Coagulation/flocculation process for textile mill effluent treatment: experimental and numerical perspectives
This study investigates the feasibility of applying coagulation/flocculation process for real textile wastewater treatment. Batch experiments were performed to detect the optimum performance of four different coagulants; Ferric Sulphate (Fe2(SO4)3), Aluminium Chloride (AlCl3), Aluminium Sulphate (Al2(SO4)3) and Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) at diverse ranges of pH (1–11) on the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), colour, total nitrogen (TN) and turbidity from real textile wastewater. At pH 9, FeCl3 demonstrated the most effective removal for all studied
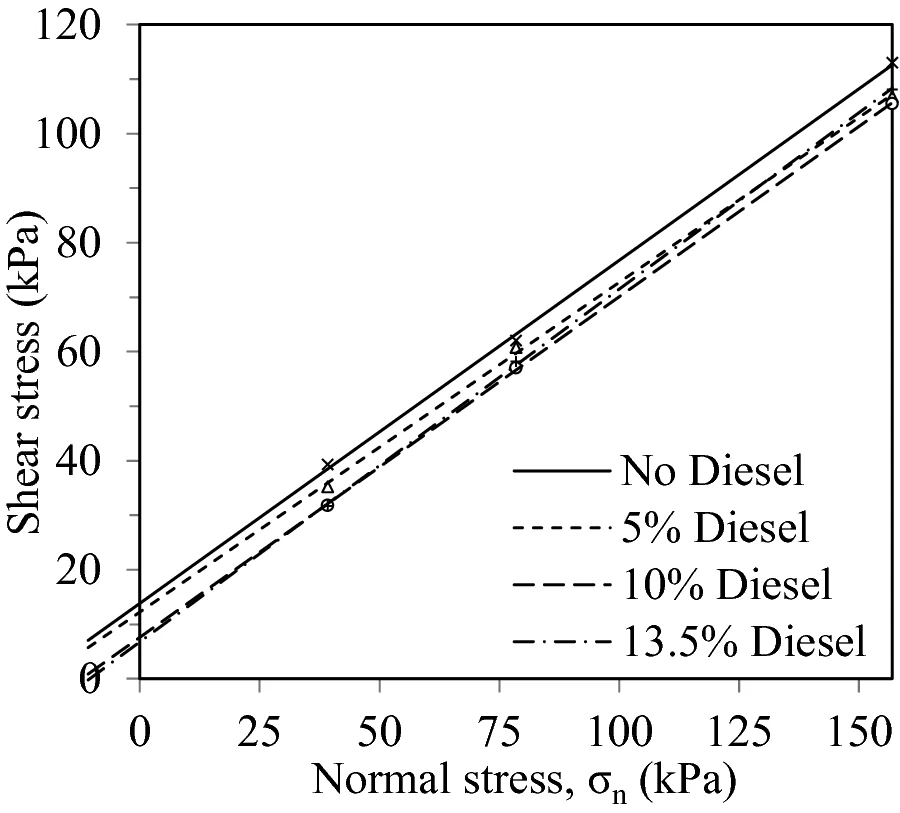
Characterization of Shear Strength and Compressibility of Diesel Contaminated Sand
Soil contamination with petroleum products and/or waste are a problem that can be detected nearby industrial areas and other amenities that include underground leaking tanks or pipelines. The negative effect of oil contamination on the soil properties is significant and can completely alter the strength as well as the serviceability limit states of the bearing stratum. In this study, Diesel was mixed with cohesionless soils using four different mixing percentages, starting with 5% up to 13.5% by weight, to cover a wide range of contamination ratios. The effects of contamination on the soil
Application of nano waste particles in concrete for sustainable construction: a comparative study
Nano particles contribute as a partial substitute in the production of eco-friendly building materials. This research presents a quantitative assessment of the sustainability effect of partially replacing cement in the green concrete mix with two types of nano-waste particles. The assessment is achieved using two weighing criteria developed by a Sustainable Decision Support System (SDSS) model. This assesses the alternatives using scoring systems based on both the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) technique and Multi-Criteria decision analysis method. Ten sustainable aspects comprising four
EPS inclusion to reduce vertical stresses on shallow tunnels
