
Synthesis of non-aggregated nicotinic acid coated magnetite nanorods via hydrothermal technique
Non-aggregated magnetite nanorods with average diameters of 20-30 nm and lengths of up to 350 nm were synthesized via in situ, template free hydrothermal technique. These nanorods capped with different concentrations (1, 1.5, 2 and 2.5 g) of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3); possessed good magnetic properties and easy dispersion in aqueous solutions. Our new synthesis technique maintained the uniform shape of the nanorods even with increasing the coating material concentration. The effect of nicotinic acid on the shape, particle size, chemical structure and magnetic properties of the prepared
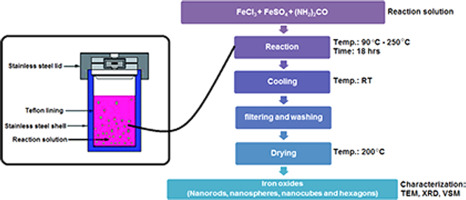
Tailored super magnetic nanoparticles synthesized via template free hydrothermal technique
Magnetite nanoparticles of controlled shape and dimensions were synthesized using a modified hydrothermal technique. The influence of different synthesis conditions on the shape, size (length and diameter), structure and magnetic properties of the prepared nanoparticles is presented. The mineral phases, the morphologies, size distribution of the resulting magnetic nanoparticles and their magnetic properties were characterized using different characterization methods. We designed magnetite nanoparticles with different morphologies (nanospheres, nanorods, nanocubes and hexagons) and with
Synthesis of CuO-distributed carbon nanofiber: Alternative hybrid for solid propellants
Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) possess superior catalytic abilities and high surface area. Moreover, energetic particles can be loaded on them by acting as carriers. The current study reports an electroless plating, effective deposition of copper particles (Cu) on the surface of CNFs. The prepared Cu–CNFs hybrid was annealed at 250 °C to form CuO–CNFs. Homogeneous loading of CuO particles on CNFs was revealed via TEM analysis, while the crystalline structure was studied using XRD analysis. In addition, ammonium perchlorate (AP) oxidizer with endothermic initial decomposition was mixed with the
Chitosan/carbon nanotube composite beads: Preparation, characterization, and cost evaluation for mercury removal from wastewater of some industrial cities in Egypt
Composite beads composed of chitosan (CS) with different carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were prepared by the incorporation of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and carboxylic multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-COOHs). A protected crosslinking method was used for the preparation of the CS/CNTs beads by the reaction of the beads with Hg(II) as the protector. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis were used to characterize the prepared beads. The adsorption performance of the prepared beads was

Carbon-dot-loaded CoxNi1−xFe2O4; x = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial potential: An engineered nanocomposite for wastewater treatment
Water scarcity is now a serious global issue resulting from population growth, water decrease, and pollution. Traditional wastewater treatment plants are insufficient and cannot meet the basic standards of water quality at reasonable cost or processing time. In this paper we report the preparation, characterization and multiple applications of an efficient photocatalytic nanocomposite (CoxNi1−xFe2O4; x = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2/C-dots) synthesized by a layer-by-layer method. Then, the photocatalytic capabilities of the synthesized nanocomposite were extensively-studied against aqueous solutions of
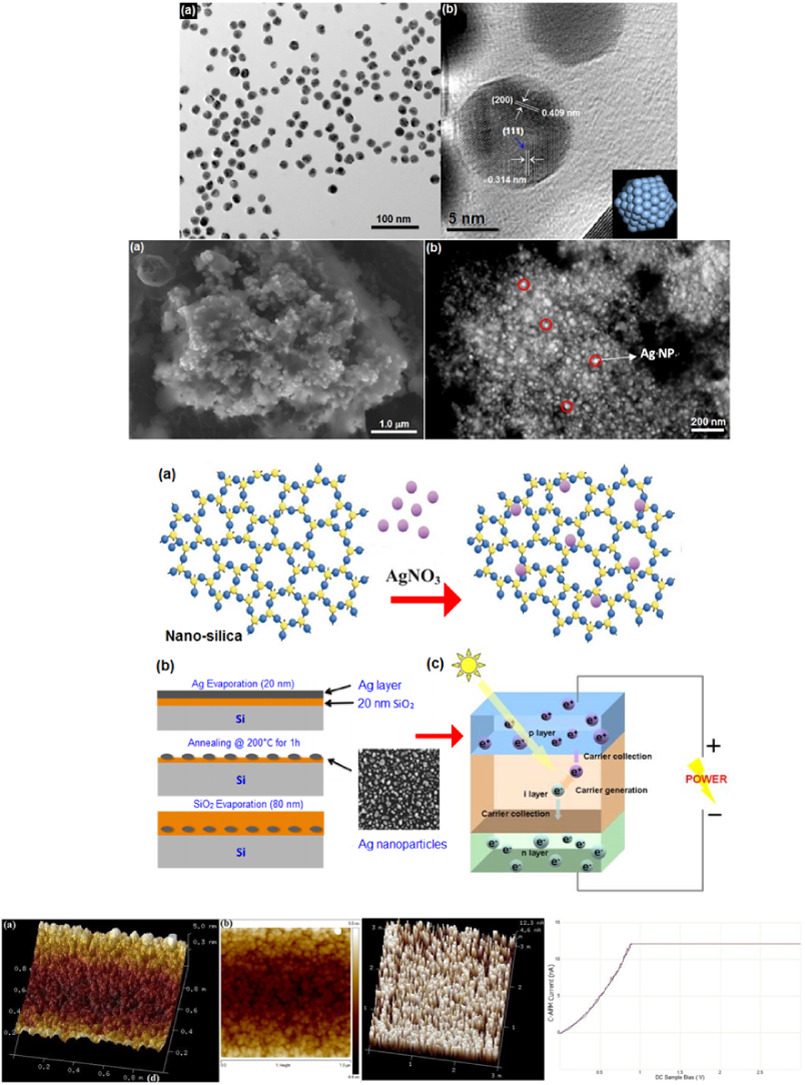
Aggrandize efficiency of ultra-thin silicon solar cell via topical clustering of silver nanoparticles
