Modelling and Analysis the Population Density Effect on the Infectiousness Rate of COVID-19 Novel Virus and the Mortality Rate Percentage Regarding Oxford’s Stringency Index Model of Governmental Response in MATLAB
Numerical data on fifty pioneer adopting countries of Covid-19 novel pandemic has been put into study each on their first month of the virus’s spread. Ten groups were created with each including the countries of around the same average population density. This was meant to study the difference between each group’s growth of infected cases in addition to their mortality percentage rates (MPR). Modeling was done for each group with the use of MATLAB; for the growth rate, the exponential growth equation was considered, and for the mortality rate percentage, the equation was modeled over the span
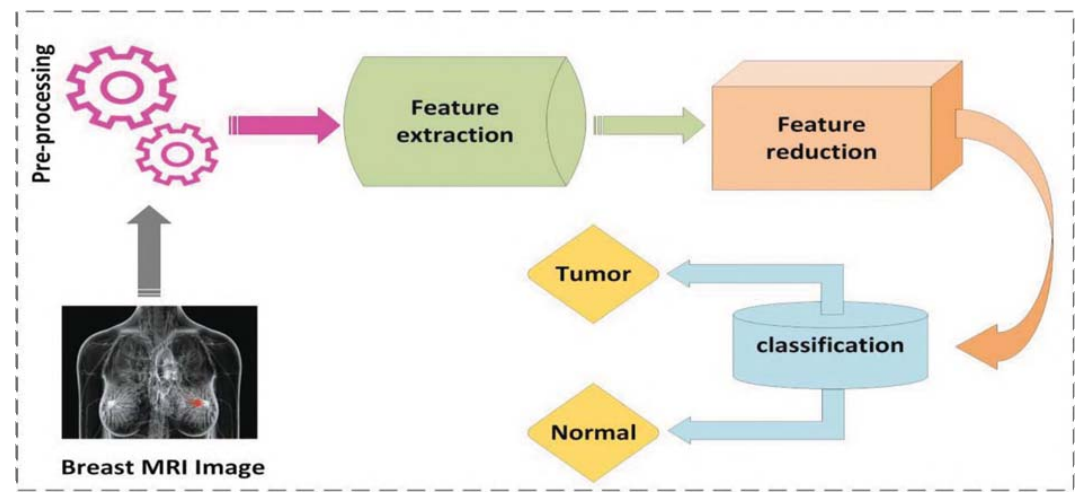
Automatic mri breast tumor detection using discrete wavelet transform and support vector machines
The human right is to live a healthy life free of serious diseases. Cancer is the most serious disease facing humans and possibly leading to death. So, a definitive solution must be done to these diseases, to eliminate them and also to protect humans from them. Breast cancer is considered being one of the dangerous types of cancers that face women in particular. Early examination should be done periodically and the diagnosis must be more sensitive and effective to preserve the women lives. There are various types of breast cancer images but magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become one of
Evaluation of Different Sudan Dyes in Egyptian Food Samples Utilizing Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry
A sensitive and a precise method was developed for the quantification of different Sudan dyes in some Egyptian food samples. They were analyzed utilizing two-fragment ion transition under multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. Separation was carried out on Kinetex 2.6u C18 100 A (75 mm × 4.6 mm) phenomenex using isocratic elution with 10:90% water and acetonitrile containing 2.0 mmol/L ammonium formate and 0.2% formic acid. The validation parameters were obtained and verified. The linearity was 0.2–10.0 ng/mL with r2 > 0.9975. LOD and LOQ were 0.06 and 0.19 ng/mL, respectively, for Sudan (I
An eco-concerned development of a fast, precise and economical spectrophotometric assay for the antiviral drug simeprevir based on ion-pair formation
Simeprevir sodium (SMV) is one of the antiviral drugs used for the treatment of virus C. The current strategy develops and validates a new eco-concerned tool for its quantification in the pure and pharmaceutical formulations. Sulfonephthalein acid dyes were used for this purpose, applying visible analyses based on ion-pair formation. A linear relation between the absorbed signal and the drug concentration is obtained up to 67.0 μg mL-1 with r2 of 0.9989-0.9999. The measurement is carried out at 410, 415, 410, and 403 nm for bromocresol green, bromoxelenol blue, bromothymol blue, and
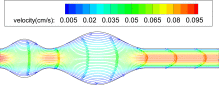
Numerical simulation of blood flow in abdominal aortic aneurysms: Effects of blood shear-thinning and viscoelastic properties
In this study numerical simulation of blood flow in abdominal aortic aneurysms is presented. The novelty in this study is the consideration of the blood viscoelastic properties to account for the presence of red blood cells in addition to the shear-thinning behavior. The Oldroyd-B model is used to account for the viscoelasticity while the Carreau–Yasuda model is used to represent the shear-thinning property. The artery with its aneurysms is modeled as a planar channel with rigid wavy walls. The governing equations are solved numerically using the Galerkin/least-squares finite element method