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) has long been used to reduce stresses acting on buried structures. In this study, the efficiency of utilising EPS in reducing vertical stresses acting on cut-and-cover tunnels was investigated. To gauge this, short- and long-term shear strength parameters of EPS with densities of 25, 30, and 35 kg/m3 were determined. Interface friction of EPS with various materials was measured considering the use of geotextile as a protective cover for EPS. Laboratory testing included unconfined compression, creep strain based on time-temperature-stress superposition, and modified
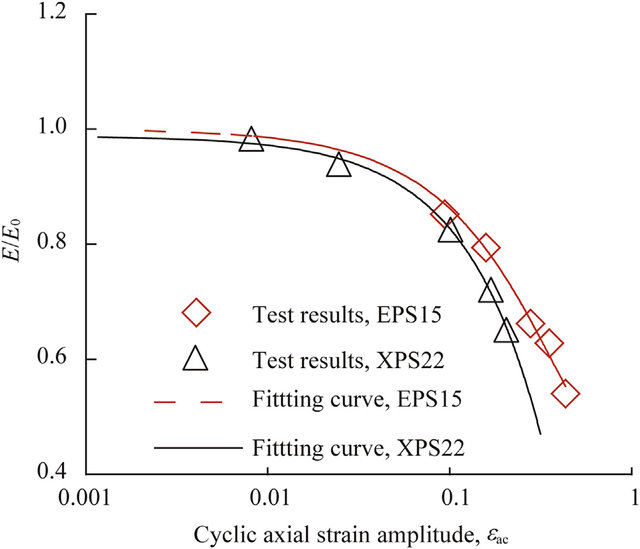
Ultrasonic characterization of expanded polystyrene used for shallow tunnels under seismic excitation
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is used as an inclusion to mitigate stresses acting on tunnels. In this study, the efficiency of utilizing EPS in reducing dynamic loads acting on shallow tunnels was studied. To gauge this, dynamic modulus of elasticity (Ed) and shear modulus (G) of EPS with densities equal to 25, 30, and 35 kg/m3 were characterized based on series of ultrasonic tests, where Ed ranged from 3500 to 6578 kPa, and G ranged from 1535 to 2741 kPa. A correlation was developed between EPS density and damping coefficient, which ranged from 1% to 2.3% based on G and the ultrasonic wave decay
Digitizing material passport for sustainable construction projects using BIM
Several aspects hinder the application sustainability in construction industry. The most prominent problems are related to the conservation of natural resources and the generation of construction and demolition wastes. Previous studies indicated that these problems are due to lack of information available to construction projects stakeholders on the proper handling of building materials in their different lifecycle stages. This paper presents Material Passport (MP) tool that provides information on how to handle building materials at the construction stage and how to benefit from them at their
CHARACTERIZATION of CONCRETE MIXES for IRRIGATION CANALS
Recently, the construction of water structures and seepage reduction are critical issues. This importance was induced due to the required specifications for the desired type of concrete. Mechanical strength and permeability are the two major parameters in achieving the design mix efficiently. This study investigates the effect of different types of admixures on the performance of concrete. The performance of concrete was evaluated using the mechanical strength and permeability tests. The concrete mixes admixtures include A retarder (Sika R2004 type G), water proofing material (addicrete DM2)
