Chitosan/carbon nanotube composite beads: Preparation, characterization, and cost evaluation for mercury removal from wastewater of some industrial cities in Egypt
Composite beads composed of chitosan (CS) with different carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were prepared by the incorporation of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and carboxylic multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-COOHs). A protected crosslinking method was used for the preparation of the CS/CNTs beads by the reaction of the beads with Hg(II) as the protector. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis were used to characterize the prepared beads. The adsorption performance of the prepared beads was
Synthesis of CuO-distributed carbon nanofiber: Alternative hybrid for solid propellants
Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) possess superior catalytic abilities and high surface area. Moreover, energetic particles can be loaded on them by acting as carriers. The current study reports an electroless plating, effective deposition of copper particles (Cu) on the surface of CNFs. The prepared Cu–CNFs hybrid was annealed at 250 °C to form CuO–CNFs. Homogeneous loading of CuO particles on CNFs was revealed via TEM analysis, while the crystalline structure was studied using XRD analysis. In addition, ammonium perchlorate (AP) oxidizer with endothermic initial decomposition was mixed with the
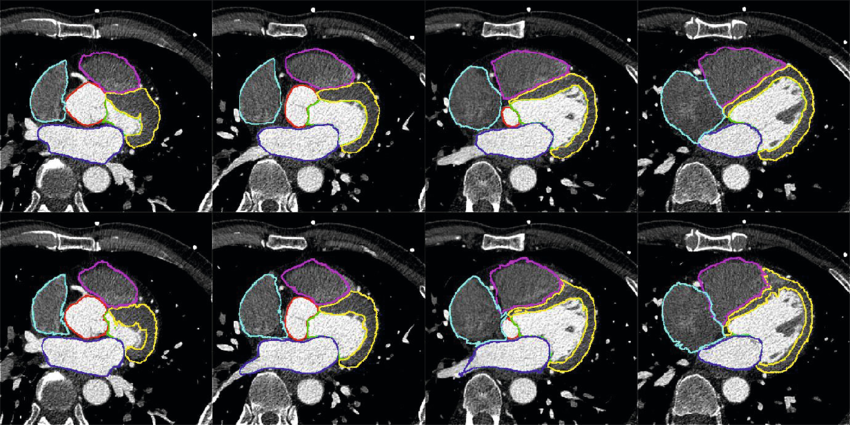
Myocardial segmentation using constrained multi-seeded region growing
Multi-slice short-axis acquisitions of the left ventricle are fundamental for estimating the volume and mass of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI scans. Manual segmentation of the myocardium in all time frames per each cross-section is a cumbersome task. Therefore, automatic myocardium segmentation methods are essential for cardiac functional analysis. Region growing has been proposed to segment the myocardium. Although the technique is simple and fast, non uniform intensity and low-contrast interfaces of the myocardium are major challenges of the technique that limit its use in myocardial

Synthesis of non-aggregated nicotinic acid coated magnetite nanorods via hydrothermal technique
