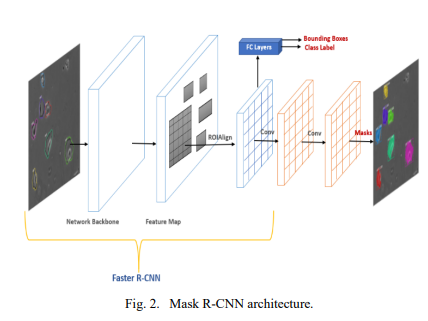
Instance Segmentation of 2D Label-Free Microscopic Images using Deep Learning
The precise detection and segmentation of cells in microscopic image sequences is an essential task in biomedical research, such as drug discovery and studying the development of tissues, organs, or entire organisms. However, the detection and segmentation of cells in phase contrast images with a halo and shade-off effects is still challenging. Lately, Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN) has been introduced for object detection and instance segmentation of natural images. This study investigates the efficacy of the Mask R-CNN to instantly detect and segment label-free
In-Silico Comparative Analysis of Egyptian SARS CoV-2 with Other Populations: A Phylogeny and Mutation Analysis
In the current SARS-CoV2 pandemic, identification and differentiation between SARS-COV2 strains are vital to attain efficient therapeutic targeting, drug discovery and vaccination. In this study, we investigate how the viral genetic code mutated locally and what variations is the Egyptian population most susceptible to in comparison with different strains isolated from Asia, Europe and other countries in Africa. Our aim is to evaluate the significance of these variations and whether they constitute a change on the protein level and identify if any of these variations occurred in the conserved

Supply Chain Risk Assessment Using Fuzzy Logic
Business's strength arises from the strength of its supply chain. Therefore, a proper supply chain management is vital for business continuity. One of the most challenging parts of SCM is the contract negotiation, and one main aspect of the negotiation is to know the risk associated with each range of quantity agreed on. Currently Managers assess the quantity to be supplied based on a binary way of either full or 0 supply, This paper aims to assess the corresponding quantities risks of the suppliers on a multilayer basis. The proposed approach uses fuzzy logic as an artificial intelligence
Assessing lean systems using variability mapping
A new approach to assess lean manufacturing based on system's variability is proposed. The assessment utilizes a new tool called variability source mapping (VSMII) which focuses on capturing and reducing variability across the production system. The new tool offers a new metric called variability index to measure the overall variability level of the system. Based on the mapping and the new metric, VSMII suggests a variability reduction plan guided by a recommendation list of both lean techniques as well as production control policies. An industrial application is used to demonstrate the new
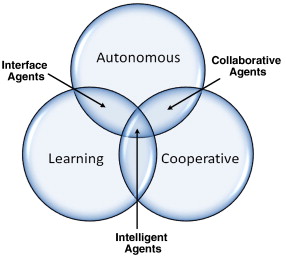
Agent-based simulation of urban infrastructure asset management activities
This paper presents a case for adopting agent-based modeling (ABM) as a framework for representing the complex interactions that occur within the context of urban infrastructure management. A generic ABM is proposed with four key agents namely; assets, users, operators and politicians. For each agent a set of generic attributes, actions and behaviors are defined. A detailed behavioral model is adapted from the service quality domain to represent customer perceptions and actions related to infrastructure level of service. An illustrative example of 20 assets and 50 user agents is simulated to
Neural Network Based Switching State Selection for Direct Power Control of Three Phase PWM-Rectifier
This article proposes an intelligent approach to the Direct Power Control technique of the PWM rectifier, this control technique improves the performance of PWM converter, called Direct Power Control Based on Artificial Neural Network (ANN), applied for the selection of the optimal control vector. DPC-ANN ensures smooth control of active and reactive power in all Sectors and reduces current ripple. Finally, the developed DPC was tested by simulation, the simulation results proved the excellent performance of the proposed DPC scheme. © 2018 IEEE.

Multistep deposition of Cu2Si(S,Se)3 and Cu2ZnSiSe4high band gap absorber materials for thin film solar cells
Cu2ZnSi(S,Se)4 and Cu2Si(S,Se)3 are potential materials to obtain cost effective high band gap absorbers for tandem thin film solar cell devices. A method to synthesize Cu2SiS3, Cu2SiSe3and Cu2ZnSiSe4thin film absorbers is proposed. This method is based on a multistep process, using sequential deposition and annealing processes. X-ray diffraction analysis performed on the final thin films have confirmed the presence of the Cu2Si(S,Se)3 and Cu2ZnSiSe4phases. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed the formation of polycrystalline layers with grains size up to 1 μm. The band gap of the
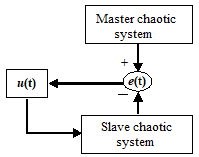
Multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems
This paper investigates the multi-switching master–slave synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems in which state variables of a master system are synchronized with different state variables of a slave system using the sliding mode control technique. To design the appropriate controllers via sliding mode control for different switches, Lyapunov stability theory is taken into account. Theoretical results are applied by considering two non-identical chaotic systems where one is considered as master system and another is considered as slave system. Numerical simulations are performed to
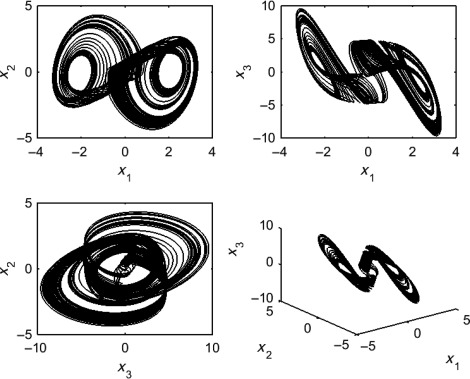
Multiswitching synchronization of commensurate fractional order hyperchaotic systems via active control
In this chapter, the multiswitching synchronization scheme has been investigated for a class of nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems. The multiswitching complete synchronization scheme has been examined such that the state variables of the slave system synchronize with different state variables of the master system. For the synchronization of two nonidentical fractional order hyperchaotic systems suitable controllers have been designed using active control technique. The stability of fractional order chaotic systems has been used to stabilize the error dynamical system. Two
New Control Schemes for Fractional Chaos Synchronization
Chaos theory deals with the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. Chaotic systems are characterized by the property that small changes in the initial conditions result in widely diverging responses. In this paper, new control schemes of synchronization for different arbitrary incommensurate and commensurate fractional order chaotic systems are presented. Synchronization stability, based on stability of linear fractional-order systems and fractional Lyapunov stability, is proved theoretically. Numerical examples are given to show the effectiveness of the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