A highly efficient photovoltaic nanocomposite device is demonstrated by fabrication of structural clusters of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) on silicon solar cells via a boil deposition method. The efficiency of silicon solar cell was augmented by coating Ag NPs ultra-thin-film deposition on silicon solar cell. Chemically synthesized silver NP's, their consumption on a silicon thin layer and the operation of photovoltaic nanocomposite device were characterized by using several electron probe microscopic pectroscopic and spectrometric techniques viz. x-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron
Recent Trends of Recycled Carbon-Based Nanomaterials and Their Applications
“There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom: An Invitation to Enter a New Field of Physics” said Richard Feynman in 1959, this lecture opened the way to the new field of science which we know today as nanotechnology. Materials’ manipulation at a very small size, ranges from 1 to 100 nm (nanoworld or the nano-edge) is well-known as nanotechnology. Since then, a lot of investigations and research were devoted by many researchers around the globe to keep an eye on the different properties and behavior of nanomaterials. Materials with at least one nanoscale dimension are called nanomaterials that have
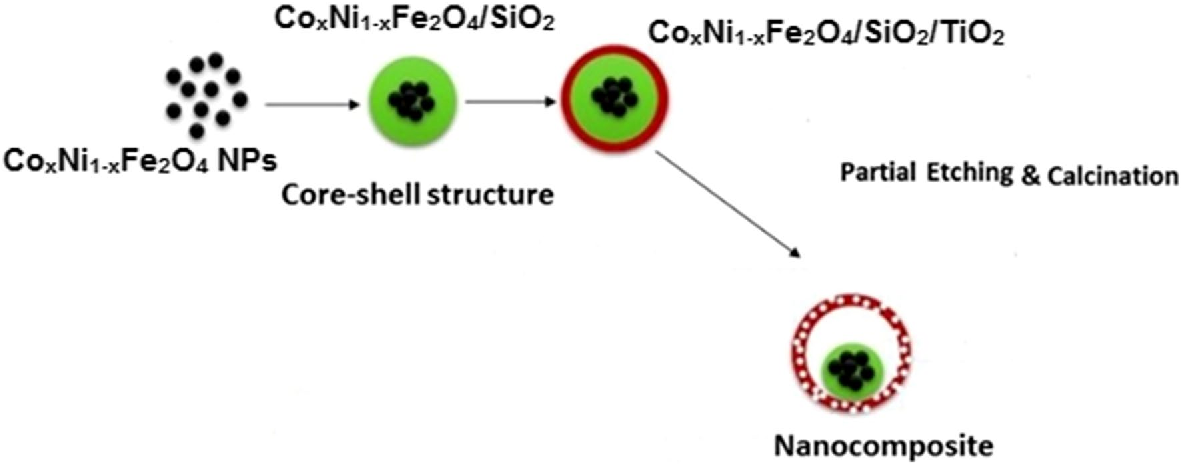
Layer-by-layer preparation and characterization of recyclable nanocomposite (CoxNi1−xFe2O4; X = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2)
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanocomposites have been extensively employed in many fundamental optoelectronic and photocatalytic applications due to their outstanding optical, electronic and chemical properties. In the present work, we introduce a simple layer-by-layer approach to design a magnetic TiO2 nanocomposite that could be easily recycled using an external magnetic field without affecting its quantum efficiency. The crystallinity, size, surface area, stability, morphology, purity and other optical, thermal and magnetic properties of the composite have been investigated. Surface topology

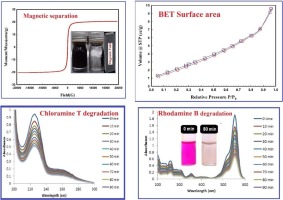
Nanocomposite matrix conjugated with carbon nanomaterials for photocatalytic wastewater treatment
The problem of hazardous wastewater remediation is a complicated issue and a global challenge. Herein, a layered Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4/SiO2/TiO2 composite matrix was prepared and incorporated with three carbon nanomaterials having different dimensionalities, carbon dots (C-dots, 0D), single-walled carbon nanotubes (1D), and reduced graphene oxide (2D), in an effort to create effective photocatalytic nanocomposites for chloramine-T removal from water. Microstructural analyses confirmed the formation of nanocomposites and revealed their chemistry and structure. Elemental mapping revealed a uniform
Nanostructured Mg substituted Mn-Zn ferrites: A magnetic recyclable catalyst for outstanding photocatalytic and antimicrobial potentials
With recently increasing the environmental problems and expected energy crisis, it is necessary to synthesis a low-cost, efficient, and UV-light responsive photocatalyst for contaminants’ degradation. The nanostructured spinel ferrite Mn0.5Zn0.5-xMgxFe2O4 NPs (x = 0.0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.375 and 0.50) were synthesized via the sol-gel method. The crystallite size was lied in nano regime ranging from 21.8 to 36.5 nm. The surface chemical composition of the Mn0.5Zn0.5-xMgxFe2O4 NPs was investigated via XPS analysis. Mossbauer spectra showed that the peaks were shifted to higher values of the maximum
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