Non-aggregated magnetite nanorods with average diameters of 20-30 nm and lengths of up to 350 nm were synthesized via in situ, template free hydrothermal technique. These nanorods capped with different concentrations (1, 1.5, 2 and 2.5 g) of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3); possessed good magnetic properties and easy dispersion in aqueous solutions. Our new synthesis technique maintained the uniform shape of the nanorods even with increasing the coating material concentration. The effect of nicotinic acid on the shape, particle size, chemical structure and magnetic properties of the prepared
Merits of photocatalytic and antimicrobial applications of gamma-irradiated Co: XNi1- xFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; X = 0.9 nanocomposite for pyridine removal and pathogenic bacteria/fungi disinfection: Implication for wastewater treatment
In this paper, we report a layer-by-layer approach for the preparation of a concentric recyclable composite (CoxNi1-xFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; x = 0.9) designed for wastewater treatment. The prepared composite was investigated by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) supported with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy to analyze crystallinity, average particle size, morphology and elemental composition, respectively. The antimicrobial activities of the prepared composite have been investigated against multi-drug
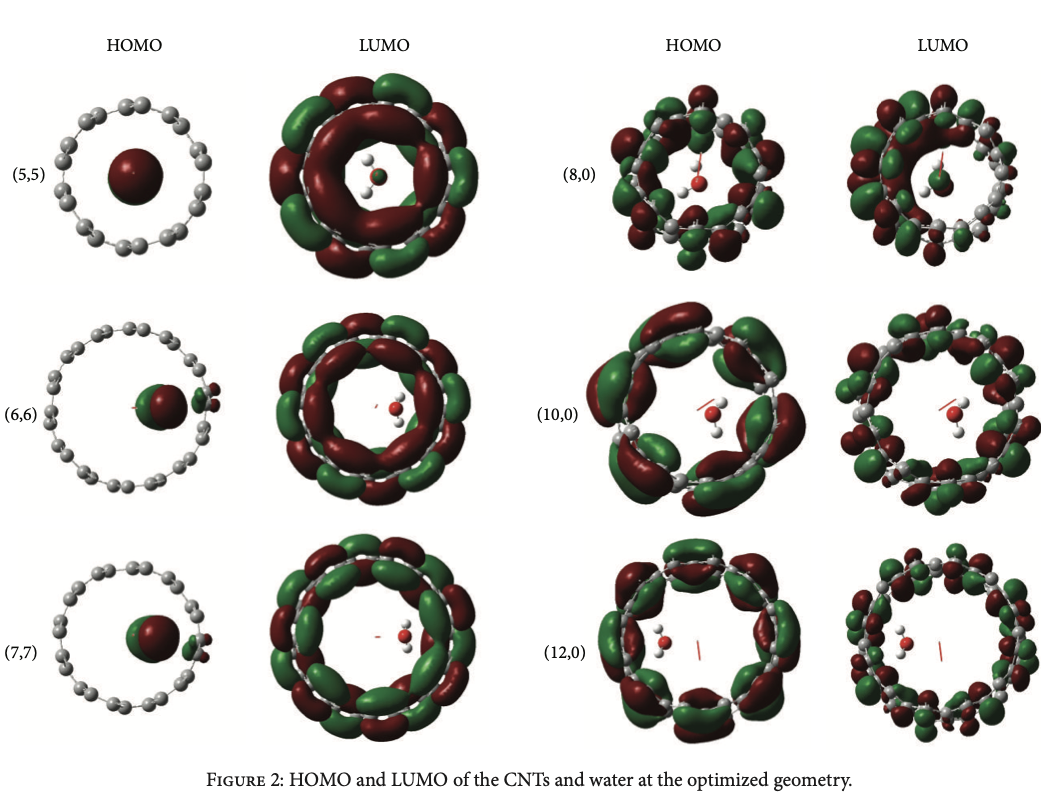
Ab initio density functional theory investigation of the interaction between carbon nanotubes and water molecules during water desalination Process
Density functional theory calculations using B3LYP/3-21G level of theory have been implemented on 6 carbon nanotubes (CNTs) structures (3 zigzag and 3 armchair CNTs) to study the energetics of the reverse osmosis during water desalination process. Calculations of the band gap, interaction energy, highest occupied molecular orbital, lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, electronegativity, hardness, and pressure of the system are discussed. The calculations showed that the water molecule that exists inside the CNT is about 2-3 Å away from its wall. The calculations have proven that the zigzag
Engineered Nanomaterials as Potential Candidates for HIV Treatment: Between Opportunities and Challenges
Nanomaterials have received considerable attention due to their unique properties; they have high surface area compared to volume ratio, giving them superior chemical, optical and thermal characteristics. Nanomaterials have also both diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In this mini review, we are highlighting valuable data about human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), its relationship with cancer and its potential treatment with some nanomaterials such as silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs). © 2019, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
