Implementing earned value management using bridge information modeling
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has widely become an effective tool in engineering and construction fields. It could be used in: generating shop drawings; detecting clashes; estimating quantities; and controlling documents. Applying BIM technology on bridges is named Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM). Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM) is an intelligent representation of bridges since it contains all information needed about bridges through their whole lifecycle. This paper presents the use of Building Information Modeling in cost and time management of infrastructure bridges. BIM-based
Influence of Periodic Surface Nanopatterning Profiles on Series Resistance in Thin-Film Crystalline Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells
In the frame of the development of thin crystalline silicon solar cell technologies, surface nanopatterning of silicon is gaining importance. Its impact on the material quality is, however, not yet fully controlled.We investigate here the influence of surface nanotexturing on the series resistance of a contacting scheme relevant for thin-film crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cells. Twodimensional periodic nanotextures are fabricated using a combination of nanoimprint lithography and either dry or wet etching, while random pyramid texturing is used for benchmarking. We compare these
Multistability Analysis and Function Projective Synchronization in Relay Coupled Oscillators
Regions of stability phases discovered in a general class of Genesio-Tesi chaotic oscillators are proposed. In a relatively large region of two-parameter space, the system has coexisting point attractors and limit cycles. The variation of two parameters is used to characterize the multistability by plotting the isospike diagrams for two nonsymmetric initial conditions. The parameters window in which the jerk system exhibits the unusual and striking feature of multiple attractors (e.g., coexistence of six disconnected periodic chaotic attractors and three-point attraction) is investigated. The
Study of alternative back contacts for thin film Cu2ZnSnSe4-based solar cells
Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin film solar cells are usually fabricated on a soda lime glass substrate with a molybdenum (Mo) back contact. It is suspected that degradation in electrical performance occurs due to the formation of a barrier between the absorber and Mo back contact. To overcome such degradation, Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Tungsten (TiW), Chromium (Cr), Titanium (Ti) and Aluminum (Al) deposited on Mo-coated glass substrates are investigated as alternative back contact materials. Physical and electrical characterization as well as photoluminescence measurements are performed. Compositional
New Control Schemes for Fractional Chaos Synchronization
Chaos theory deals with the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. Chaotic systems are characterized by the property that small changes in the initial conditions result in widely diverging responses. In this paper, new control schemes of synchronization for different arbitrary incommensurate and commensurate fractional order chaotic systems are presented. Synchronization stability, based on stability of linear fractional-order systems and fractional Lyapunov stability, is proved theoretically. Numerical examples are given to show the effectiveness of the
Multiswitching synchronization of commensurate fractional order hyperchaotic systems via active control
In this chapter, the multiswitching synchronization scheme has been investigated for a class of nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems. The multiswitching complete synchronization scheme has been examined such that the state variables of the slave system synchronize with different state variables of the master system. For the synchronization of two nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems suitable controllers have been designed using active control technique. The stability of fractional order chaotic systems has been used to stabilize the error dynamical system. Two
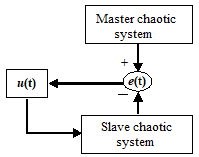
Multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems
This paper investigates the multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems in which state variables of a master system are synchronized with different state variables of a slave system using the sliding mode control technique. To design the appropriate controllers via sliding mode control for different switches, Lyapunov stability theory is taken into account. Theoretical results are applied by considering two non-identical chaotic systems where one is considered as master system and another is considered as slave system. Numerical simulations are performed to

Multistep deposition of Cu2Si(S,Se)3 and Cu2ZnSiSe4high band gap absorber materials for thin film solar cells
Cu2ZnSi(S,Se)4 and Cu2Si(S,Se)3 are potential materials to obtain cost effective high band gap absorbers for tandem thin film solar cell devices. A method to synthesize Cu2SiS3, Cu2SiSe3and Cu2ZnSiSe4thin film absorbers is proposed. This method is based on a multistep process, using sequential deposition and annealing processes. X-ray diffraction analysis performed on the final thin films have confirmed the presence of the Cu2Si(S,Se)3 and Cu2ZnSiSe4phases. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed the formation of polycrystalline layers with grains size up to 1 μm. The band gap of the
Neural Network Based Switching State Selection for Direct Power Control of Three Phase PWM-Rectifier
This article proposes an intelligent approach to the Direct Power Control technique of the PWM rectifier, this control technique improves the performance of PWM converter, called Direct Power Control Based on Artificial Neural Network (ANN), applied for the selection of the optimal control vector. DPC-ANN ensures smooth control of active and reactive power in all Sectors and reduces current ripple. Finally, the developed DPC was tested by simulation, the simulation results proved the excellent performance of the proposed DPC scheme. © 2018 IEEE.
Agent-based simulation of urban infrastructure asset management activities
This paper presents a case for adopting agent-based modeling (ABM) as a framework for representing the complex interactions that occur within the context of urban infrastructure management. A generic ABM is proposed with four key agents namely; assets, users, operators and politicians. For each agent a set of generic attributes, actions and behaviors are defined. A detailed behavioral model is adapted from the service quality domain to represent customer perceptions and actions related to infrastructure level of service. An illustrative example of 20 assets and 50 user agents is simulated to
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