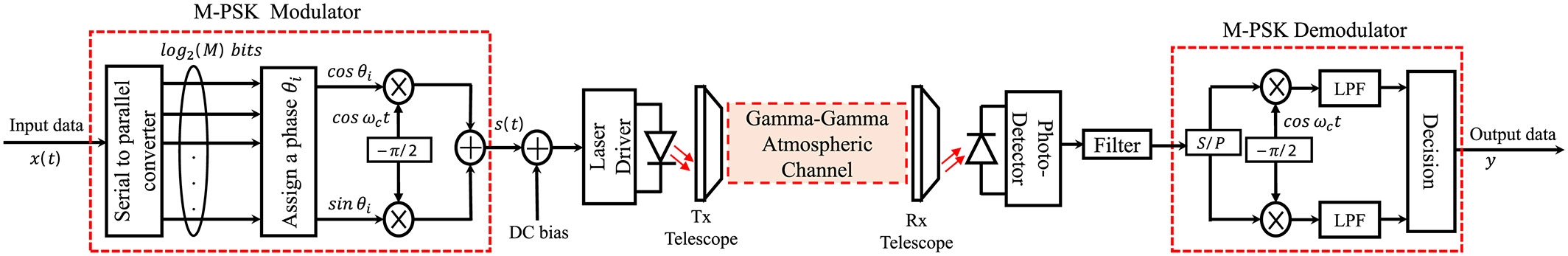
Enhancing spectral efficiency of FSO system using adaptive SIM/M-PSK and SIMO in the presence of atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors
This paper proposes an adaptive transmission modulation (ATM) technique for free-space optical (FSO) links over gamma-gamma turbulence channels.The ATM technique provides efficient utilization of the FSO channel capacity for improving spectral efficiency, by adapting the order of the phase-shift keying modulation scheme, according to the channel conditions and the required bit error rate (BER). To overcome the channel degradation resulting from the turbulence effects as well as the pointing errors (PEs), single-input multiple-output (SIMO) system with maximal ratio combining (MRC) is proposed
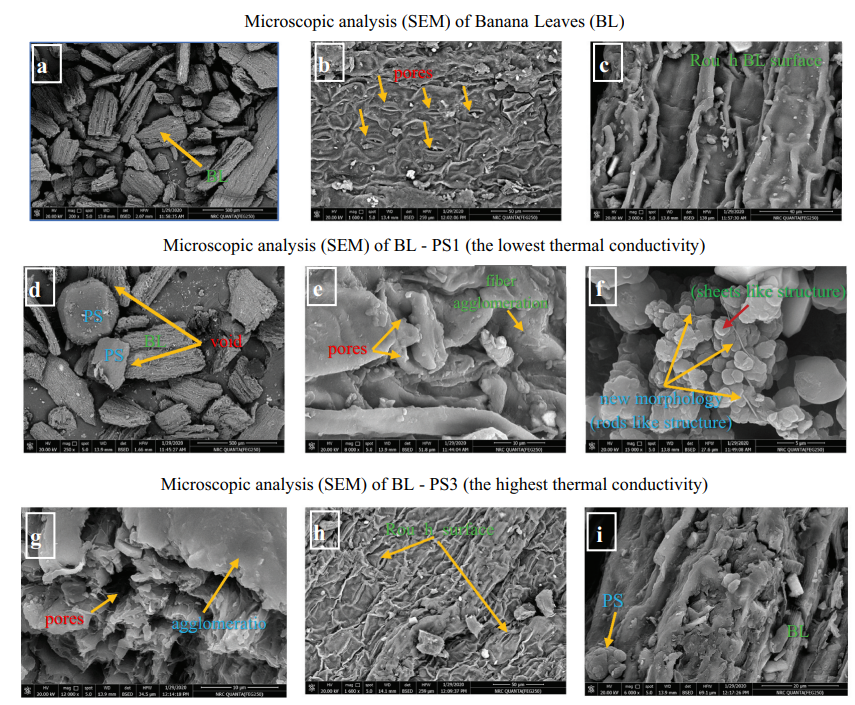
Bio-composite Thermal Insulation Materials Based on Banana Leaves Fibers and Polystyrene: Physical and Thermal Performance
Thermal insulators have a crucial role in reducing the operational building energy. They are commonly fabricated from petrochemical materials that mostly cause negative environmental impacts. This study aims to develop banana leaves-polystyrene composites (BL-PS) as a sustainable and low-cost thermal insulator. The BL powder was mixed with PS in different weight ratios (90:10, 80:20, 70:30, and 60:40). Thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, SEM, XRD, FTIR, TGA, and DSC were carried out on BL and BL-PS composites that were prepared with 10 wt.% of PS powder (BL-PS1) and 30 wt.% of PS
The economic potential of using cotton stalks to produce alternative wooden materials
The wooden industry depends heavily on logging activities which have negative impacts on the environment and a shortage of supply. The industry is starting to depend on composite boards from agricultural waste materials. Composite boards have been shown in the literature. However, some wooden applications still depend on hardwoods. Besides, most of these composite boards use synthetic formaldehyde as binders. Formaldehydes have negative impacts on human health. On the other hand, Egypt has an abundance of cotton waste that can produce composite woods. In this paper, the researchers compared
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