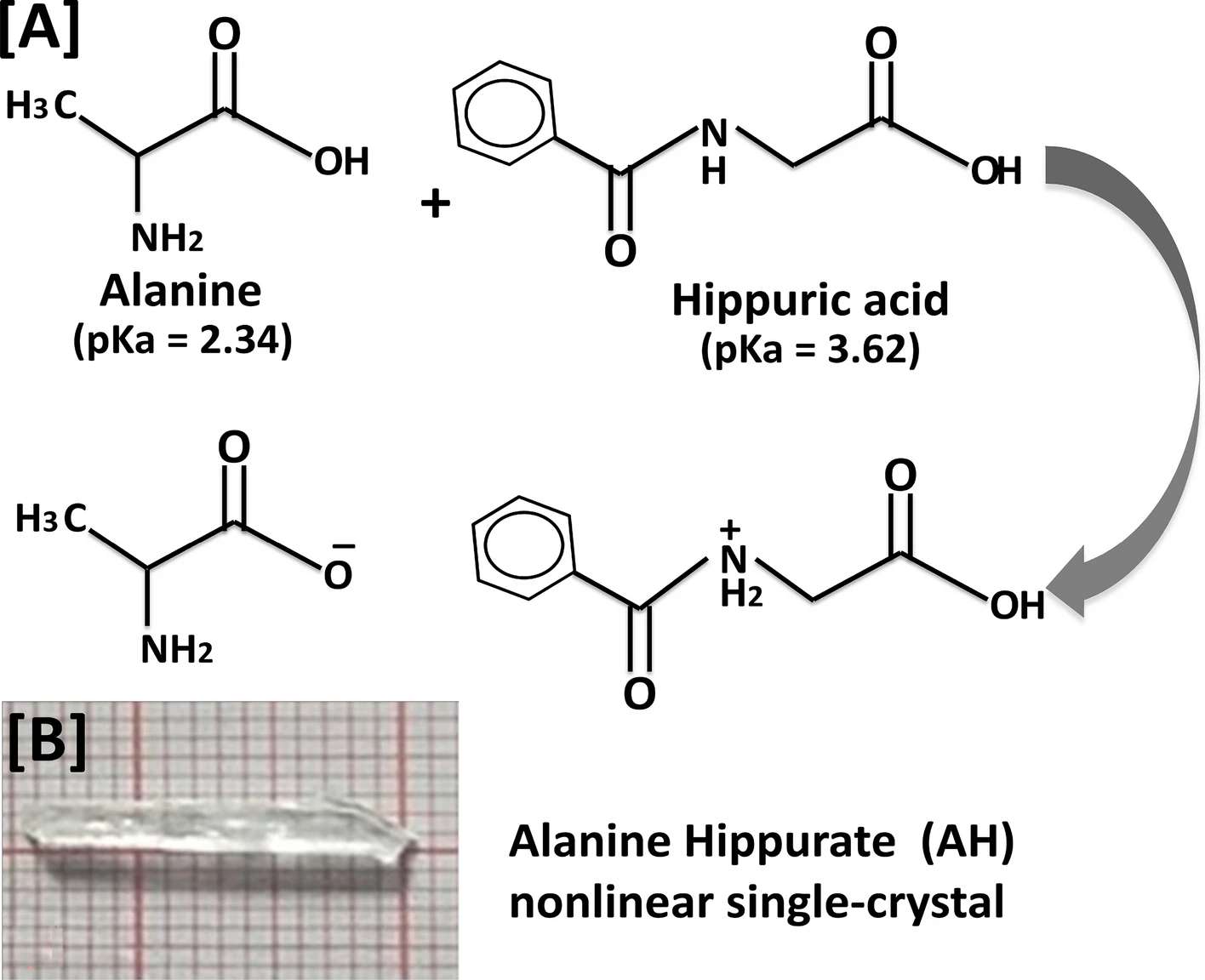
Fabrication, Characterization and Optical Investigation of Semi-organic Nonlinear Alanine Hippurate Single Crystals
In the present work, a single crystal of alanine and hippuric acid was prepared through the slow growth dynamics of sample evaporation. The crystallinity, structure, and cell parameters of the produced single crystals were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. While, frequency shifting and the various functional groups of alanine with hippuric acid were investigated by FTIR and FT-Raman studies. In addition, grain size and the morphological shape of alanine hippurate (AH) single crystals were examined by FE-SEM analysis. Transmission of light through the grown material was defined by
Microbial acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s therapy: recent trends on extraction, detection, irradiation-assisted production improvement and nano-structured drug delivery
Abstract: Neurodegenerative disorders especially Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are significantly threatening the public health. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors are compounds of great interest which can be used as effective agents for the symptomatic treatment of AD. Although plants are considered the largest source for these types of inhibitors, the microbial production of AChE inhibitors represents an efficient, easily manipulated, eco-friendly, cost-effective, and alternative approach. This review highlights the recent advances on the microbial production of AChE inhibitors and summarizes
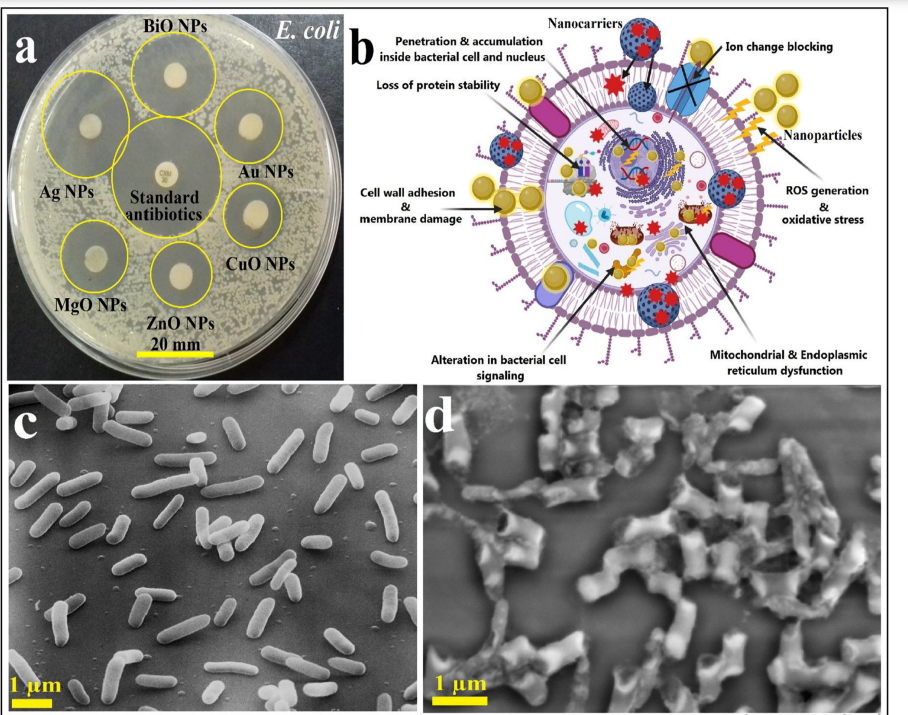
Engineered nanomaterials as fighters against SARS-CoV-2: The way to control and treat pandemics
In this editorial trend, we aim to collect and present recently available data about the characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 virus, severity, infection, replication, diagnosis, and current medications. In addition, we propose the role of nanomaterials in controlling and treating COVID-19 through their antiviral and antibacterial potential with suggested action mechanisms indicating the capability of interaction between these nanomaterials and SARS-CoV-2. These nanomaterials might be among the possible and most effective cures against coronavirus. © 2020, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
