Assessing lean systems using variability mapping
A new approach to assess lean manufacturing based on system's variability is proposed. The assessment utilizes a new tool called variability source mapping (VSMII) which focuses on capturing and reducing variability across the production system. The new tool offers a new metric called variability index to measure the overall variability level of the system. Based on the mapping and the new metric, VSMII suggests a variability reduction plan guided by a recommendation list of both lean techniques as well as production control policies. An industrial application is used to demonstrate the new

Supply Chain Risk Assessment Using Fuzzy Logic
Business's strength arises from the strength of its supply chain. Therefore, a proper supply chain management is vital for business continuity. One of the most challenging parts of SCM is the contract negotiation, and one main aspect of the negotiation is to know the risk associated with each range of quantity agreed on. Currently Managers assess the quantity to be supplied based on a binary way of either full or 0 supply, This paper aims to assess the corresponding quantities risks of the suppliers on a multilayer basis. The proposed approach uses fuzzy logic as an artificial intelligence
In-Silico Comparative Analysis of Egyptian SARS CoV-2 with Other Populations: A Phylogeny and Mutation Analysis
In the current SARS-CoV2 pandemic, identification and differentiation between SARS-COV2 strains are vital to attain efficient therapeutic targeting, drug discovery and vaccination. In this study, we investigate how the viral genetic code mutated locally and what variations is the Egyptian population most susceptible to in comparison with different strains isolated from Asia, Europe and other countries in Africa. Our aim is to evaluate the significance of these variations and whether they constitute a change on the protein level and identify if any of these variations occurred in the conserved
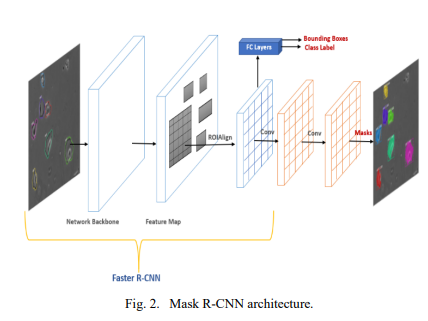
Instance Segmentation of 2D Label-Free Microscopic Images using Deep Learning
The precise detection and segmentation of cells in microscopic image sequences is an essential task in biomedical research, such as drug discovery and studying the development of tissues, organs, or entire organisms. However, the detection and segmentation of cells in phase contrast images with a halo and shade-off effects is still challenging. Lately, Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN) has been introduced for object detection and instance segmentation of natural images. This study investigates the efficacy of the Mask R-CNN to instantly detect and segment label-free
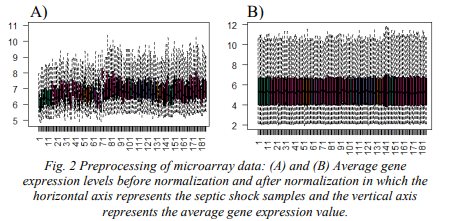
Studying Genes Related to the Survival Rate of Pediatric Septic Shock
Pediatric septic shock is generally considered as a devastating clinical syndrome that can lead to tissue damage and organ failure due to the over exaggerated immune response to an infection. Therefore, in this paper, we attempted to early identify the clinical course of such disease with the aid of peripheral blood T-cells of 181 pediatric patients who admitted to Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Accordingly, 34 differential expressed genes have been identified as biological genetic biomarkers. Minimum redundancy and maximum relevance feature selection strategy has been proposed for the discovery
Improved Semantic Segmentation of Low-Resolution 3D Point Clouds Using Supervised Domain Adaptation
One of the key challenges in applying deep learning to solve real-life problems is the lack of large annotated datasets. Furthermore, for a deep learning model to perform well on the test set, all samples in the training and test sets should be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), which means that test samples should be similar to the samples that were used to train the model. In many cases, however, the underlying training and test set distributions are different. In such cases, it is common to adapt the test samples by transforming them to their equivalent counterparts in the
Innovative human-robot interaction for a robot tutor in biology game
Robots nowadays, are introduced to many domains and fields. One of these fields is education. We introduce integrating robots and games in education. We have designed a humanoid robot tutoring biology. Our robot is interacting with a student to play a game to enhance and examine the student's knowledge. In our game, we developed cognitive capabilities for the robot. We analyzed the features that both the robot and the game have to possess, and we developed a system for organ detection and recognition with the highest possible accuracy and lowest processing time. Our game introduces a multi
Interactive 3D visualization for wireless sensor networks
Wireless sensor networks open up a new realm of ubiquitous computing applications based on distributed large-scale data collection by embedded sensor nodes that are wirelessly connected and seamlessly integrated within the environment. 3D visualization of sensory data is a challenging issue, however, due to the large number of sensors used in typical deployments, continuous data streams, and constantly varying network topology. This paper describes a practical approach for interactive 3D visualization of wireless sensor network data. A regular 3D grid is reconstructed using scattered sensor
Neural Machine Based Mobile Applications Code Translation
Although many cross platform mobile development software used a trans-compiler-based approach, it was very difficult to generalize it to work in both directions. For example, to convert between Java for Android Development and Swift for iOS development and vice versa. This is due to the need of writing a specific parser for each source language, and a specific code generator for each destination language. Neural network-based models are used successfully to translate between natural languages, including English, French, German any many others by providing enough datasets and without the need
New governance framework to secure cloud computing
Cloud computing is enabling proper, on-demand network access to a shared pool of computing resources that is elastic in reserve and release with minimal interaction from cloud service provider. As cloud gains maturity, cloud service providers are becoming more competitive, which increase the percentage of cloud adoption. But security remains the most cited challenge in Cloud. So, while we are progressing in cloud adoption, we have to define key elements of our cloud strategy and governance. Governance is about applying policies relating to used services. Therefore, it has to include the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