Classifying Upper Limb Activities Using Deep Neural Networks
This paper presents a classification method using Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in order to classify six human upper limb activities. The study was also carried out to investigate whether theses activities are being performed normally or abnormally using two different neural networks: Artificial neural network (ANN) and convolutional neural network (CNN). Human activities that were included in the study: arm flexion and extension, arm pronation and supination, shoulder internal and external rotations. Before activities categorization, training data was obtained by the means of an IMU sensor
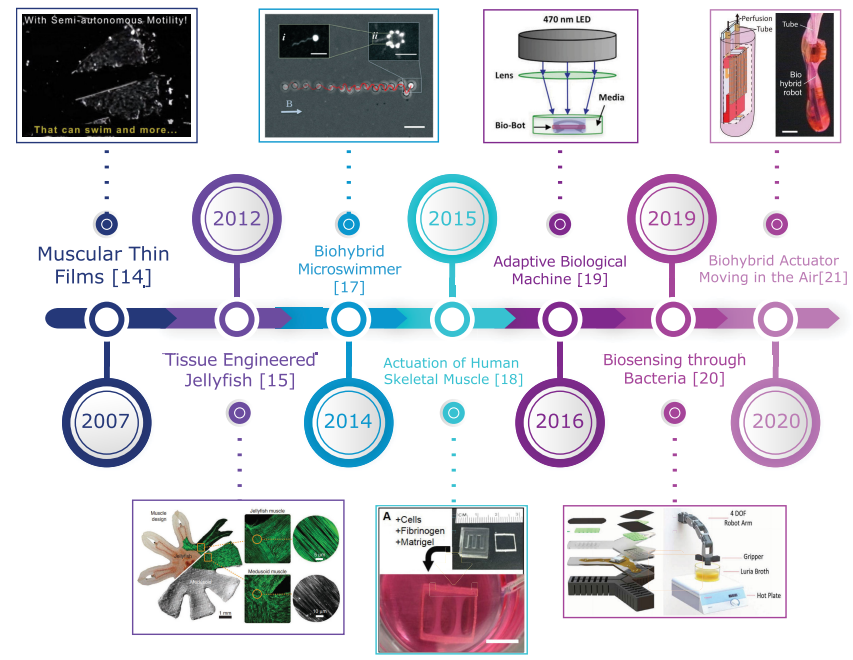
Biohybrid soft robots, E-skin, and bioimpedance potential to build up their applications: A review
Soft Robotics is a new approach towards better human-robot interaction and biomimicry in the robotics field. Its integration with biological materials (Biohybrid soft robotics) is one of the topics being focused on in the soft robotics research in the last fifteen years. The motive for this approach is to combine the best of biological and artificial systems. In this article, Biohybrid soft robots and Electronic Skin (E-skin), which is considered one of the advances of soft robotics, are reviewed. Their most significant milestones and the highlights of their most researched applications are
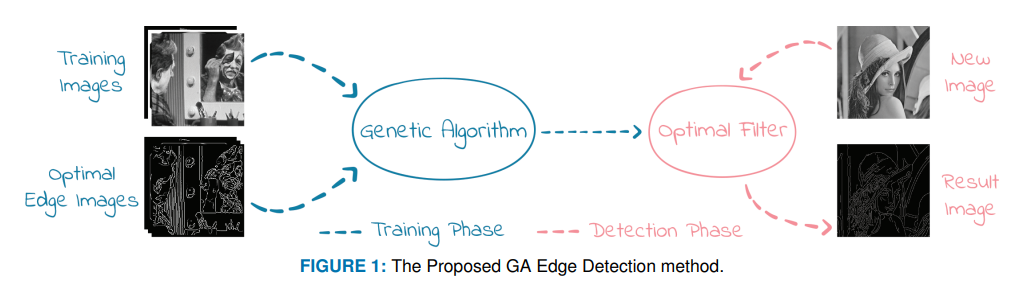
Optimized Edge Detection Technique for Brain Tumor Detection in MR Images
Genetic algorithms (GAs) are intended to look for the optimum solution by eliminating the gene strings with the worst fitness. Hence, this paper proposes an optimized edge detection technique based on a genetic algorithm. A training dataset that consists of simple images and their corresponding optimal edge features is employed to obtain the optimum filter coefficients along with the optimum thresholding algorithm. Qualitative and quantitative performance analyses are investigated based on several well-known metrics. The performance of the proposed genetic algorithm-based cost minimization
FPGA Realizations of Chaotic Epidemic and Disease Models including Covid-19
The spread of epidemics and diseases is known to exhibit chaotic dynamics; a fact confirmed by many developed mathematical models. However, to the best of our knowledge, no attempt to realize any of these chaotic models in analog or digital electronic form has been reported in the literature. In this work, we report on the efficient FPGA implementations of three different virus spreading models and one disease progress model. In particular, the Ebola, Influenza, and COVID-19 virus spreading models in addition to a Cancer disease progress model are first numerically analyzed for parameter
Medical nanorobots: Design, applications and future challenges
Following the current technological revolution, the concept of emerging fields and getting a common benefit becomes a bright way to follow. Going deeper in nanotechnology, nanorobotics has been the glimpse of hope in many fields; particularly, in the medical field. Nanorobotics applications in medicine are divided into two main categories, diagnosis and treatment, and extensive efforts have been given to research about its operation principles and design. Unfortunately, problem have emerged regarding the implementation, methods of actuation, and customized components of nanorobotics to be used
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
