems and a robust adaptive controller is needed for perfect control. In this chapter, a fractional order fuzzy sliding mode proportional derivative (FOFSMCPD) controller is presented to control a two-link planar rigid robotic manipulator system. Literature reveals that sliding mode controllers (SMC) have the serious issue of fast oscillations, called chattering, in
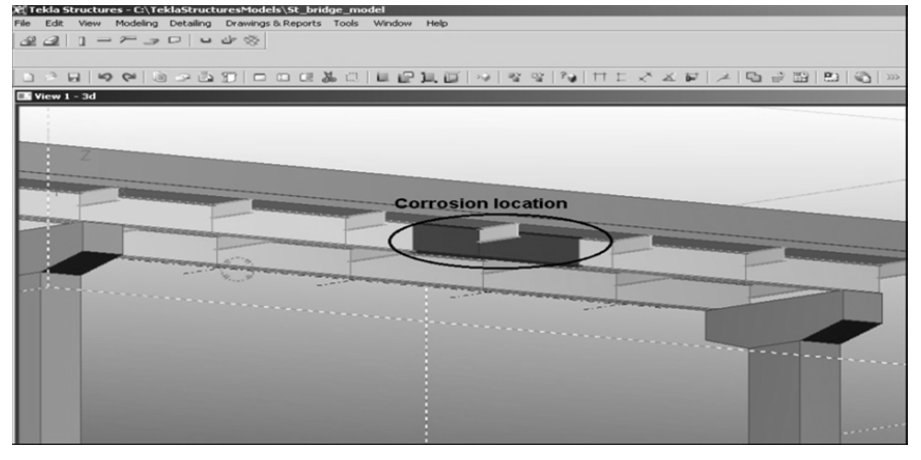
Bridge information modeling in sustainable bridge management
Bridge Management Systems (BMS) play a crucial role in maintenance and rehabilitation decisions related to bridges. This paper presents using Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM) framework that adopts BMS features including; databases, inspection module, and condition assessment module. The proposed BrIM framework creates a database of bridges' components and generates inspection spreadsheets. It also visualizes bridge components considering the information stored in the database and inspection spreadsheets, using Structured Query Language (SQL) statements. The paper presents the integration of
Conceptual cost estimation of pump stations projects using fuzzy clustering
Conceptual cost estimates, are prepared at the very early stages of a project, and generally before the construction drawings and specifications are available. At this stage, cost estimates are needed by the owner, contractor, designer, or funding agencies for determination of the feasibility of a project, financial evaluation of a number of alternative projects, or establishment of an initial budget. Traditional approaches rely heavily on experienced engineers. This paper presents a method using fuzzy clustering technique for pump station projects cost estimation. The proposed conceptual cost
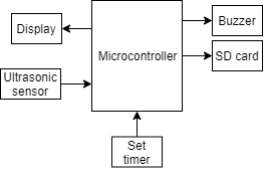
Simulation of vitiligo therapy equipment
Vitiligo is a skin disorder caused by a lack of melanin pigment in the skin, which causes white patches on certain parts of the skin because this melanin pigment is not able to produce the skin color. Previously, one of the treatments for vitiligo was using a UVB lamp with a 311 nm wavelength that could not yet be adjusted to dim the lights as safety when conducting therapy. Therefore, the research aims to design a simulation of the vitiligo therapy device equipped with a timer LED lamp, a safety of lighting, and the data storage. The data are stored in the SD Card to make it easier for
Fractional Order Two Degree of Freedom PID Controller for a Robotic Manipulator with a Fuzzy Type-2 Compensator
In this paper a novel strategy for the position control and trajectory tracking of robotic manipulators is proposed. This strategy consists of an independent two degree of freedom PID controller for a two links robotic arm. Due to the capability of two degree of freedom PID controllers to deal with disturbances, each link is controlled independently considering that the disturbance does not affect the system performance due to the robustness of the closed loop system. Then, a fuzzy type-2 centralized compensator is implemented to drive the orientation variables with the desired trajectory in
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
