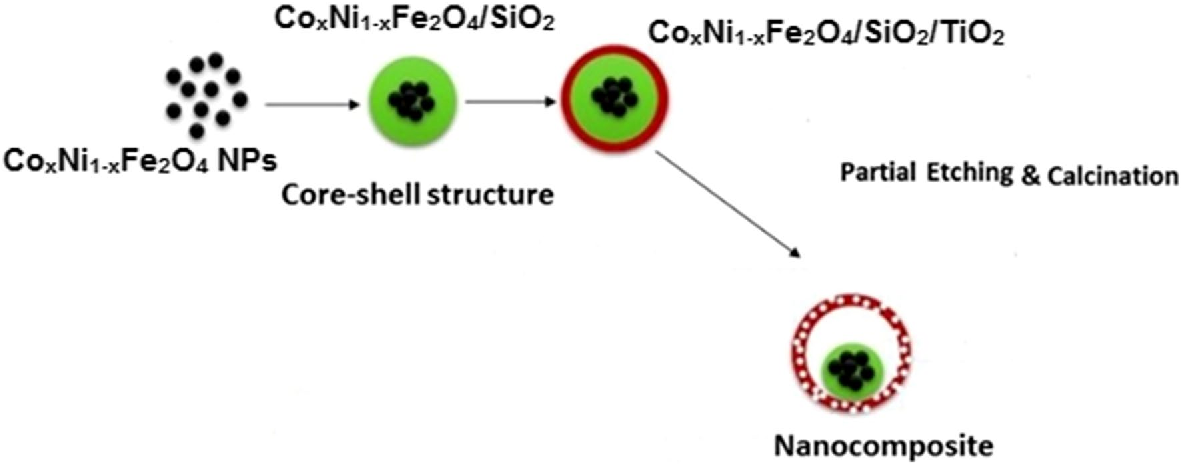
Layer-by-layer preparation and characterization of recyclable nanocomposite (CoxNi1−xFe2O4; X = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2)
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanocomposites have been extensively employed in many fundamental optoelectronic and photocatalytic applications due to their outstanding optical, electronic and chemical properties. In the present work, we introduce a simple layer-by-layer approach to design a magnetic TiO2 nanocomposite that could be easily recycled using an external magnetic field without affecting its quantum efficiency. The crystallinity, size, surface area, stability, morphology, purity and other optical, thermal and magnetic properties of the composite have been investigated. Surface topology, thickness and thermal conduction were also demonstrated by AC conductivity measurements at a specific temperature (55 °C). Our results revealed that the prepared composite has a semi-spherical concentric shape with an average size of about (123.4 nm), surface area of (46.13 m2/g) and zeta potential of (− 24.3 mV) as confirmed by HRTEM, surface area analyzer and zeta potential measurements. TGA and DSC analysis recorded the thermal stability of the composite up to (500 °C) while a band gap of about (3.35 eV) has been calculated. VSM analysis showed that the composite has good magnetic properties. Atomic force microscopy recorded a surface roughness of the composite of about (125 nm) while the average thickness was approximately (10.3 nm). Significant responses of the capacitance–voltage profiles in the employed Preisach model, have been also recorded. © 2019, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.